Question 1
What does a dotted line from a "Group By" component to a "Filter" component mean?
- A. There is a one-to-one relationship between the "Group By" and the "Filter" components.
- B. To evaluate the "Group By" component, the "Filter" component is evaluated first.
- C. A property from the "Group By" is referenced by the “Filter" component.
- D. Information from the "Group By" is copied over to the "Filter" component.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A dotted line from a “Group By” component to a “Filter” component means that a property from the
“Group By” is referenced by the “Filter” component. For example, if you group customers by age and
then filter them by average spending, you need to reference a property from the “Group By”
component, such as .pxSegment, in the “Filter” component. A dotted line does not indicate a one-to-
one relationship, an evaluation order, or a copying of information between components
Comments
Question 2
In a decision strategy, to use a customer property in an expression, you
- A. define the property as a strategy property
- B. define Customer page in Pages & Classes
- C. use the property as defined without any prefix
- D. prefix the property with the keyword Customer
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In a decision strategy, to use a customer property in an expression, you need to define Customer
page in Pages & Classes and specify its class as Data-Customer. This allows you to access customer
properties by using dot notation, such as Customer.Age or Customer.Gender. You do not need to
define the property as a strategy property, use it without any prefix, or prefix it with the keyword
Customer. Verified Reference: [Certified Pega Decisioning Consultant | Pega Academy], Decision
strategies
Comments
Question 3
DRAG DROP
You are a deaccessioning architect on a next-best-action project and are responsible for designing
and implementing decision strategies. Select each component on the left and drag it to the correct
requirement on the right.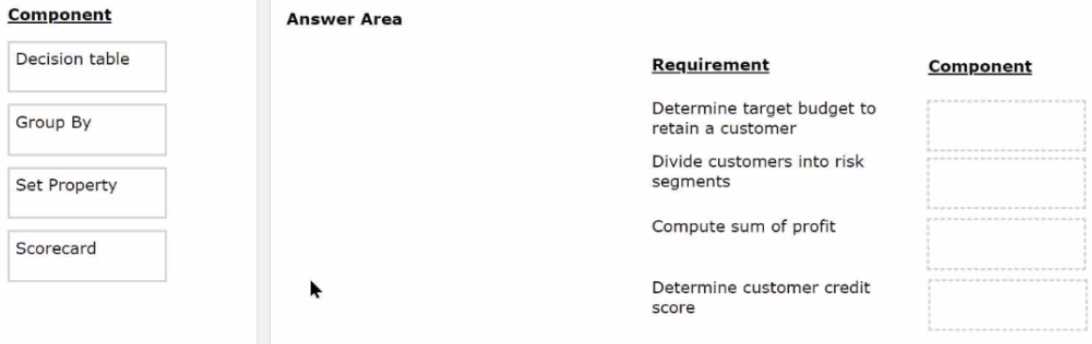
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Comments
Question 4
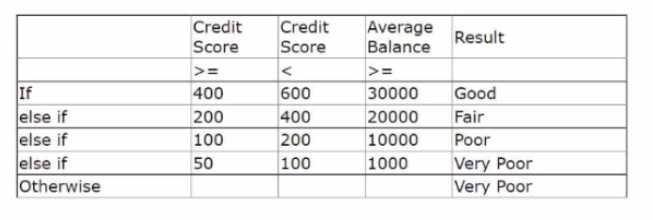
U+ Bank wants to offer credit cards only to low-risk customers. The customers are divided into
various risk segments from Good to Very Poor. The risk segmentation rules that the business
provides use the Average Balance and the customer Credit Score.
As a decisioning architect, you decide to use a decision table and a decision strategy to accomplish
this requirement in Pega Customer Decision Hub™.
Using the decision table, which label is returned for a customer with a credit score of 240 and an
average balance 35000?
- A. Very Poor
- B. Good
- C. Fair
- D. Poor
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Using the decision table, you can find the label for a customer with a credit score of 240 and an
average balance of 35000 by following these steps:
Start from the top row and check if the customer’s credit score is less than 150. If yes, then the label
is Very Poor. If no, then move to the next row.
Check if the customer’s credit score is less than 175 and their average balance is less than 25000. If
yes, then the label is Poor. If no, then move to the next row.
Check if the customer’s credit score is less than 200 and their average balance is less than 50000. If
yes, then the label is Fair. If no, then move to the next row.
Check if the customer’s credit score is less than 250 and their average balance is less than 75000. If
yes, then the label is Good. If no, then move to the last row.
The last row applies to all other cases that do not match any of the previous conditions. The label for
this row is Very Poor.
In this case, the customer’s credit score is not less than 150, so the first row does not apply. The
customer’s credit score is less than 175, but their average balance is not less than 25000, so the
second row does not apply either. The customer’s credit score is not less than 200, so the third row
does not apply. The customer’s credit score is less than 250 and their average balance is less than
75000, so the fourth row applies. Therefore, the label for this customer is Poor.
Comments
Question 5
HOTSPOT
U+ Bank, a retail bank, presents offers on its website by using Pega Customer Decision Hub™. The
bank wants to leverage Customer Decision Hub capabilities to present relevant offers to qualified
customers. As a decisioning consultant, you are responsible for configuring the business
requirements with the Next-Best-Action Designer, which involves several tasks. To accomplish these
tasks, you might have to use auto-generated decision strategies, create new decision strategies, or
edit existing strategies.
In the Answer Area, select the correct execution for each Task.
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Comments
Question 6
In a decision strategy, you can use aggregation components to____________.
- A. set a text value to a strategy property
- B. make calculations based upon a list of actions
- C. choose between actions
- D. filter actions based on priority and relevance
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Aggregation components are used to perform calculations on a list of actions, such as sum, average,
count, minimum, or maximum. For example, you can use an aggregation component to calculate the
total value of all the actions in a group. Verified Reference:
Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant -
Aggregating actions
Comments
Question 7
U+ Bank has recently implemented Pega Customer Decision Hub™. As a first step, the bank went live
with the contact center to improve customer engagement. Now, U+ Bank wants to extend its
customer engagement through the web channel. As a decisioning architect, you have created the
new set of actions, the corresponding treatments, and defined a new trigger in the Next-Best-Action
Designer for the new web channel.
What else do you configure for the new treatments to be present in the next-best-action
recommendations?
- A. Create a channel strategy specifically for web.
- B. Change the generated decision strategy.
- C. Modify the Next-Best-Action Framework strategy to cater to the new web channel.
- D. No need to do anything. The strategy is auto-generated.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When you create a new trigger in the Next-Best-Action Designer, Pega Customer Decision Hub
automatically generates a decision strategy for that trigger and channel. You do not need to create or
modify any strategies manually. Verified Reference:
Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant -
Creating triggers
Comments
Question 8
To access a property from an unconnected component, you use the
- A. customer-dot-property construct
- B. property value
- C. component-dot-property construct
- D. dot-property value directly
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To access a property from an unconnected component, you use the component-dot-property
construct. For example, if you want to access the property .Rank from an unconnected component
named ActionRanking, you use ActionRanking.Rank. Verified Reference:
Pega Academy - Decisioning
Consultant - Accessing properties from unconnected components
Comments
Question 9
The following decision strategy outputs the most profitable shoe a retailer can sell. The profit is the
selling Prices of the shoe, minus the Cost to acquire the shoe.
The details of the shoes are provided in the following table: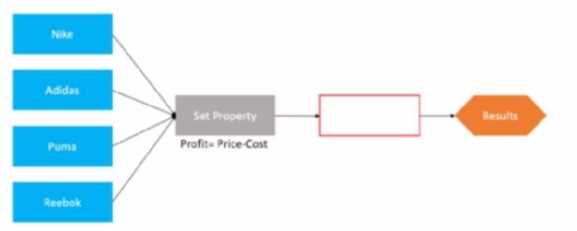
The details of the shoes are provided in the following table: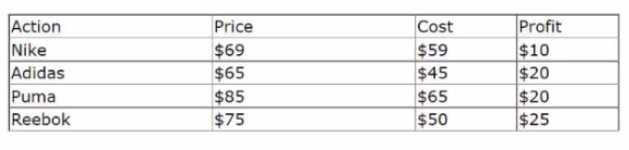
To output the most profitable shoe, which component do you add in the blank space that is
highlighted in red?
- A. Filter
- B. Group By
- C. Decision table
- D. Prioritize
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To output the most profitable shoe, you need to add a Prioritize component in the blank space. A
Prioritize component allows you to rank actions based on one or more properties. In this case, you
can rank the shoes based on the Profit property and select the highest ranked shoe as the output.
Verified Reference:
Pega Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Prioritizing actions
Comments
Question 10
U+ Bank wants to offer credit cards only to customers with a low-risk profile. The customers are
divided into various risk segments from AAA to CCC. The risk segmentation rules that the business
provides use the Age and the customer Credit Score based on the following table. The bank uses a
scorecard model to determine the customer Credit Score.
As a decisioning architect, how do you implement the business requirement?
- A. Add a decision table to a decision strategy and reference it in the scorecard component.
- B. Add the risk segmentation rules in the Results tab of the scorecard rule.
- C. Add three contact policies that correspond to the three risk segments.
- D. Add a decision table to a decision strategy and pass the credit score as the parameter.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To implement the business requirement, you need to add a decision table to a decision strategy and
pass the credit score as the parameter. A decision table allows you to define rules based on one or
more input parameters and return an output value. In this case, you can use the credit score as an
input parameter and return the risk category/grade as an output value. You can then use this output
value to filter out customers who are not in the low-risk segment (AAA). Verified Reference:
Pega
Academy - Decisioning Consultant - Using decision tables
Comments
Page 1 out of 5
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 60
page 2