Question 1
...event center has a case type that allows customers to book a dining room for events. After
customers provide basic information and indicate whether they want catering for the event, the
following behavior occurs:
If customers do not ask for catering, they receive a rental rate quote for the dining room.
If customers indicate that they want catering for the event, they must choose a menu before they
can receive a quote.
Which two options do you use to configure the case type to achieve the requested behavior?
(Choose Two)
- A. Create parallel processes for providing menu preferences and for providing the customer with the rental rate quote.
- B. Configure the menu preferences and appointment date fields with a visibility condition if the customer selects the catering checkbox.
- C. Create a process for customers to indicate menu preferences. Add the process as a case-wide optional action.
- D. Create a checkbox for customers to indicate whether they want catering for the event. Add a decision shape that evaluates whether the customer checks the box.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
To achieve the requested behavior in the event center case type:
Create a checkbox for customers to indicate whether they want catering for the event. This allows
customers to specify their preference for catering.
Add a decision shape to evaluate whether the customer has checked the catering checkbox. Based
on this decision, the case will either proceed to provide a rental rate quote or prompt the customer
to choose a menu before receiving a quote.
Configure the menu preferences and appointment date fields with a visibility condition that displays
these fields only if the customer selects the catering checkbox. This ensures that customers who do
not want catering do not see these fields, streamlining the process.
Reference: Pega Academy - Configuring visibility conditions: Visibility conditions control the display
of fields based on user inputs, such as the selection of a checkbox, ensuring dynamic and context-
specific case processing. Decision shapes allow for branching logic in the case flow based on specific
conditions.
Comments
Question 2
You are designing a credit transaction case type and have the following requirement: Transaction
disputes must be resolved within 3 days.
To meet this requirement, you need to set the___________in the service level to 3 days.
- A. goal
- B. deadline
- C. passed deadline
- D. urgency
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To meet the requirement that transaction disputes must be resolved within 3 days, you need to set
the deadline in the service level agreement (SLA) to 3 days. The deadline specifies the maximum
time allowed to resolve the transaction disputes, ensuring that the case is handled within the
required timeframe.
Reference: Pega Academy - Service Level Agreements (SLAs): SLAs define the expected time frames
for case resolution, including goals, deadlines, and escalation actions. Setting the deadline ensures
that the case meets the required resolution time frame of 3 days.
Comments
Question 3
Life insurance company has satellite offices in various countries. Each satellite office has a work
queue. Company policy requires that life insurance underwriting be signed to offices based on the
policy owner's residential address.
Which routing approach supports this requirement?
- A. Route the assignment to a specific underwriter based on business logic.
- B. Route the assignment to the correct work queue by using an authority matrix.
- C. Route the assignment to the correct work queue by using a reporting structure.
- D. Route the assignment to the correct work queue based on business logic.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To route life insurance underwriting assignments to the correct satellite office based on the policy
owner's residential address, using business logic is the most appropriate approach. This approach
involves:
Define Routing Rules: Create decision rules or decision tables that map the policy owner's residential
address to the corresponding satellite office's work queue.
Implement Business Logic: Configure the routing step in the case type to use these decision rules.
The business logic will determine the correct work queue based on the address.
Route to Work Queue: The assignment is routed to the work queue of the satellite office that
corresponds to the policy owner's residential address.
This method ensures that each assignment is accurately directed to the appropriate office based on
predefined business logic.
Reference:
Pega Academy: Assignments and Routing
Pega Documentation: Using Business Logic for Assignment Routing
Comments
Question 4
You configure a service level to adjust assignment urgency to 100 when the goal interval lapses.
What does the assignment urgency impact the deadline and passed deadline intervals?
- A. Urgency value remains at 100, but other service level processing continues.
- B. Service level processing is halted until the assignment is completed.
- C. The user is notified that the maximum urgency has been reached.
- D. Urgency value continues to increment as configured.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When a service level (SLA) adjusts the assignment urgency to 100 upon the goal interval lapsing, the
following impacts occur:
Urgency Value Adjustment: The urgency value of the assignment is set to 100, indicating high
priority.
Continued SLA Processing: Other SLA processing, such as escalating actions and notifications,
continues as configured.
Urgency Cap: The urgency value remains at 100, which is the maximum urgency, but this does not
halt other service level processing.
Therefore, setting the urgency to 100 indicates maximum priority but allows for continued SLA
actions such as further escalation and notifications.
Reference:
Pega Academy: Service Level Agreements
Pega Documentation: SLA Urgency and Escalation Mechanisms
Comments
Question 5
Managers want to create an environment in which peers exchange ideas about initiatives to retain
employees,
Select the collaboration tool that best suites this type of communication.
- A. Insights
- B. Dashboards
- C. Pulse
- D. Spaces
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Pega offers several collaboration tools, each suited for different types of communication and
interaction. For an environment where peers exchange ideas about initiatives to retain employees,
the best collaboration tool is "Spaces."
Spaces: This tool is designed for collaborative environments where team members can share ideas,
discuss initiatives, and collaborate on projects.
Interactive Environment: Spaces provide a platform for ongoing discussions, file sharing, and real-
time collaboration, making it ideal for exchanging ideas and initiatives.
Reference:
Pega Academy: Collaboration Tools
Pega Documentation: Using Spaces for Team Collaboration
Comments
Question 6
DRAG DROP
Select each Use Case on the left and drag it to the appropriate Automation on the right.
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Use Case: "A medical specialist completes their review of an insurance claim, and the system
attaches the report to the case."
Automation: Create PDF
Use Case: "Employees of a financial services firm receive confirmation when they register for the
required certification classes."
Automation: Send email
Use Case: "A Fraud department manager receives a mobile notification that an approval request is in
their worklist."
Automation: Push notification
Use Case: "When an approver rejects an expense report, an employee can modify and resend the
report for approval."
Automation: Change to a stage
A medical specialist completes their review of an insurance claim, and the system attaches the
report to the case.
Automation: Create PDF
Explanation: In this use case, the system needs to generate a report that can be attached to the case.
The appropriate automation for generating documents like reports is creating a PDF. This ensures the
report is in a standardized, non-editable format that can be easily attached to the case.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Case Design.
Employees of a financial services firm receive confirmation when they register for the required
certification classes.
Automation: Send email
Explanation: This use case involves sending a confirmation to employees upon registration. The most
suitable method for sending such confirmations is through an email. Email notifications ensure that
the employee receives a record of their registration.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Notifications and
Correspondence.
A Fraud department manager receives a mobile notification that an approval request is in their
worklist.
Automation: Push notification
Explanation: The manager needs to be alerted promptly about an approval request. Push
notifications are ideal for this purpose as they provide real-time alerts directly to the mobile device.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Mobile and Multi-Channel.
When an approver rejects an expense report, an employee can modify and resend the report for
approval.
Automation: Change to a stage
Explanation: When an expense report is rejected, the case needs to move back to a stage where the
employee can modify and resubmit it. This involves changing the stage of the case to enable the
necessary actions.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Case Management and Workflow.
Comments
Question 7
The business process for an automobile insurance claim consists of the following phases:
• Submission: The customer contacts a customer service representative (CSR) to file the claim.
• Review: An adjuster reviews the claim, assesses the damages to each vehicle, and provides an
estimate of the cost of repairs.
• Repair: A third party performs the repairs on each vehicle, communicating with the adjuster and
customer as necessary.
• Verification: After each vehicle repair, the adjuster closes the claim.
According to Pega best practices, which phase can you implement as a child case?
- A. Verification
- B. Submission
- C. Review
- D. Repair
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Submission: This phase involves the initial contact and filing of the claim, which typically doesn't
need to be a separate case as it's an initial action.
Reference: Pega Academy, Case Management Essentials, Case Lifecycle Design.
Review: This phase involves an adjuster reviewing the claim and assessing damages, which can be
handled within the primary case.
Reference: Pega Academy, Case Management Essentials, Case Lifecycle Design.
Repair: The repair phase involves interaction with third-party vendors and ongoing communication,
making it suitable to be implemented as a child case to track each repair separately.
Reference: Pega Academy, Case Management Essentials, Child Cases.
Verification: This phase is a closing action performed after repairs, which doesn't typically require a
separate case.
Reference: Pega Academy, Case Management Essentials, Case Lifecycle Design.
Comments
Question 8
DRAG DROP
Select each Process Step Description on the left and drag it to the appropriate Process Step on the
right.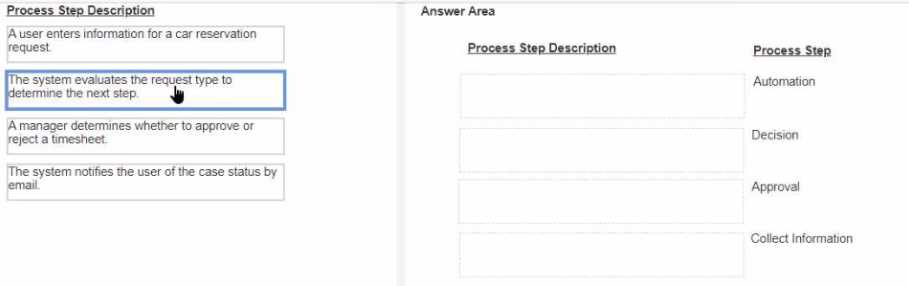
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Process Step Description: "A user enters information for a car reservation request."
Process Step: Collect Information
Process Step Description: "The system evaluates the request type to determine the next step."
Process Step: Decision
Process Step Description: "A manager determines whether to approve or reject a timesheet."
Process Step: Approval
Process Step Description: "The system notifies the user of the case status by email."
Process Step: Automation
A user enters information for a car reservation request.
Process Step: Collect Information
Explanation: This step involves gathering data from the user. In Pega, collecting information typically
involves prompting the user to enter necessary details to move the case forward.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Data Collection.
The system evaluates the request type to determine the next step.
Process Step: Decision
Explanation: This step involves the system making a determination based on the provided
information. A decision step in Pega is used to evaluate conditions and determine the next path or
action in the case workflow.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Decision Management.
A manager determines whether to approve or reject a timesheet.
Process Step: Approval
Explanation: This step is about reviewing and making an approval decision. In Pega, approval steps
are used when a human needs to review the case and make a decision to approve or reject it.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Case Life Cycle Management.
The system notifies the user of the case status by email.
Process Step: Automation
Explanation: This step involves automated communication. Automation steps in Pega can be
configured to perform tasks like sending emails, updating records, or other system actions without
manual intervention.
Reference: Pega Platform Business Architect Essentials, Chapter on Notifications and
Correspondence.
Comments
Question 9
Your client is planning their next Minimum Lovable Product (MLP) release.
Which three pillars of case design must the Pega Business Architect ensure are taken into account, to
capture information for the release? (Choose Three)
- A. Personas and Channels
- B. Reports
- C. Case types
- D. Data and Interfaces
- E. Dashboards
Answer:
A, D C
Explanation:
When planning the next Minimum Lovable Product (MLP) release, a Pega Business Architect should
focus on the three pillars of case design: Personas and Channels, Case Types, and Data and
Interfaces.
Personas and Channels:
Personas: Identify the different user roles (personas) that will interact with the application.
Understanding personas helps in designing user experiences that meet their needs.
Channels: Determine the channels (e.g., web, mobile) through which users will interact with the
system. This ensures that the application is accessible and user-friendly across different platforms.
Case Types:
Case Types: Define the different types of cases that the application will manage. Case types are
fundamental to structuring the application and ensuring that it can handle various processes and
workflows efficiently.
Data and Interfaces:
Data: Identify the data required to support the case types and processes. This includes understanding
data sources, data structures, and how data will be captured and used.
Interfaces: Determine the interfaces needed to integrate with external systems. Interfaces are crucial
for ensuring that the application can interact with other systems and exchange information
seamlessly.
Reference:
Pega Academy: Case Design
Pega Documentation: Minimum Lovable Product (MLP)
Comments
Question 10
Identify the name of Pega's business architecture design that aligns human intelligence and process
automation with business logic to deliver high-value software solitons.
- A. Center-out
- B. Customer-centric
- C. Business-first
- D. Pega Express
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The name of Pega's business architecture design that aligns human intelligence and process
automation with business logic to deliver high-value software solutions is Center-out.
Center-out Design:
This approach focuses on designing the core business logic and processes first (the "center") and then
extending outwards to include the user interface (UI) and channels.
By centering on the core logic, Pega ensures that the most critical aspects of the business process are
well-defined and robust. This approach supports scalability and adaptability as the system grows and
evolves.
Reference:
Pega Academy: Center-out Business Architecture
Pega Documentation: Center-out Design Principles
Comments
Page 1 out of 4
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 50
page 2