Question 1
Based on the image below, which two statements describe the reason and action required to resolve
the errors? (Choose two.)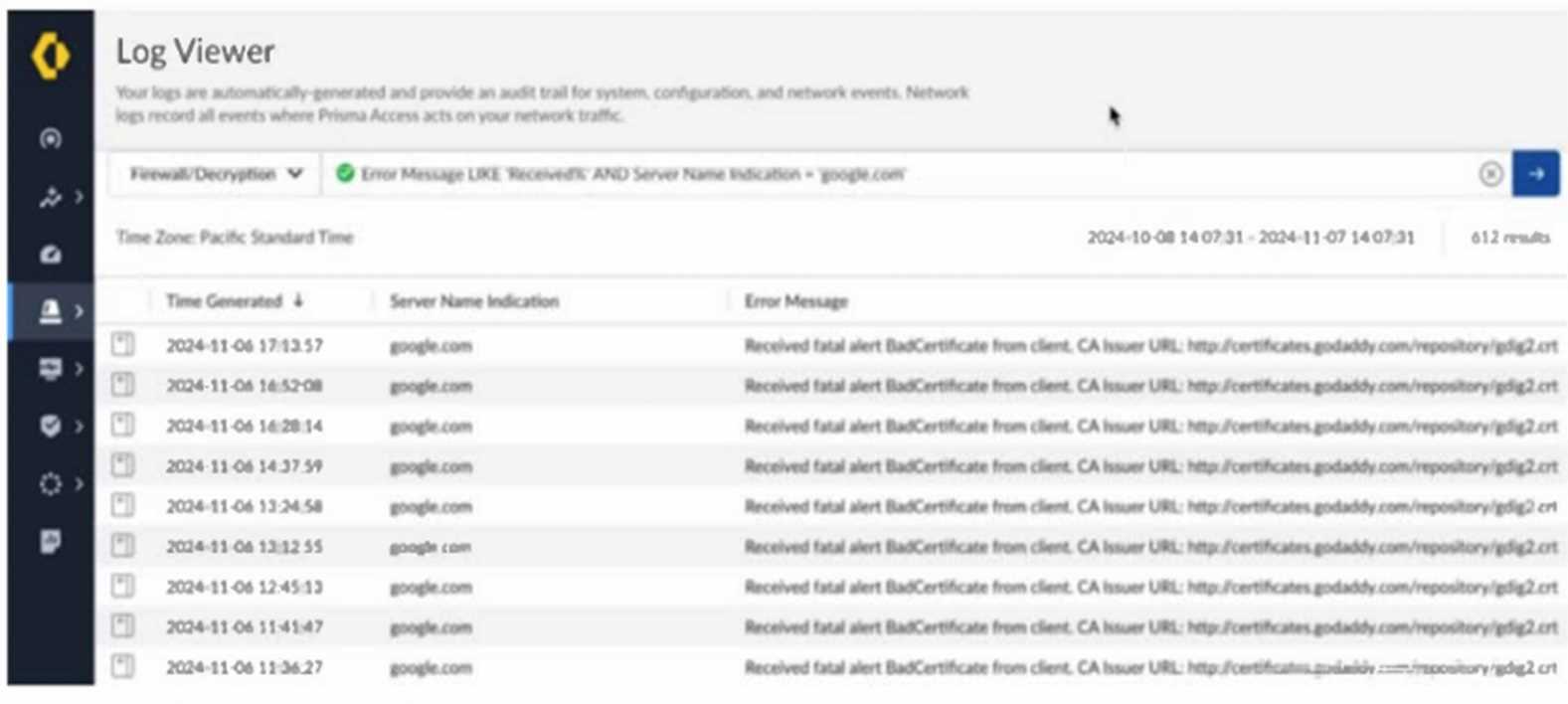
- A. The client is misconfigured.
- B. Create a do not decrypt rule for the hostname “google.com.”
- C. The server has pinned certificates.
- D. Create a do not decrypt rule for the hostname “certificates.godaddy.com.”
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
The error messages indicate that Prisma Access is encountering certificate issues while attempting to
decrypt traffic to "google.com." This suggests that the server has pinned certificates, meaning it does
not allow man-in-the-middle (MITM) decryption by Prisma Access. Since pinned certificates prevent
traffic decryption, a solution is to create a "do not decrypt" rule for the hostname "google.com." This
will allow traffic to flow without triggering certificate errors while maintaining secure communication
with Google's servers.
Comments
Question 2
How can a network security team be granted full administrative access to a tenant's configuration
while restricting access to other tenants by using role-based access control (RBAC) for Panorama
Managed Prisma Access in a multitenant environment?
- A. Create an Access Domain and restrict access to only the Device Groups and Templates for the Target Tenant.
- B. Create a custom role enabling all privileges within the specific tenant's scope and assign it to the security team's user accounts.
- C. Create a custom role with Device Group and Template privileges and assign it to the security team's user accounts.
- D. Set the administrative accounts for the security team to the "Superuser" role.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In a Panorama Managed Prisma Access multitenant environment, Access Domains provide granular
role-based access control (RBAC). By defining an Access Domain, the network security team can be
granted full administrative privileges for a specific tenant's configuration while ensuring they cannot
access or modify other tenants. This method enforces proper segmentation and ensures compliance
with multitenant security policies.
Comments
Question 3
An engineer has configured a Web Security rule that restricts access to certain web applications for a
specific user group. During testing, the rule does not take effect as expected, and the users can still
access blocked web applications.
What is a reason for this issue?
- A. The rule was created with improper threat management settings.
- B. The rule was created in the wrong scope, affecting only GlobalProtect users instead of all users.
- C. The rule was created at a higher level in the rule hierarchy, giving priority to a lower-level rule.
- D. The rule was created at a lower level in the rule hierarchy, giving priority to a higher-level rule.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Prisma Access applies security rules in a hierarchical order, where rules at higher levels take
precedence over those at lower levels. If a more permissive rule is placed higher in the hierarchy, it
may allow traffic before the restrictive Web Security rule is evaluated. To resolve this, the engineer
should reorder the rules to ensure the restrictive Web Security rule is positioned higher in the
hierarchy so it is applied before any broader or conflicting rules.
Comments
Question 4
What will cause a connector to fail to establish a connection with the cloud gateway during the
deployment of a new ZTNA Connector in a data center?
- A. There is a misconfiguration in the DNS settings on the connector.
- B. The connector is deployed behind a double NAT.
- C. The connector is using a dynamic IP address.
- D. There is a high latency in the network connection.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A ZTNA Connector requires a stable and direct connection to the cloud gateway. When the connector
is deployed behind a double NAT (Network Address Translation), it can cause issues with reachability
and session establishment because the cloud gateway may not be able to properly identify and
communicate with the connector. Double NAT can interfere with secure tunneling, IP address
resolution, and authentication mechanisms, leading to connection failures. To resolve this, the
connector should be placed in a network segment with a single NAT or a public IP assignment.
Comments
Question 5
Which feature will fetch user and group information to verify whether a group from the Cloud
Identity Engine is present on a security processing node (SPN)?
- A. SASE Health Dashboard
- B. User Activity Insights
- C. Prisma Access Locations
- D. Region Activity Insights
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The SASE Health Dashboard provides visibility into user and group synchronization between the
Cloud Identity Engine and the Security Processing Nodes (SPNs). It allows administrators to verify
whether a group from the Cloud Identity Engine is properly fetched and available on the SPN for
policy enforcement. This feature helps in troubleshooting identity-based access control issues and
ensures that user group mappings are correctly applied within Prisma Access.
Comments
Question 6
An engineer configures User-ID redistribution from an on-premises firewall connected to Prisma
Access (Managed by Panorama) using a service connection. After committing the configuration,
traffic from remote network connections is still not matching the correct user-based policies.
Which two configurations need to be validated? (Choose two.)
- A. Ensure the Remote_Network_Template is selected when adding the User-ID Agent in Panorama.
- B. Confirm there is a Security policy configured in Prisma Access to allow the communication on port 5007.
- C. Confirm the Collector Pre-Shared Keys match between Prisma Access and the on-premises firewall.
- D. Ensure the Service_Conn_Template is selected when adding the User-ID Agent in Panorama.
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
Ensuring that the Remote_Network_Template is selected when adding the User-ID Agent in
Panorama is crucial because User-ID information must be associated with the correct Remote
Network configuration for policies to apply properly. Additionally, the Service_Conn_Template must
be selected when adding the User-ID Agent in Panorama, as the service connection is responsible for
distributing User-ID mappings between the on-premises firewall and Prisma Access. If either of these
configurations is incorrect, the user information will not be properly mapped, and traffic will not
match user-based policies.
Comments
Question 7
What is the purpose of embargo rules in Prisma Access?
- A. Rate-limiting connections originating from specific countries
- B. Allowing traffic only from specific countries
- C. Blocking connections from specific countries
- D. Blocking traffic from Russia. China, and North Korea only
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Embargo rules in Prisma Access are designed to block traffic from specific countries that are subject
to regulatory or policy-based restrictions. These rules help organizations enforce compliance by
preventing inbound and outbound connections to or from regions that may pose security risks or are
restricted due to legal or geopolitical reasons. They are commonly used to align with government
sanctions and corporate security policies.
Comments
Question 8
Strata Logging Service is configured to forward logs to an external syslog server; however, a month
later, there is a disruption on the syslog server.
Which action will send the missing logs to the external syslog server?
- A. Configure a replay profile with the affected time range and associate it with the affected syslog server profile.
- B. Delete the affected syslog server profile and create a new one.
- C. Export the logs from Strata Logging Service, and then manually import them to the syslog server.
- D. Configure a log filter under the syslog server profile with the affected time range.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Strata Logging Service allows log replay, which enables resending logs that were not successfully
forwarded to an external syslog server due to disruptions. By configuring a replay profile with the
affected time range and associating it with the syslog server profile, Prisma Access will resend the
missing logs, ensuring that all relevant data is restored in the external logging system. This approach
is the most efficient and automated way to recover missing logs.
Comments
Question 9
A large retailer has deployed all of its stores with the same IP address subnet. An engineer is
onboarding these stores as Remote Networks in Prisma Access. While onboarding each store, the
engineer selects the “Overlapping Subnets” checkbox.
Which Remote Network flow is supported after onboarding in this scenario?
- A. To private applications
- B. To the internet
- C. To remote network
- D. To mobile users
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When the "Overlapping Subnets" checkbox is selected during the Remote Network onboarding
process in Prisma Access, the deployment enables Private Application access using Prisma Access for
Users (ZTNA or Private Access). This feature is designed to handle scenarios where multiple sites use
the same IP subnet by leveraging NAT (Network Address Translation) and segmentation to avoid
conflicts.
Since overlapping subnets can create routing challenges for direct remote network-to-remote
network communication, Prisma Access does not support Remote Network-to-Remote Network or
Mobile User communication in this case. Private application access is supported as Prisma Access
correctly routes requests based on application-layer intelligence rather than IP-based routing.
Comments
Question 10
An intern is tasked with changing the Anti-Spyware Profile used for security rules defined in the
GlobalProtect folder. All security rules are using the Default Prisma Profile. The intern reports that
the options are greyed out and cannot be modified when selecting the Default Prisma Profile.
Based on the image below, which action will allow the intern to make the required modifications?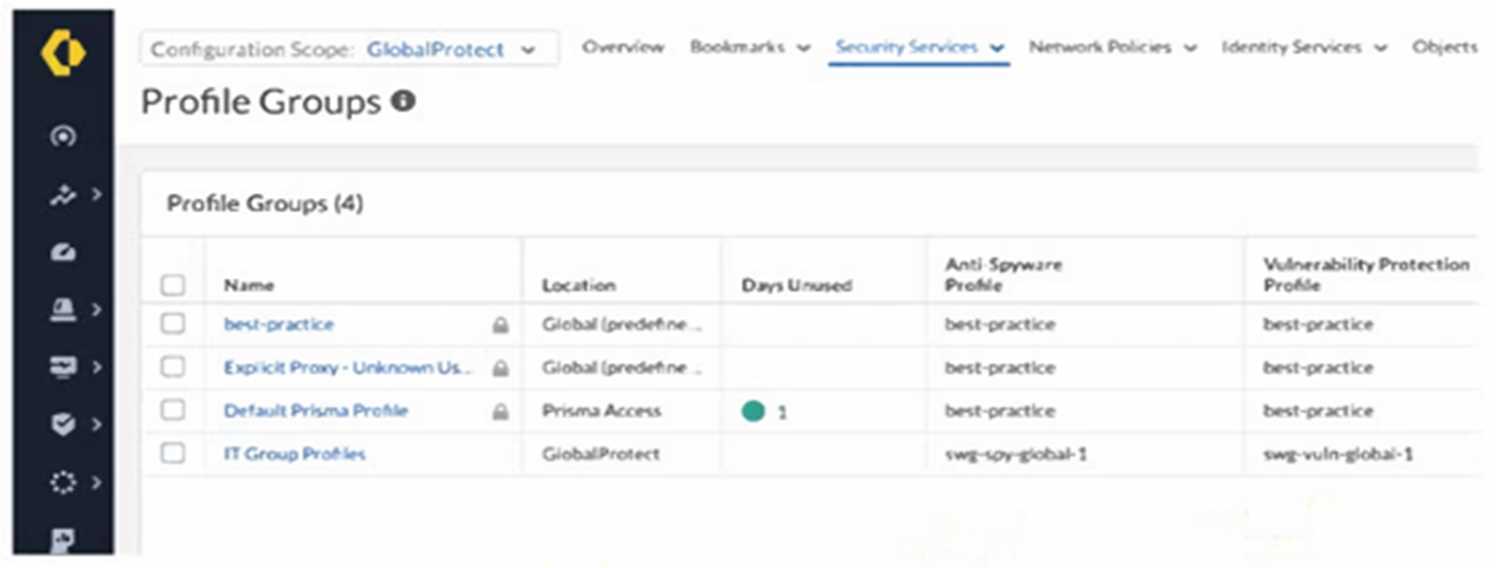
- A. Request edit access for the GlobalProtect scope.
- B. Change the configuration scope to Prisma Access and modify the profile group.
- C. Create a new profile, because default profile groups cannot be modified.
- D. Modify the existing anti-spyware profile, because best-practice profiles cannot be removed from a group.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Palo Alto Networks best practices and the behavior of Strata Cloud Manager (SCM) dictate that
predefined or default objects, including profile groups like "Default Prisma Profile," cannot be
directly modified. These default objects serve as baseline configurations and are often locked to
prevent accidental or unintended changes that could impact the overall security posture.
The intern's experience of the options being greyed out when selecting "Default Prisma Profile" is a
direct indication of this immutability of default objects.
Therefore, the correct action is to:
Create a new Profile Group: The intern should create a new profile group within the appropriate
configuration scope (likely GlobalProtect, given the task).
Configure the new Profile Group: In this new profile group, the intern can select the desired Anti-
Spyware Profile (which might be an existing custom profile or a new one they create).
Modify Security Rules: The security rules currently using the "Default Prisma Profile" in the
GlobalProtect folder need to be modified to use this newly created profile group.
Let's analyze why the other options are incorrect based on official documentation:
A . Request edit access for the GlobalProtect scope. While having the correct scope permissions is
necessary for making any changes within GlobalProtect, it will not override the inherent immutability
of default objects like "Default Prisma Profile." Edit access will allow the intern to create new objects
and modify rules, but not directly edit the default profile group.
B . Change the configuration scope to Prisma Access and modify the profile group. The image shows
that "Default Prisma Profile" has a "Location" of "Prisma Access." However, even within the Prisma
Access scope, default profile groups are generally not directly editable. The issue is not the scope but
the fact that it's a default object.
D . Modify the existing anti-spyware profile, because best-practice profiles cannot be removed from a
group. The question is about changing the profile group, not the individual Anti-Spyware Profile.
While "best-practice" profiles might be part of default groups, the core issue is the inability to modify
the default group itself. Creating a new group allows the intern to choose which Anti-Spyware Profile
to include.
In summary, the fundamental principle in Palo Alto Networks management is that default objects are
typically read-only to ensure a consistent and predictable baseline. To make changes, you need to
create custom objects.
Comments
Page 1 out of 4
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 50
page 2