Question 1
A customer needs to ensure that the number of threads servicing an application does not exceed the
number of database connections available to the application.
What step must you take to address this situation?
- A. Configure a Max Threads Constraint and add your application to the list of applications for the Constraint.
- B. Configure a Work Manager with a Maximum Threads Constraint tied to the Connection Pool and configuration your application to use the Work Manager.
- C. Configure a Work Manager with a Minimum Threads Constraint tied to the Connection Pool and configure your application to use the Work Manager.
- D. Configure a global MaxThreads constraint and target it to the server or clusters where your application is deployed.
- E. Configure the startup parameter "-Dwls-maxThreads" to be the same as the number of database connections configured.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To manage work in your applications, you define one or more of the following Work Manager
components:
Fair Share Request Class:
Response Time Request Class:
Min Threads Constraint:
Max Threads Constraint:
Capacity Constraint
Context Request Class:
Note:
* max-threads-constraintThis constraint limits the number of concurrent threads executing
requests from the constrained work set. The default is unlimited. For example, consider a constraint
defined with maximum threads of 10 and shared by 3 entry points. The scheduling logic ensures that
not more than 10 threads are executing requests from the three entry points combined.
A max-threads-constraint can be defined in terms of a the availability of resource that requests
depend upon, such as a connection pool.
A max-threads-constraint might, but does not necessarily, prevent a request class from taking its fair
share of threads or meeting its response time goal. Once the constraint is reached the server does
not schedule requests of this type until the number of concurrent executions falls below the limit.
The server then schedules work based on the fair share or response time goal.
* WebLogic Server prioritizes work and allocates threads based on an execution model that takes
into account administrator-defined parameters and actual run-time performance and throughput.
Administrators can configure a set of scheduling guidelines and associate them with one or more
applications, or with particular application components.
* WebLogic Server uses a single thread pool, in which all types of work are executed. WebLogic
Server prioritizes work based on rules you define, and run-time metrics, including the actual time it
takes to execute a request and the rate at which requests are entering and leaving the pool.
The common thread pool changes its size automatically to maximize throughput. The queue
monitors throughput over time and based on history, determines whether to adjust the thread
count. For example, if historical throughput statistics indicate that a higher thread count increased
throughput, WebLogic increases the thread count. Similarly, if statistics indicate that fewer threads
did not reduce throughput, WebLogic decreases the thread count. This new strategy makes it easier
for administrators to allocate processing resources and manage performance, avoiding the effort and
complexity involved in configuring, monitoring, and tuning custom executes queues.
Reference: Using Work Managers to Optimize Scheduled Work
Comments
Question 2
What are the three steps you should take to tune a JDBC Connection pool in WebLogic from the
initial settings in a production environment?
- A. Ensure the maximum size is increased to an appropriate setting.
- B. Set the minimum and maximum size of the connection pool to the same value.
- C. Increase the statement cache size.
- D. Add more heap to the JVM.
- E. Add more nodes to the cluster.
Answer:
A, C, E
Explanation:
A:
* Troubleshooting Slow Response Time from the Client and Low Database Usage
These symptoms are usually caused by a bottleneck upstream of the database, perhaps in the JDBC
connectionpooling. Monitor the active JDBC connections in the WebLogic Console and watch for
excessive waiters and wait times; increase the pool size, if necessary.
* Attribute: Maximum Capacity
Maximum number of physical database connections that this connection pool can contain. Different
JDBC Drivers and database servers may limit the number of possible physical connections.
C: Attribute: Statement Cache Size
The algorithm used to maintain the statement cache:
LRU - After the statementCacheSize is met, the Least Recently Used statement is removed when a
new statement is used.
Fixed - The first statementCacheSize number of statements is stored and stay fixed in the cache. No
new statements are cached unless the cache is manually cleared.
E: If the queue appears starved but adding execute threads does not improve performance,
there may be resource contention. Because CPU utilization is low, the threads are probably
spending much of their time waiting for some resource, quite often a database connection.
Use the JDBC monitoring facilities in the console to check for high levels of waiters or long
wait times. Adding connections to the JDBC connection pool may be all that is required to
fix the problem.
Note:
* If you had a JDBC connection pool where the Initial Capacity and Maximum Capacity attributes
were different, you might want to create a gauge monitor to monitor the maximum and minimum
number of connections.
By setting the Threshold Low value to be one less than the Initial Capacity, your gauge monitor
trapcould monitor the ActiveConnectionsCurrentCount attribute of the JDBCDataSourceRuntime
MBean and alert you whenever the number of active connections are less than the Initial Capacity
(which might indicate database connectivity problems).
Comments
Question 3
You have a durable subscriber, and the subscriber is down or not reachable when the message is
produced. Which two options regarding the expiry of these messages are true?
- A. after the subscriber is unavailable for 10 minutes
- B. when the subscriber is available
- C. after the subscriber is unavailable for after an hour
- D. are available until the specified time elapses
- E. are expired instantly
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
By default, JMS messages never expire. When applications send messages to queues or topics with
durable subscribers, WebLogic must retain the message until it is consumed. This is fine in most
point-to-point messaging applications because consumers are constantly consuming messages. Any
message sent to a queue will typically be consumed in a relatively short period of time. If the
consumers get disconnected, they will usually reconnect as soon as possible and start processing any
messages that might have built up in the queue.
D: For durable subscribers to a topic, this is not necessarily true. The messaging system is forced to
retain any message that has not been consumed by a durable subscriber, regardless of whether that
durable subscriber will ever return. In this case, WebLogic is at the mercy of the durable subscriber
to unsubscribe when it no longer wishes to receive the messages. If the durable subscriber logic is
flawed in such a way that the subscribers do not unsubscribe properly, the messaging system will
start to fill up with messages that may never be delivered. This calls for real caution in using durable
subscribers. Fortunately, there is another way to help deal with this problem. Message expiration can
be set at the connection factory level. Using a connection factorys default time-to-live attribute, we
can specify the number of milliseconds that WebLogic should retain an undelivered message after it
is sent.
Comments
Question 4
Identify the two options that can be used to patch WebLogic Server without Incurring application
downtime.
- A. automated process using the Admin Server
- B. automated using JDeveloper
- C. manual process with or without Smart Update
- D. scripted with WLST
- E. automated process using Enterprise Manager 12c
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
Note:
* Rolling Upgrade is the process of upgrading a running WebLogic Server cluster with a patch,
maintenance pack, or minor release without shutting down the entire cluster or domain. During the
rolling upgrade of a cluster, each server in the cluster is individually upgraded and restarted while the
other servers in the cluster continue to host your application.
Comments
Question 5
WebLogic 12c, the Maven plug-in has been enhanced with which Maven goal?
- A. wls:unzip, wls:install-domain, wls:start-domain, wls:wlst, wls:appc
- B. wls:install, wls:install-domain, wls:start-domain, wls:wlst, wls:appc
- C. wls:unzip, wls:create-domain, wls:start-domain, wls:wlst, wls:appc
- D. wls:install, wls:create-domain, wls:start-server, wls:wlst, wls:appc:
Answer:
D
Explanation:
wls-maven-pluginDelivered in WebLogic Server 12c, provides enhanced
functionality to install, start and stop servers, create domains, execute WLST
scripts, and compile and deploy applications.
Reference: Developing Applications for Oracle WebLogic Server, Using the WebLogic Development
Maven Plug-In
Comments
Question 6
Assume that you would like to clone an existing WebLogic Domain and enable some customizations.
What scenario would you choose?
- A. In the Enterprise Manager, find the domain to be cloned. Choose "Clone WebLogic Domain" from the context menu. In the graphical wizard, customize and extend the domain if needed. These steps will only clone only the domain configuration. Binaries with deployments are needed to be cloned by operation on the file system.
- B. In the Enterprise Manager, find the domain to be cloned. Choose "Clone WebLogic Domain" from the context menu. In the graphical wizard, customize the domain. These steps clone the binaries and domain configuration. If the extension is needed, perform it after cloning in the WebLogic web-based console.
- C. In the Enterprise Manager, find the domain to be cloned. Choose "Clone WebLogic Domain" from the context menu. In the graphical wizard, customize and extend the domain if it is needed. These steps clone the binaries and domain configuration.
- D. In the Enterprise Manager, find the domain to be cloned. Choose "Clone WebLogic Domain" from the context menu. These steps clone the binaries and domain configuration. If the customization or extension is needed, complete that after cloning in the WebLogic web-based console.
- E. In the file system, copy the domain structure of the configuration directory and paste it in the new location. Modify configuration files for address and port. If further customization is needed, open the WebLogic web-based console and perform these modifications.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The Clone WebLogic Domain option launches a wizard that enables you to clone a WebLogic Domain
from an existing reference domain that is already discovered with Cloud Control. It allows you to
clone the Middleware Home and its binaries, and the domain configuration.
* If you selected the Cloning a WebLogic Domain option, the Middleware Provisioning: Domain
Configuration page appears. This page contains a set of links to several pages where you can enter
the properties that are most likely to be reconfigured like domain name, listen addresses for the
administration server and managed servers, Node Manager/Machine configuration, and JDBC data
sources.
Comments
Question 7
Which three scenarios are true about Domains?
- A. Domains can be created using the Configuration Wizard.
- B. Domains can be created using WLST.
- C. Domain configuration files are located in the WebLogic home directory.
- D. Domains can be created based on a domain template.
Answer:
ABD
Explanation:
A: a WebLogic domain can be created by using the Configuration Wizard in graphical mode.
B: WLST enables you to create a new domain or update an existing domain
D: A domain template is a JAR file that contains domain configuration documents, applications,
security data, startup scripts, and other information needed to create a domain.
Comments
Question 8
Identify three components of the WebLogic JMS architecture.
- A. JMS Server
- B. JMS Module
- C. Node Manager
- D. Queue Manager
- E. Persistent Store
Answer:
A, B, E
Explanation:
The major components of the WebLogic JMS Server architecture, as illustrated in the figure below.
* (A) JMS servers that can host a defined set of modules and any associated persistent storage that
reside on a WebLogic Server instance.
* (B) JMS modules contains configuration resources (such as queues, topics, and connections
factories) and are defined by XML documents that conform to the weblogic-jmsmd.xsd schema.
* Client JMS applications that either produce messages to destinations or consume messages from
destinations.
* JNDI (Java Naming and Directory Interface), which provides a resource lookup facility. JMS
resources such as connection factories and destinations are configured with a JNDI name. The
runtime implementations of these resources are then bound into JNDI using the given names.
* (E) WebLogic persistent storage (file store or JDBC-accessible) for storing persistent message data.
The following figure illustrates the WebLogic JMS architecture.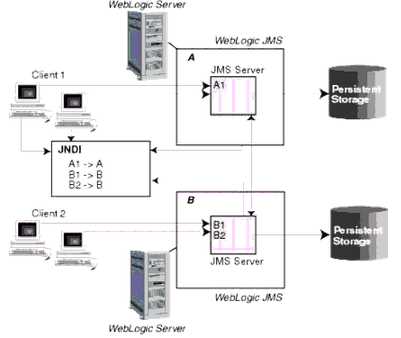
Reference: Understanding WebLogic JMS
Comments
Question 9
How can you configure High Availability for interacting with a non-Oracle database using WebLogic?
- A. Configure multiple physical data sources and reuse the same JNDI name for each.
- B. Use the "compatibility" option of Active GridLink to enable compatibility with non-Oracle databases.
- C. Configure a single physical data source for each node in a database cluster and wrap it using Multi Data Source.
- D. Configure a Data Source Group that contains a physical connection pool to each node in the database cluster.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Note:
* A multi data source can be thought of as a pool of data sources. Multi data sources are best used
for failover or load balancing between nodes of a highly available database system, such as
redundant databases or Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC).
* (not B)
A single GridLink data source provides connectivity between WebLogic Server and an
Oracle Database service, which may include multiple Oracle RAC clusters
* High Availability Storage Solutions
If you have applications that need access to persistent stores that reside on remote machines after
the migration of a JMS server or JTA transaction log, then you should implement one of the following
highly-available storage solutions:
/ File-based stores (default or custom)Implement a hardware solution, such as a dual-ported SCSI
disk or Storage Area Network (SAN) to make a file store available from shareable disks or remote
machines.
/ JDBC-accessible storesConfigure a JDBC store or JDBC TLOG store and use JDBC to access this
store, which can be on yet another server. Applications can then take advantage of any high-
availability or failover solutions offered by your database vendor. In addition, JDBC stores support
GridLink data sources and multi data sources, which provide failover between nodes of a highly
available database system, such as Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC).
Reference: Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuring Server Environments for Oracle WebLogic Server
12c, High Availability Storage Solutions
Comments
Question 10
Which feature is enabled when you start a WebLogic server with the –DserverType=wlx option?
- A. JDBC
- B. JCA
- C. JMS
- D. EJB
- E. Java EE
Answer:
A
Explanation:
-DserverType={"wls" | "wlx"}
Specifies the Server Type, which determines the set of services that are started in the server runtime.
The default is "wls", which starts all WebLogic Server services, including EJB, JMS, Connector,
Clustering, Deployment, and Management.
The "wlx" option starts a server instance that excludes the following services, making for a lighter
weight runtime footprint:
* (not D) Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB)
* (not B, not E) Java EE Connecter Architecture (JCA)
* (not C) Java Message Service (JMS)
Reference: Oracle Fusion Middleware Command Reference for Oracle WebLogic Server , Options for
Configuring Deployment Attributes
Comments
Page 1 out of 8
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 90
page 2