Question 1
You want to set up access control lists on your NameNode in your Big Data Appliance. However,
when you try to do so, you get an error stating “the NameNode disallows creation of ACLs.”
What is the cause of the error?
A. During the Big Data Appliance setup, Cloudera's ACLSecurity product was not installed.
B. Access control lists are set up on the DataNode and HadoopNode, not the NameNode.
C. During the Big Data Appliance setup, the Oracle Audit Vault product was not installed.
D. dfs.namenode.acls.enabled must be set to true in the NameNode configuration.
Answer:
D
To use ACLs, first you’ll need to enable ACLs on the NameNode by adding the following configuration
property to hdfs-site.xml and restarting the NameNode.
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.acls.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
//hortonworks.com/blog/hdfs-acls-fine-grained-permissions-hdfs-files-hadoop/
Comments
Question 2
Your customer has an older starter rack Big Data Appliance (BDA) that was purchased in 2013. The
customer would like to know what the options are for growing the storage footprint of its server.
Which two options are valid for expanding the customer’s BDA footprint? (Choose two.)
- A. Elastically expand the footprint by adding additional high capacity nodes.
- B. Elastically expand the footprint by adding additional Big Data Oracle Database Servers.
- C. Elastically expand the footprint by adding additional Big Data Storage Servers.
- D. Racks manufactured before 2014 are no longer eligible for expansion.
- E. Upgrade to a full 18-node Big Data Appliance.
Answer:
D,E
Comments
Question 3
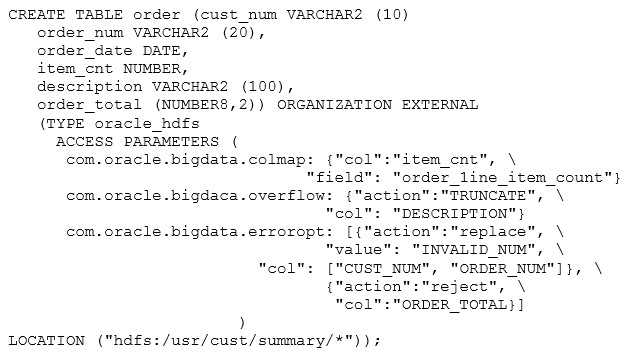
What are three correct results of executing the preceding query? (Choose three.)
A. Values longer than 100 characters for the DESCRIPTION column are truncated.
B. ORDER_LINE_ITEM_COUNT in the HDFS file matches ITEM_CNT in the external table.
C. ITEM_CNT in the HDFS file matches ORDER_LINE_ITEM_COUNT in the external table.
D. Errors in the data for CUST_NUM or ORDER_NUM set the value to INVALID_NUM.
E. Errors in the data for CUST_NUM or ORDER_NUM set the value to 0000000000.
F. Values longer than 100 characters for any column are truncated.
Answer:
A,C,D
Truncates string data. Values longer than 100 characters for the
DESCRIPTION column are truncated.
Truncates string data. Values longer than 100 characters for the
DESCRIPTION column are truncated.
Replaces bad data. Errors in the data for CUST_NUM or ORDER_NUM
set the value to INVALID_NUM.
//docs.oracle.com/cd/E55905_01/doc.40/e55814/bigsql.htm#BIGUG76679
Comments
Question 4
What does the following line do in Apache Pig?
products = LOAD ‘/user/oracle/products’ AS (prod_id, item);
A. The products table is loaded by using data pump with prod_id and item.
B. The LOAD table is populated with prod_id and item.
C. The contents of /user/oracle/products are loaded as tuples and aliased to products.
D. The contents of /user/oracle/products are dumped to the screen.
Answer:
C
The LOAD function loads data from the file system.
LOAD 'data' [USING function] [AS schema];
'data'
The name of the file or directory, in single quote
//pig.apache.org/docs/r0.11.1/basic.html#load
Comments
Question 5
What is the output of the following six commands when they are executed by using the Oracle XML
Extensions for Hive in the Oracle XQuery for Hadoop Connector?
1. $ echo "xxx" > src.txt
2. $ hive --auxpath $OXH_HOME/hive/lib -i $OXH_HOME/hive/init.sql
3. hive> CREATE TABLE src (dummy STRING);
4. hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH 'src.txt' OVERWRITE INTO TABLE src;
5. hive> SELECT * FROM src;
OK
xxx
6. hive> SELECT xml_query ("x/y", "<x><y>123</y><z>456</z></x>") FROM src;
A. xyz
B. 123
C. 456
D. xxx
E. x/y
Answer:
B
Using the Hive Extensions
To enable the Oracle XQuery for Hadoop extensions, use the --auxpath and -i arguments when
$ hive --auxpath $OXH_HOME/hive/lib -i $OXH_HOME/hive/init.sql
The first time you use the extensions, verify that they are accessible. The following procedure creates
a table named SRC, loads one row into it, and calls the xml_query function.
//docs.oracle.com/cd/E53356_01/doc.30/e53067/oxh_hive.htm#BDCUG693
Comments
Question 6
The NoSQL KVStore experiences a node failure. One of the replicas is promoted to primary.
How will the NoSQL client that accesses the store know that there has been a change in the
architecture?
A. The KVLite utility updates the NoSQL client with the status of the master and replica.
B. KVStoreConfig sends the status of the master and replica to the NoSQL client.
C. The NoSQL admin agent updates the NoSQL client with the status of the master and replica.
D. The Shard State Table (SST) contains information about each shard and the master and replica
status for the shard.
Answer:
D
Given a shard, the Client Driver next consults the Shard State Table (SST). For each shard, the SST
contains information about each replication node comprising the group (step 5). Based upon
information in the SST, such as the identity of the master and the load on the various nodes in a
shard, the Client Driver selects the node to which to send the request and forwards the request to
the appropriate node. In this case, since we are issuing a write operation, the request must go to the
master node.
If the machine hosting the master should fail in any way, then the master automatically fails
over to one of the other nodes in the shard. That is, one of the replica nodes is automatically
promoted to master.
//www.oracle.com/technetwork/products/nosqldb/learnmore/nosql-wp-1436762.pdf
Comments
Question 7
Your customer is experiencing significant degradation in the performance of Hive queries. The
customer wants to continue using SQL as the main query language for the HDFS store.
Which option can the customer use to improve performance?
A. native MapReduce Java programs
B. Impala
C. HiveFastQL
D. Apache Grunt
Answer:
B
Cloudera Impala is Cloudera's open source massively parallel processing (MPP) SQL query engine for
data stored in a computer cluster running Apache Hadoop.
Impala brings scalable parallel database technology to Hadoop, enabling users to issue low-latency
SQL queries to data stored in HDFS and Apache HBase without requiring data movement or
transformation.
//en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloudera_Impala
Comments
Question 8
Your customer keeps getting an error when writing a key/value pair to a NoSQL replic
a.
What is causing the error?
A. The master may be in read-only mode and as result, writes to replicas are not being allowed.
B. The replica may be out of sync with the master and is not able to maintain consistency.
C. The writes must be done to the master.
D. The replica is in read-only mode.
E. The data file for the replica is corrupt.
Answer:
C
Replication Nodes are organized into shards. A shard contains a single Replication Node which is
responsible for performing database writes, and which copies those writes to the other Replication
Nodes in the shard. This is called the master node. All other Replication Nodes in the shard are used
to service read-only operations.
Oracle NoSQL Database provides multi-terabyte distributed key/value pair storage that offers
scalable throughput and performance. That is, it services network requests to store and retrieve data
which is organized into key-value pairs.
//docs.oracle.com/cd/E26161_02/html/GettingStartedGuide/introduction.html
Comments
Question 9
The log data for your customer's Apache web server has seven string columns.
What is the correct command to load the log data from the file 'sample.log' into a new Hive table
LOGS that does not currently exist?
A. hive> CREATE TABLE logs (t1 string, t2 string, t3 string, t4 string, t5 string, t6 string, t7 string) ROW
FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ' ';
B. hive> create table logs as select * from sample.log;
C. hive> CREATE TABLE logs (t1 string, t2 string, t3 string, t4 string, t5 string, t6 string, t7 string) ROW
FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ' ';hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH 'sample.log'
OVERWRITE INTO TABLE logs;
D. hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH 'sample.log' OVERWRITE INTO TABLE logs;hive> CREATE TABLE
logs (t1 string, t2 string, t3 string, t4 string, t5 string, t6 string, t7 string) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY ' ';
E. hive> create table logs as load sample.1og from hadoop;
Answer:
C
The CREATE TABLE command creates a table with the given name.
Load files into existing tables with the LOAD DATA command.
//cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+DML#LanguageManualDML-
InsertingdataintoHiveTablesfromqueries
//cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+DDL
Comments
Question 10
Your customer’s Oracle NoSQL store has a replication factor of 3. One of the customer’s replica nodes
goes down.
What will be the long-term performance impact on the customer’s NoSQL database if the node is
replaced?
A. There will be no performance impact.
B. The database read performance will be impacted.
C. The database read and write performance will be impacted.
D. The database will be unavailable for reading or writing.
E. The database write performance will be impacted.
Answer:
C
The number of nodes belonging to a shard is called its Replication Factor. The larger a shard's
Replication Factor, the faster its read throughput (because there are more machines to service the
read requests) but the slower its write performance (because there are more machines to which
writes must be copied).
Replication Nodes are organized into shards. A shard contains a single Replication Node which
is responsible for performing database writes, and which copies those writes to the other Replication
Nodes in the shard. This is called the master node. All other Replication Nodes in the shard are used
to service read-only operations.
//docs.oracle.com/cd/E26161_02/html/GettingStartedGuide/introduction.html#replicationfact
or
Comments
Page 1 out of 7
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 72
page 2