oracle 1z0-1085-21 practice test
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Foundations 2021 Associate Exam
Last exam update: Jul 20 ,2024
Question 1
Which SLA type is not offered by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure compute service?
- A. Always on data encryption for data-at-rest.
- A. Data Plane
- B. Certificate Management service
- B. Performance Plane
- C. Captcha
- C. Service Plane
- D. Key Management service
- D. Control Plane
- E. Managed Active Directory service
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Service Plane isNOTan SLA provided by OCI. See the table below: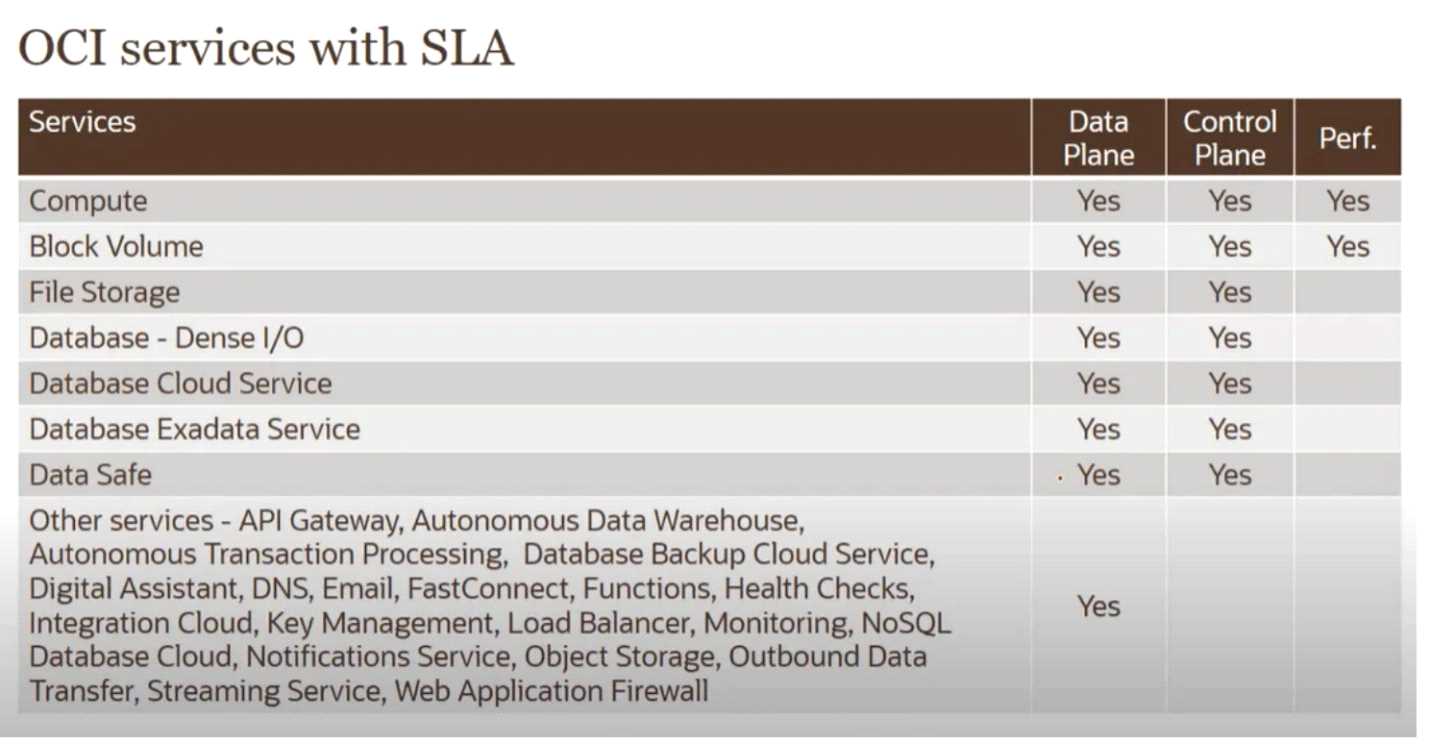
Reference:
https://k21academy.com/1z0-1085/service-level-agreement-sla-in-oracle-cloud-oci/
Question 2
Which of the following is an example of an edge service in OCI?
- A. stopping/starting the instance
- A. DNS Zone Management
- B. backing up data to object storage
- B. Virtual Machines
- C. adding additional compute instances
- C. OCI compute instances
- D. changing compute instance size
- D. Oracle Data Guard
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Domain Name System (DNS) service lets you
create and manage your
DNS zones
. You can create zones, add records to zones, and allow Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's edge
network to handle your domain's DNS queries.
Reference:
https://www.oracle.com/a/ocom/docs/cloud/edge-services-100.pdf
Question 3
You are analyzing your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) usage with Cost Analysis tool in the OCI
console.
Which of the following is NOT a default feature of the tool?
- A. Fault Domains
- A. Filter costs by applications
- B. Compartments
- B. Filter costs by tags
- C. Top of Rack Switches
- C. Filter costs by compartments
- D. Power Distribution Units
- D. Filter costs by date
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Cost Analysisis an easy-to-use visualization tool to help you track and optimize your Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure spending, allows you to generate charts, and download accurate, reliable tabular
reports of aggregated cost data on your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure consumption. Use the tool for
spot checks of spending trends and for generating reports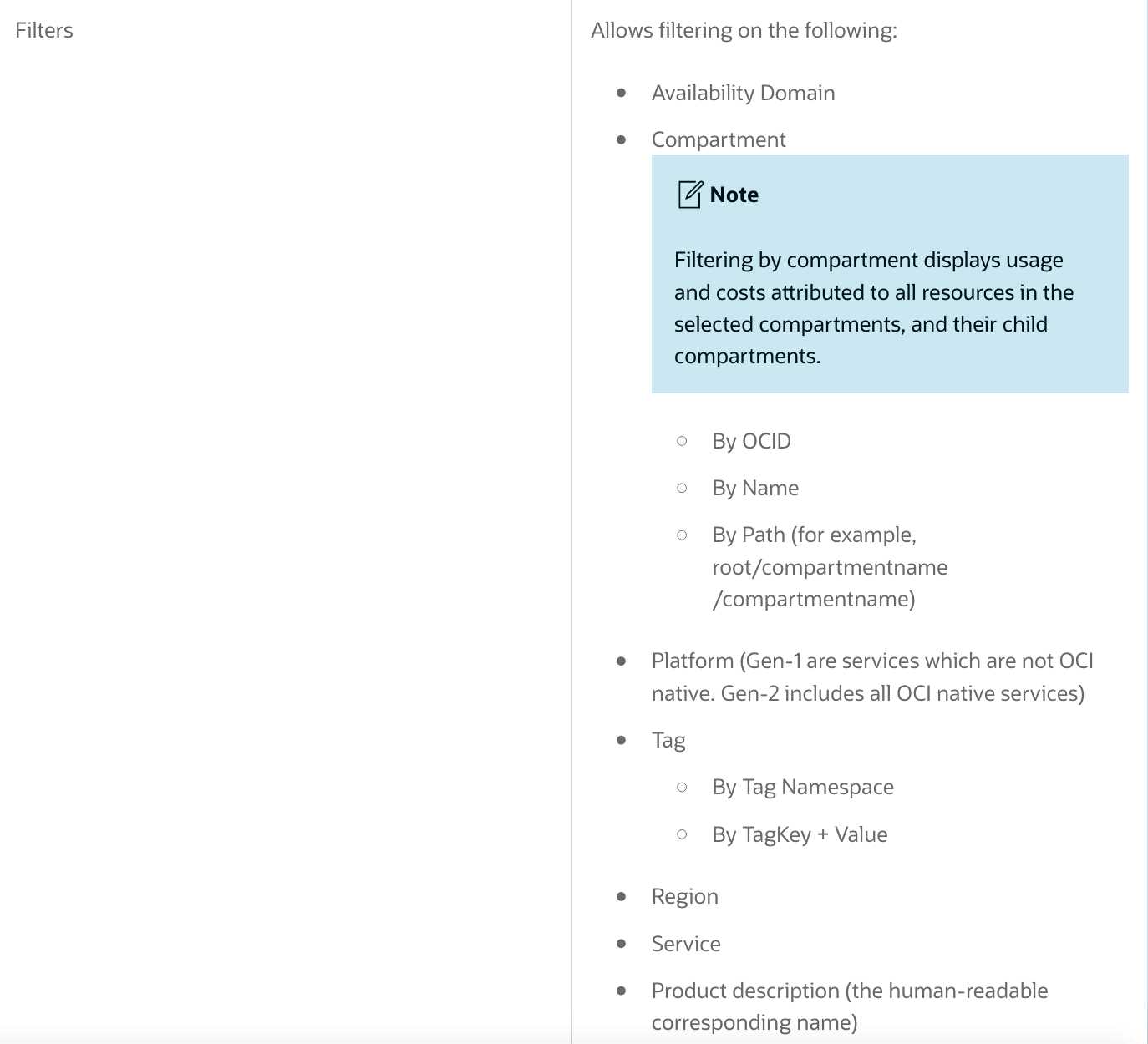
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-
us/iaas/Content/Billing/Concepts/costanalysisoverview.htm
Question 4
Which security service is offered by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure?
- A. REST APIs
- A. Certificate Management System
- B. OCI desktop client
- B. Key Management
- C. Secure Shell (SSH)
- C. Managed Active Directory
- D. OCI Console
- D. Managed Intrusion Detection
- E. Command-line Interface
- F. Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- G. Serial console connection
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud InfrastructureKey Managementis a managed service that enables you to encrypt your
data using keys that you control.
Reference:
https://www.oracle.com/in/cloud/security/cloud-services/key-management.html
Question 5
___________________ is a fully-managed, scalable, and highly available service that you can use to
deploy your containerized applications to the cloud.
- A. VCN Peering
- A. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Kubernetes
- B. FastConnect
- B. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Containerization
- C. Internet Gateway
- C. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Deployment
- D. IPSec VPN
- D. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Container Engine for Docker
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud InfrastructureContainer Engine for Kubernetesis a fully-managed, scalable, and highly
available service that you can use to deploy your containerized applications to the cloud. Use
Container Engine for Kubernetes (sometimes abbreviated to just OKE) when your development team
wants to reliably build, deploy, and manage cloud-native applications. You specify the compute
resources that your applications require, and Container Engine for Kubernetes provisions them on
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure in an existing OCI tenancy.
You can access Container Engine for Kubernetes to define and create Kubernetes clusters using the
Console and the REST API. You can access the clusters you create using the Kubernetes command line
(kubectl), the Kubernetes Dashboard, and the Kubernetes API.
Container Engine for Kubernetes is integrated with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Identity and Access
Management (IAM), which provides easy authentication with native Oracle Cloud Infrastructure
identity functionality.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-
us/iaas/Content/ContEng/Concepts/contengoverview.htm
Question 6
Your company has deployed a business critical application in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. What
should you do to ensure that your application has the highest level of resilience and availability?
- A. OCI Exadata DB Systems
- A. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Subnets
- B. OCI Autonomous Data Warehouse
- B. Deploy the application across multiple Virtual Cloud Networks
- C. OCI Virtual Machine Instance
- C. Deploy the application across multiple Regions and Availability Domains
- D. OCI Dedicated Virtual Host
- D. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Fault Domains
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To design a high availability architecture, three key elements should be considered redundancy,
monitoring, and failover:
1) Redundancymeans that multiple components can perform the same task. The problem of a single
point of failure is eliminated because redundant components can take over a task performed by a
component that has failed.
2) Monitoringmeans checking whether or not a component is working properly.
3) Failoveris the process by which a secondary component becomes primary when the primary
component fails.
The best practices introduced here focus on these three key elements. Although high availability can
be achieved at many different levels, including the application level and the cloud infrastructure
level, here we will focus on the cloud infrastructure level.
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructureregionis a localized geographic area composed of one or more
availability domains, each composed of three fault domains. High availability is ensured by a
redundancy of fault domains within the availability domains.
Anavailability domainis one or more data centers located within a region. Availability domains are
isolated from each other, fault tolerant, and unlikely to fail simultaneously. Because availability
domains do not share physical infrastructure, such as power or cooling, or the internal availability
domain network, a failure that impacts one availability domain is unlikely to impact the availability of
others.
Afault domainis a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each
availability domain contains three fault domains. Fault domains let you distribute your instances so
that they are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain. As a result, an
unexpected hardware failure or a Compute hardware maintenance that affects one fault domain
does not affect instances in other fault domains. You can optionally specify the fault domain for a
new instance at launch time, or you can let the system select one for you.
All the availability domains in a region are connected to each other by a low-latency, high bandwidth
network. This predictable, encrypted interconnection between availability domains provides the
building blocks for both high availability and disaster recovery.
Reference:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/solutions/design-ha/index.html#GUID-76ECDDB4-4CB1-
4D93-9A6D-A8B620F72369
Question 7
Which statement below is not true for Oracle Cloud infrastructure Compartments?
- A. Software as a Service (SaaS)
- A. Resources can be moved from one compartment to another
- B. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- B. Compartments cannot be nested
- C. Anything as a Service (XaaS)
- C. Each OCI resource belongs to a single compartment
- D. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- D. Resources and compartments can be added and deleted anytime
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When creating a compartment, you must provide a name for it (maximum 100 characters, including
letters, numbers, periods, hyphens, and underscores) that is unique within its parent compartment.
You must also provide a description, which is a non-unique, changeable description for the
compartment, from 1 through 400 characters. Oracle will also assign the compartment a unique ID
called an Oracle Cloud ID.
You can create subcompartments in compartments to create hierarchies that are six levels deep.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Identity/Tasks/managingcompartments.htm
When you first start working with Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, you need to think carefully about how
you want to use compartments to organize and isolate your cloud resources. Compartments are
fundamental to that process. Most resources can be moved between compartments. However, it's
important to think through your compartment design for your organization up front, before
implementing anything. For more information, see
Setting Up Your Tenancy
.
The Console is designed to display your resources bycompartmentwithin the current region. When
you work with your resources in the Console, you must choose which compartment to work in from a
list on the page. That list is filtered to show only the compartments in the tenancy that you have
permission to access. If you're an administrator, you'll have permission to view all compartments and
work with any compartment's resources, but if you're a user with limited access, you probably won't.
Compartments are tenancy-wide, across regions. When you create a compartment, it is available in
every region that your tenancy is subscribed to. You can get a cross-region view of your resources in a
specific compartment with the compartment explorer. See
Viewing All Resources in a Compartment
.
You can create subcompartments in compartments to create hierarchies that are six levels deep.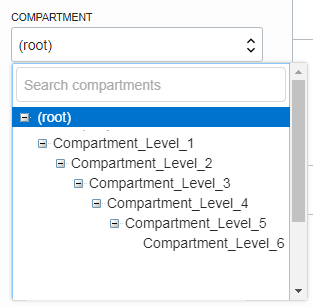
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-
us/iaas/Content/Identity/Tasks/managingcompartments.htm
Question 8
What does compute instance vertical scaling mean?
- A. Operating system
- A. Providing Fault tolerance
- B. Network
- B. Adding additional compute instances
- C. Storage
- C. Enabling Disaster recovery
- D. Servers
- D. Changing to a large or smaller shape
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Changing the Shape of an Instance (Horizontal Scaling)
You can change the shape of a virtual machine (VM) instance without having to rebuild your
instances or redeploy your applications. This lets youscale upyour Compute resources for increased
performance, orscale downto reduce cost.
Autoscaling (vertical scaling)
Autoscaling lets you automatically adjust the number of Compute instances in an instance pool based
on performance metrics such as CPU utilization. This helps you provide consistent performance for
your end users during periods of high demand, and helps you reduce your costs during periods of low
demand.
As load increases, instances are automatically provisioned: the instance poolscales out. As load
decreases, instances are automatically removed: the instance poolscales in.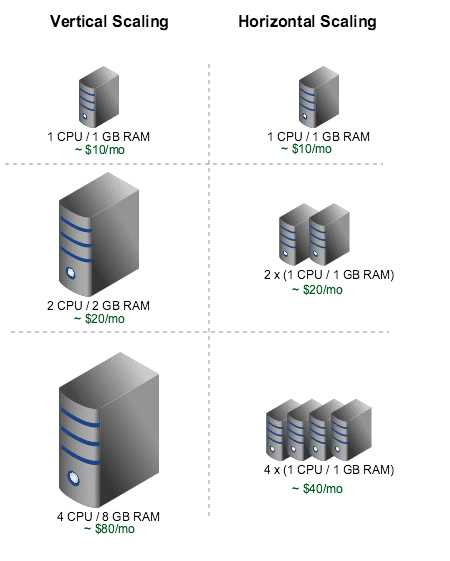
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Compute/Tasks/resizinginstances.htm
Question 9
How is total network throughput allocated to a Virtual Machine (VM) Instance?
- A. Deploy the application across multiple Regions and Availability Domains.
- A. Network bandwidth is variable
- B. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and subnet.
- B. Network bandwidth is proportional to the number of OCPUs in the Instance shape
- C. Deploy the application across multiple Virtual Cloud Networks.
- C. When launching a compute instance, customers may select the desired maximum network bandwidth
- D. Deploy the application across multiple Availability Domains and Fault Domains.
- D. Each VM is allocated 10 Gbps of network bandwidth regardless of the selected shape
Answer:
B
Explanation:
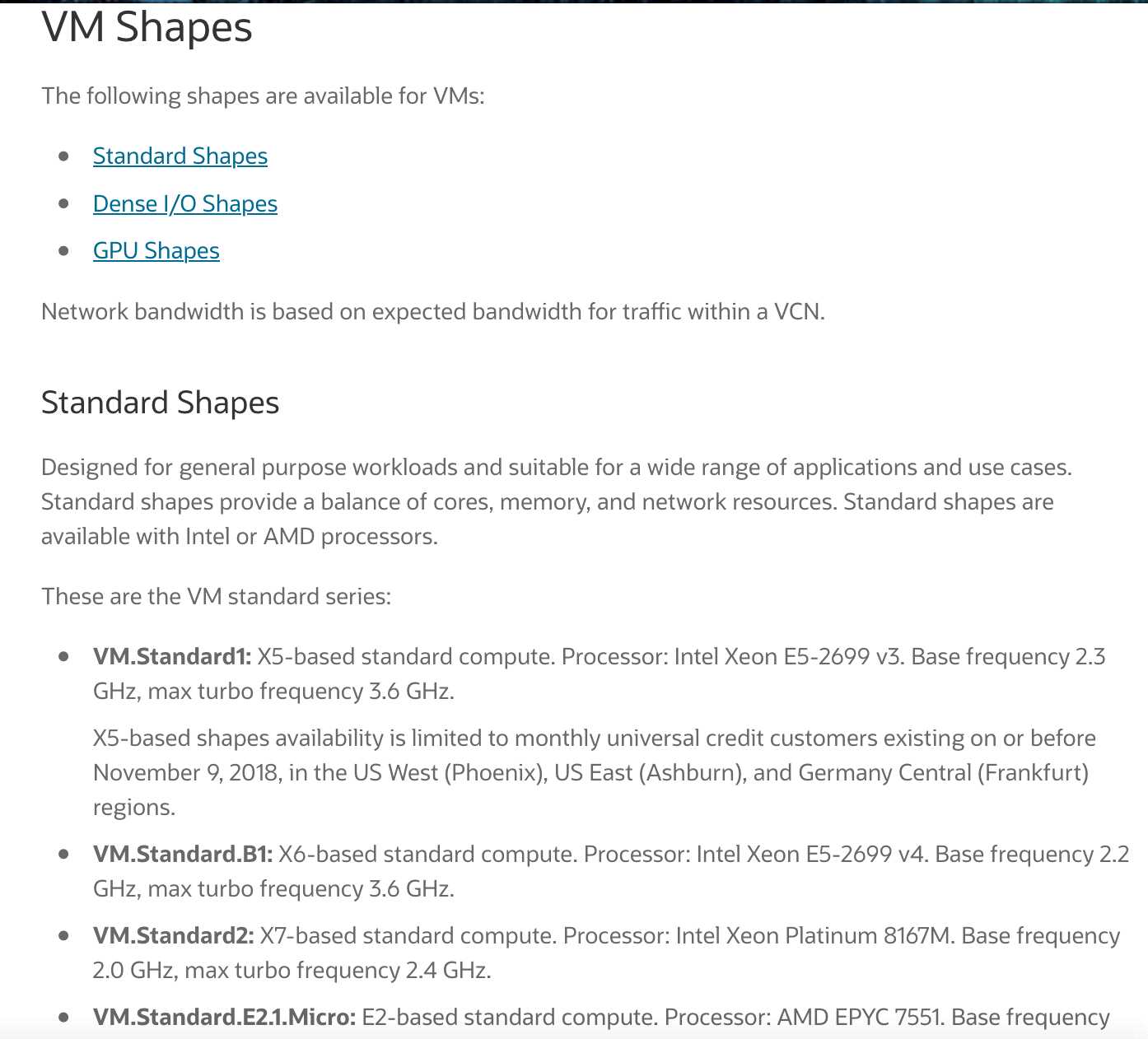
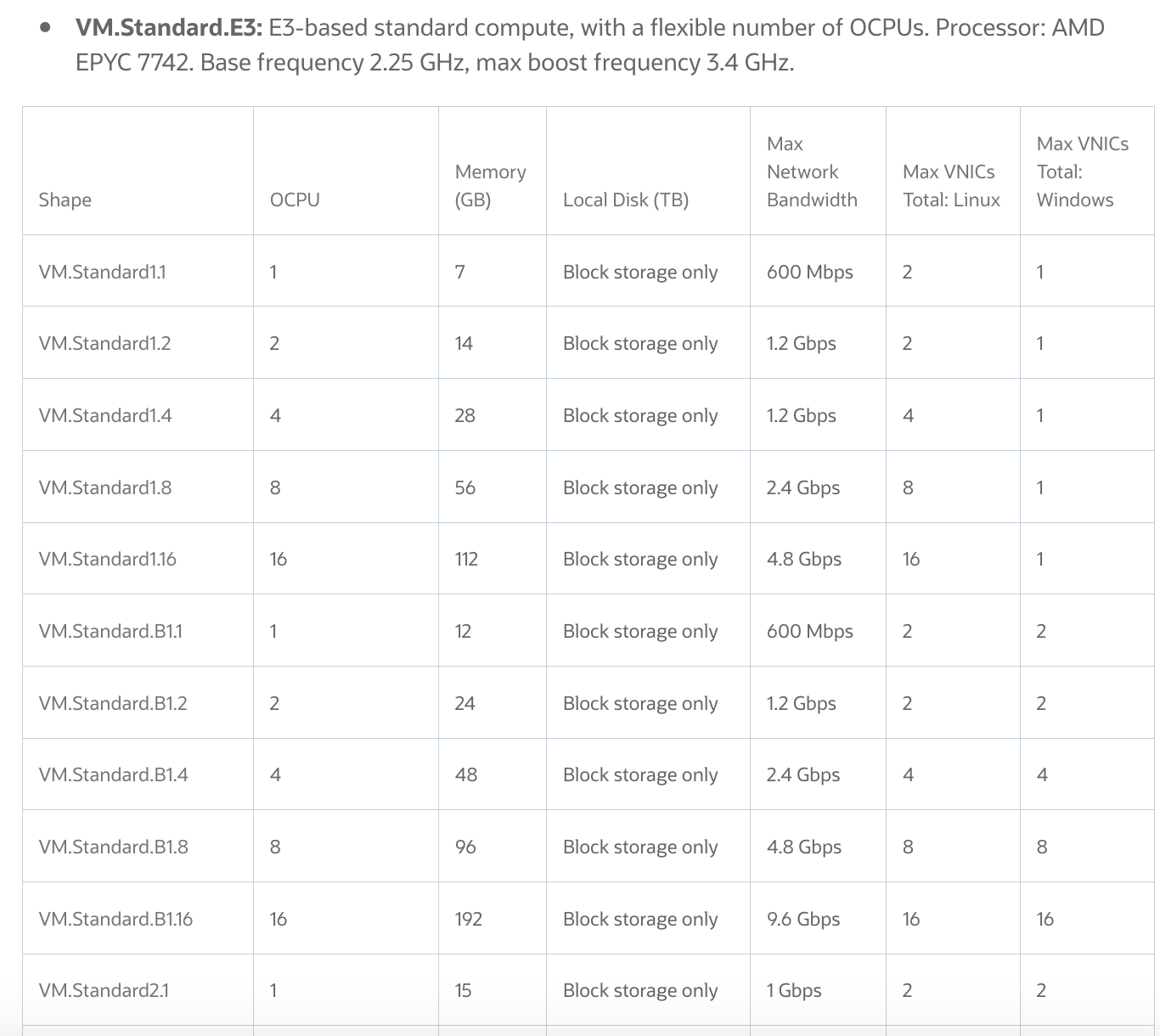
A shape is a template that determines the number of CPUs, amount of memory, and other resources
that are allocated to an instance.
The network bandwidth isdirectly proportionalto the number ofOCPUsin the instance shape!

Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-
us/iaas/Content/Compute/References/computeshapes.htm
Question 10
Which option provides the best performance for running OTLP workloads in Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure (OCI)?
- A. Replace E-Business Suite with an Oracle SaaS application
- A. OCI Autonomous Data Warehouse
- B. OCI Exadata DB Systems and OCI compute instances
- B. OCI Virtual Machine Instance
- C. OCI Exadata DB Systems and Oracle Functions
- C. OCI Dedicated Virtual Host
- D. Oracle Exadata Cloud at customer, Storage Gateway and API Gateway
- D. OCI Autonomous Transaction Processing
Answer:
D
Explanation:
https://docs.oracle.com/en/cloud/paas/atp-cloud/index.html
Question 11
Which resource do you manage in an Infrastructure-as-a-services (IAAS) offering?
- A. Oracle Functions
- A. Operating system
- B. Virtual Cloud Network
- B. Network
- C. Streaming
- C. Storage
- D. Audit
- D. Servers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
is a type of cloud service model in which computing resources are
hosted in the cloud. Businesses can use the IaaS model to shift some or all of their use of on-
premises or colocated data center infrastructure to the cloud, where it is owned and managed by a
cloud provider. These infrastructure elements can include compute, network, and storage hardware
as well as other components and software.
How Does IaaS Work?
In a typical IaaS model, a businesswhich can be of any sizeconsumes services like compute,
storage, and databases from a cloud provider. The cloud provider offers those services by hosting
hardware and software in the cloud. The business will no longer need to purchase and manage its
own equipment, or space to host the equipment, and the cost will shift to a pay-as-you-go model.
When the business needs less, it pays for less. And when it grows, it can provision additional
computing resources and other technologies in minutes.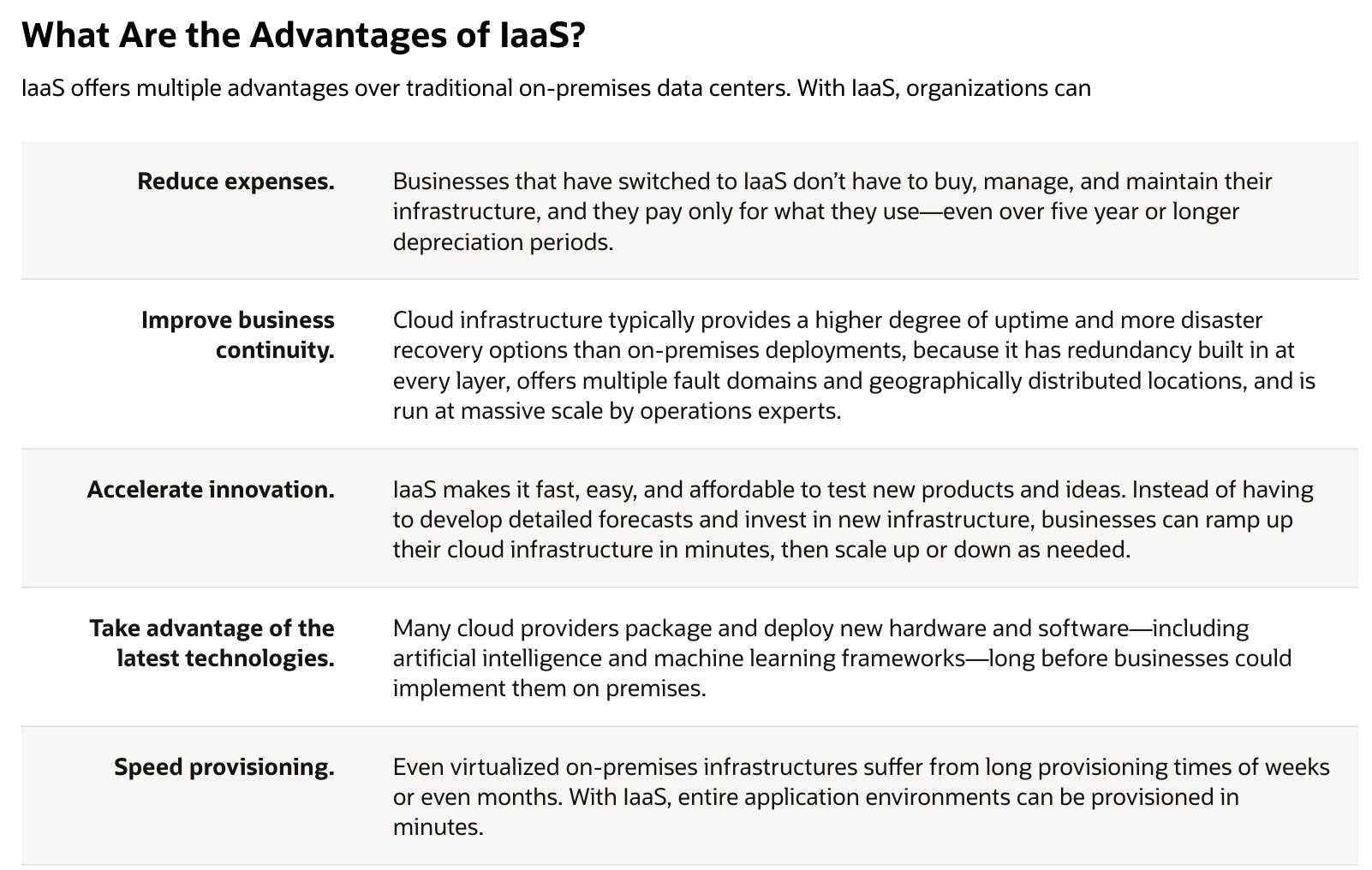
Reference:
https://www.oracle.com/in/cloud/what-is-iaas/
Question 12
Which statement is correct regarding the oracle cloud infrastructure Compute services?
- A. Virtual Cloud Network (VCN)
- A. When you stop a compute instance, all data on the boot volume is lost
- B. Object Storage
- B. You can attach a maximum of one public to each compute instance
- C. Web Application Firewall
- C. You can launch either virtual machines or bare metal instances
- D. Virtual Firewall
- D. You cannot attach a block volume to a compute instance
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Compute lets you provision and manage compute hosts, known
asinstances
. You can launch instances as needed to meet your compute and application requirements. After you
launch an instance, you can access it securely from your computer, restart it, attach and detach
volumes, and terminate it when you're done with it. Any changes made to the instance's local drives
are lost when you terminate it. Any saved changes to volumes attached to the instance are retained.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers both bare metal and virtual machine instances:
1) Bare Metal:A bare metal compute instance gives you dedicated physical server access for highest
performance and strong isolation.
2) Virtual Machine:A virtual machine (VM) is an independent computing environment that runs on
top of physical bare metal hardware. The virtualization makes it possible to run multiple VMs that are
isolated from each other. VMs are ideal for running applications that do not require the performance
and resources (CPU, memory, network bandwidth, storage) of an entire physical machine.
An Oracle Cloud Infrastructure VM compute instance runs on the same hardware as a bare metal
instance, leveraging the same cloud-optimized hardware, firmware, software stack, and networking
infrastructure.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-
us/iaas/Content/Compute/Concepts/computeoverview.htm
Question 13
You want to leverage a managed Real Application Cluster (RAC) offering in Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure. which OCI Managed database service would you choose?
- A. No username and password required
- A. Autonomous Transaction Processing (shared)
- B. Scale both CPU and Storage without downtime
- B. VM DB System
- C. Apply databasepatches as they become available
- C. Autonomous Data Warehousing (shared)
- D. Maintain root level acress to the underlying operating system
- D. Bare Metal DB Systems
Answer:
B
Explanation:
There are 2 types of DB systems on virtual machines:
A 1-node VM DB system consists of one VM.
A 2-node VM DB system consists of two VMs clustered with RAC enabled.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Database/Concepts/overview.htm
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure offers single-node DB systems on either bare metal orvirtual machines,
and 2-nodeRAC DB systemson virtual machines. If you need to provision a DB system for
development or testing purposes, then a special
fast provisioning
single-node virtual machine system
is available.
You can manage these systems by using the Console, the API, the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure CLI, the
Database CLI (DBCLI), Enterprise Manager, Enterprise Manager Express, or SQL Developer.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Database/Concepts/overview.htm
Question 14
Which Oracle cloud infrastructure capability can be used to protect against power failures within an
availability Domain?
- A. Weekly
- A. Data Plane
- B. Monthly
- B. Fault Domains
- C. Annually
- C. Services Cells
- D. Daily
- D. Top of Rack Switch
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A fault domain is a grouping of hardware and infrastructure within an availability domain. Each
availability domain contains three fault domains. Fault domains provide anti-affinity: they let you
distribute your instances so that the instances are not on the same physical hardware within a single
availability domain. A hardware failure or Compute hardware maintenance event that affects one
fault domain does not affect instances in other fault domains. In addition, the physical hardware in a
fault domain has independent and redundant power supplies, which prevents a failure in the power
supply hardware within one fault domain from affecting other fault domains.
To control the placement of your compute instances, bare metal DB system instances, or virtual
machine DB system instances, you can optionally specify the fault domain for a new instance or
instance pool at launch time. If you don't specify the fault domain, the system selects one for you.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure makes a best-effort anti-affinity placement across different fault domains,
while optimizing for available capacity in the availability domain. To change the fault domain for an
instance, terminate it and launch a new instance in the preferred fault domain.
Use fault domains to do the following things:
Protect against unexpected hardware failures or power supply failures.
Protect against planned outages because of Compute hardware maintenance.
Reference:
https://blogs.oracle.com/cloud-infrastructure/using-availibility-domains-and-fault-domains-to-
improve-application-resiliency
Question 15
Which statement is true for an oracle cloud Infrastructure (OCI) compute instance?
- A. Cost-tracking tags
- A. Compute instance always get a public IP address
- B. Free-form tags
- B. Compute instance does not use a boot volume
- C. Compartments
- C. Compute instance cannot leverage auto scaling feature
- D. Virtual Cloud Network
- D. Compute instance always get a private IP address
- E. Tenancy
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When you create an instance, the instance is automatically attached to a virtual network interface
card (VNIC) in the cloud network's subnet and given a private IP address from the subnet's CIDR. You
can let the IP address be automatically assigned, or you can specify a particular address of your
choice. The private IP address lets instances within the cloud network communicate with each other.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-us/iaas/Content/Compute/Tasks/launchinginstance.htm
Instances use IP addresses for communication. Each instance hasat leastone private IP address
andoptionallyone or more public IP addresses. A private IP address enables the instance to
communicate with other instances inside the VCN, or with hosts in your on-premises network (via an
IPSec VPN or Oracle Cloud Infrastructure FastConnect). A public IP address enables the instance to
communicate with hosts on the internet.
Reference:
https://docs.cloud.oracle.com/en-
us/iaas/Content/Network/Tasks/managingIPaddresses.htm