Question 1
Click the exhibit button.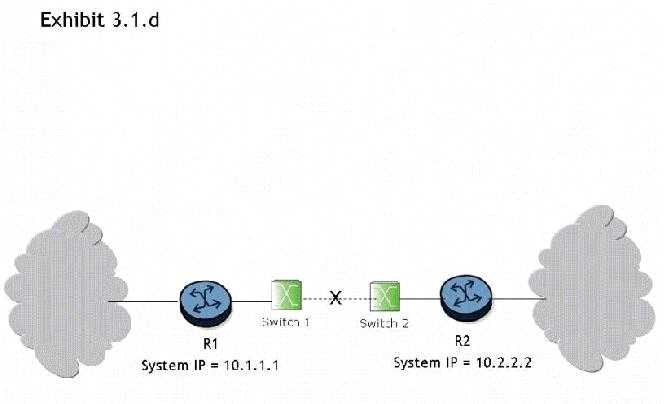
What triggers convergence of the routing protocol when the link between switch 1 and switch 2 goes
down?
- A. Convergence is triggered when the adjacency between routers R1 and R2 drops as a result of Hello timeouts. At this point, both routers R1 and R2 re-compute their link state database and send updates to their adjacent routers. Once the process is complete for all routers, the networks have converged.
- B. Convergence is triggered when the physical interfaces between routers R1 and R2 go down. At this point, both routers R1 and R2 re-compute their link state database and send updates to their adjacent routers. Once the process is complete for all routers, the networks have converged.
- C. Convergence will not be triggered because switches cannot run routing protocols between them.
- D. Convergence is triggered when the switches notify the routers about the link state information. At this point, both routers R1 and R2 re-compute their link state database and send updates to their adjacent routers. Once the process is complete for all routers, the networks have converged
- E. Convergence is triggered when an LSA is sent from router R1 to router R2 to indicate that the link is down. At this point, both routers R1 and R2 re-compute their link state database and send updates to their adjacent routers. Once the process is complete for all routers, the networks have converged.
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 2
What are the default Hello and Dead timer intervals for OSPF on the Alcatel-Lucent 7750 SR?
- A. 5 and 15 seconds
- B. 10 and 30 seconds
- C. 5 and 20 seconds
- D. 10 and 40 seconds
Answer:
D
Comments
Question 3
What causes an adjacency to change from down to two ways?
- A. When a link state update is received in response to a link state request.
- B. When a router receives a Hello packet that contains its own router ID in the neighbor list from a neighbor.
- C. When a router receives a database description packet from a neighbor.
- D. When a link state acknowledgement is received in response to a link state update.
Answer:
B
Comments
Question 4
Click the exhibit button.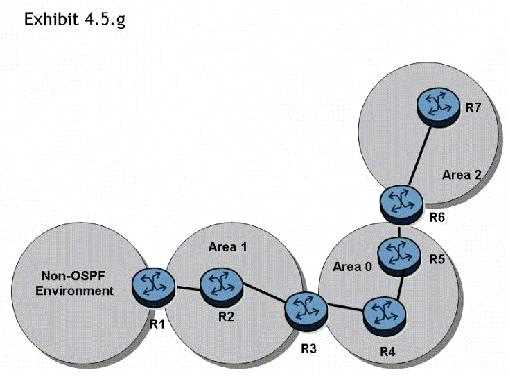
In the topology shown, router R1 is an ASBR configured to export external routes to OSPF. Assuming
that there are no stub networks, which of the following statements regarding type 4 LSA generation
is true?
- A. Router R1 generates a type 4 LSA that is flooded to areas 0, 1, and 2.
- B. Router R3 generates a type 4 LSA that is flooded to areas 0, 1, and 2.
- C. Router R3 generates a type 4 LSA that is flooded to areas 0 and 2.
- D. Router R3 generates a type 4 LSA that is flooded to area 0, and router R6 generates a type 4 LSA that is flooded to area 2.
Answer:
D
Comments
Question 5
Which of the following commands can be used to display the number of SPF computations that have
been performed on a router?
- A. show router ospf area <area-id>
- B. show router ospf neighbor
- C. show router ospf interface
- D. show router ospf status
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 6
Which of the following statements describe the major features of OSPF? Choose two answers.
- A. Fast reroute capability
- B. Control traffic prioritization
- C. Route redistribution
- D. Traffic engineering extensions
- E. Cut through forwarding
Answer:
C, D
Comments
Question 7
Click the exhibit button.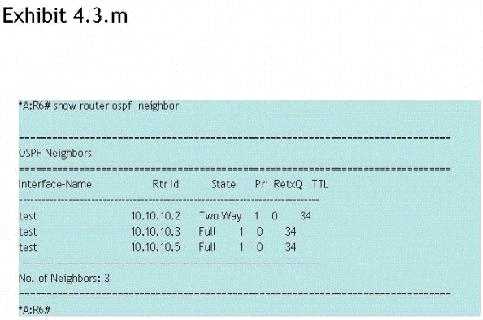
What can you deduce from the show command on router R6?
- A. The router R6 interface is in a multi-access segment. It is neither the DR nor the BDR for the segment. The DR for this segment would be the router with router ID 10.10.10.5.
- B. The router R6 interface is in a multi-access segment. It is neither the DR nor the BDR for the segment; however, this command does not indicate whether 10.10.10.3 or 10.10.10.5 is the DR or BDR.
- C. The router R6 interface is in a multi-access segment. It is the BDR, which is why it is not adjacent to the other routers.
- D. The router R6 interface is in a multi-access segment. It is neither the DR nor the BDR for the segment. The DR for this segment would be the router with router ID 10.10.10.3.
Answer:
B
Comments
Question 8
Click the exhibit button.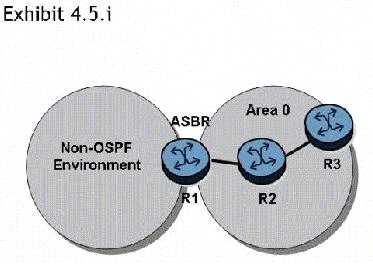
In the topology shown, router R1 is an ASBR configured to export external routes to OSPF. How many
type 4 LSAs will be present in the network?
- A. One.
- B. One for each of the routers in area 0
- C. One for each of the external routes exported by router R1.
- D. Type 4 LSAs are not generated in this network topology.
Answer:
D
Comments
Question 9
Which of the following conditions will prevent an OSPF adjacency from reaching the full state?
Choose three answers.
- A. MTU mismatch
- B. Incorrect subnet mask
- C. System interface not included in OSPF
- D. Area ID not the same
- E. Different metric set on each end of the link
- F. Router ID not defined
Answer:
A, B, D
Comments
Question 10
Click the exhibit button.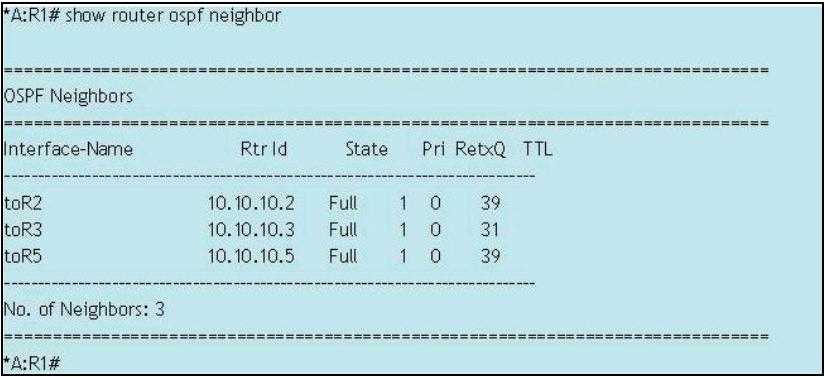
The following command sequence is executed on router R2:
A: R2# configure router ospf router-id 10.10.10.99
A: R2# configure router router-id 10.10.10.66
On router R1, what router ID appears for router R2 directly after these commands are executed?
- A. 10.10.10.99
- B. 10.10.10.66
- C. 10.10.10.2
- D. 10.10.10.1
Answer:
C
Comments
Page 1 out of 85
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 852
page 2