Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.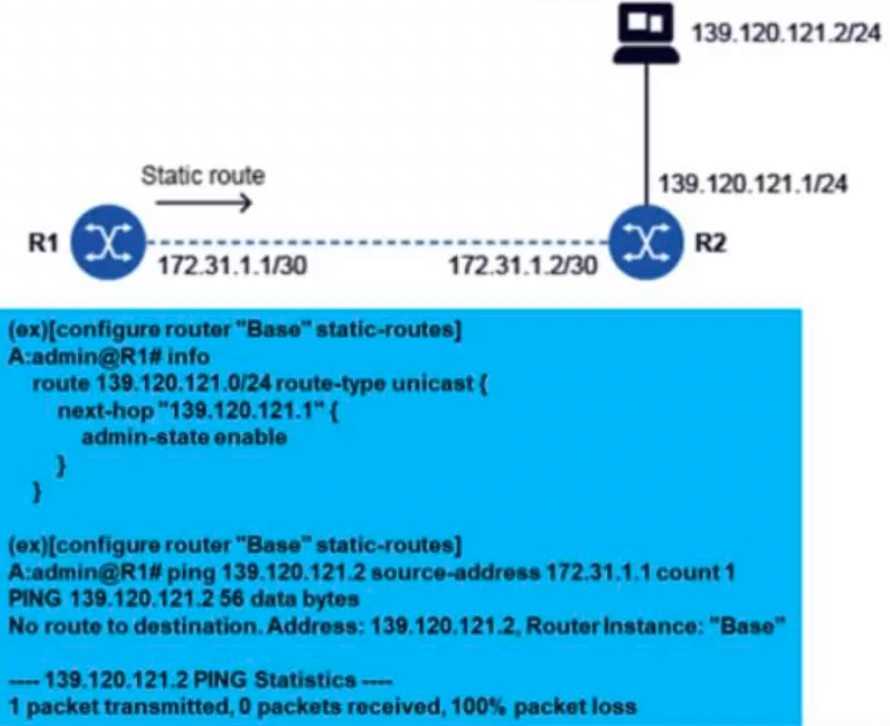
A static route has been configured on router R1 to reach the PC at 139.120.121.2.
What might be causing the ping to fail?
- A. Router R2 needs a static route to the PC.
- B. Router R1 needs a static route to router R2.
- C. The configured next hop does not belong to a subnet adjacent to R1.
- D. The configured static route needs to be a default route.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In the configuration on router R1, the static route is defined with the next-hop IP address of
139.120.121.1.
However, the next-hop IP address 139.120.121.1 does not belong to the same subnet as the directly
connected interface on R1, which is 172.31.1.1/30. For the static route to work properly, the next-
hop IP address must be reachable via a directly connected interface, meaning it must be within the
same subnet.
Therefore, this mismatch in subnet adjacency is likely causing the failure to reach the destination
(139.120.121.2).
Comments
Question 2
Refer to the exhibit.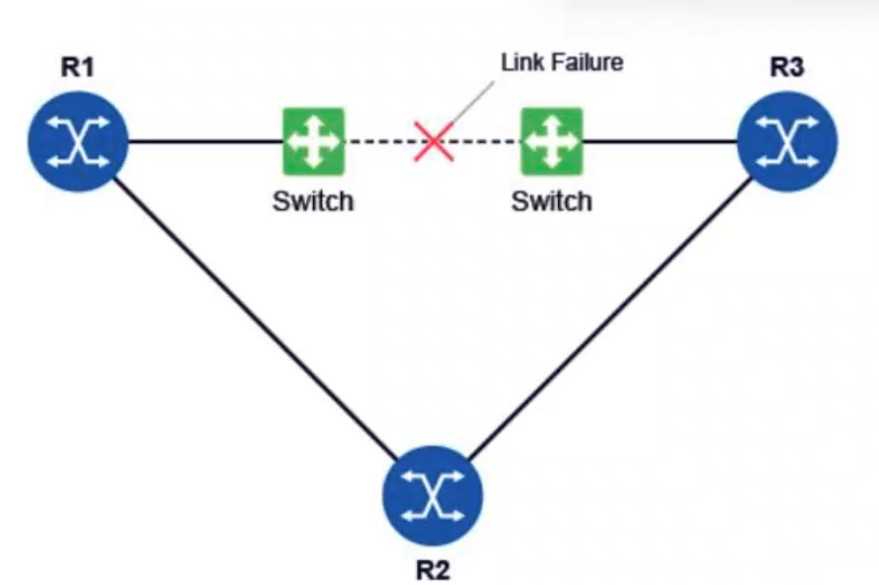
All routers in the diagram are running a link-state routing protocol. Before the link failure, all routers
have operational adjacencies with each other and there is a BFD session between routers R1 and R3.
After the link failure, which of the following affects the routing protocol’s convergence time?
- A. The value of the Ethernet hello timers on the switches.
- B. The value of the routing protocol hello timers on routers R1 and R3.
- C. The value of the BFD transmit interval, receive interval and multiplier settings on routers R1 and R3.
- D. The time taken by the switches to detect that the physical ports are down.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) is used to detect link failures quickly and helps improve
convergence time in link-state routing protocols. The BFD session between routers R1 and R3 allows
them to detect the failure of the link between them more quickly than the regular routing protocol
hello timers. The transmit interval, receive interval, and multiplier settings determine how fast BFD
detects a failure and triggers the routing protocol to converge, which directly impacts the
convergence time.
Comments
Question 3
When a router performs the SPF calculation, which router is used as the root of the shortest path
tree?
- A. The router with the fewest links.
- B. The router with the lowest router ID.
- C. The router's closest neighbor.
- D. The router doing the calculation.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When a router performs the SPF (Shortest Path First) calculation, it uses itself as the root of the
shortest path tree (SPT). This router computes the shortest paths to all other routers in the network,
treating itself as the origin and calculating the paths based on its view of the network.
Comments
Question 4
A routing domain is using a single-area link-state routing protocol. Which of the following is NOT
information that a router can share with other routers in the domain using protocol-specific
messages?
- A. The IP prefixes of subnets directly attached to the router.
- B. IP prefixes known by the router because it is running ad additional routing protocol.
- C. A copy of the local routing table.
- D. The local router ID and the router IDs of neighboring routers.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
In a single-area link-state routing protocol (such as OSPF), routers share specific information about
the network topology, not their entire routing table. They exchange link-state advertisements (LSAs)
that contain information about their directly connected interfaces and their state, allowing other
routers to build a consistent view of the network.
Comments
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.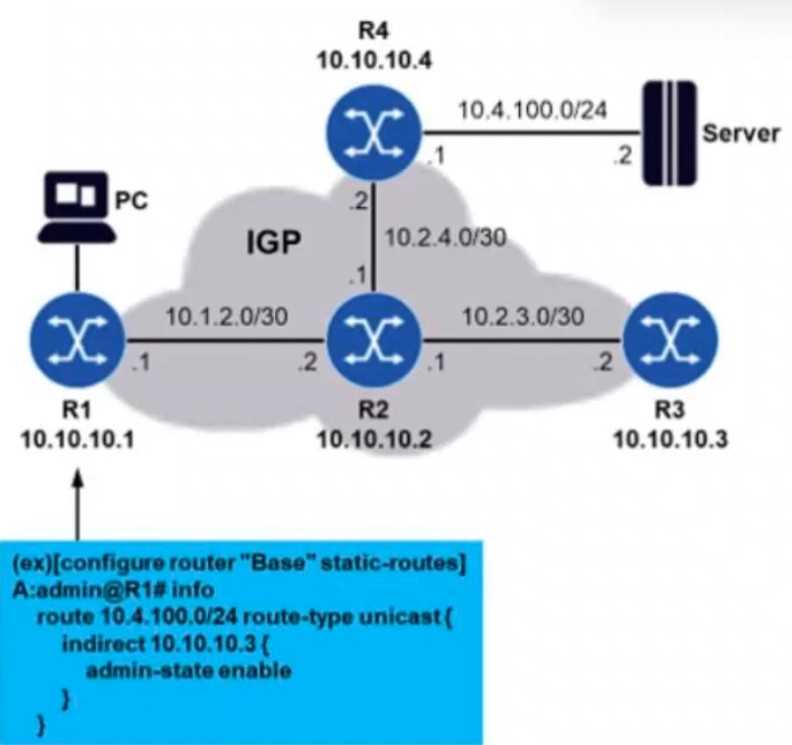
Routers R1 through R4 are running an IGP in such a way that they have each other’s system IP
addresses in their routing tables. A static route is configured on router R1 so that it can reach
subnetwork 10.4.100.0/24. The network administrator decides to use an indirect static route, as
shown in the diagram. However, pinging the server from router R1 fails. What may be the problem in
this case?
- A. Router R1 drops the echo request because address 10.10.10.3 does not belong to an adjacent router.
- B. Router R2 drops the echo request because it does not have subnet 10.4.100.0/24 in its routing table.
- C. Router R3 drops the echo request because it does not have subnet 10.4.100.0/24 in its routing table.
- D. The echo request arrives at the server but there is no path for the echo response to return to router R1.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The static route configured on router R1 uses an indirect next-hop, which is 10.10.10.3 (R3). While
the echo request from R1 reaches the server through the IGP, the problem lies in the return path for
the echo response.
The route 10.4.100.0/24 is reachable through R3, but there is no reciprocal route in R3's routing table
that allows the response to flow back towards R1. This results in a failure to return the echo response
to R1, causing the ping to fail.
Comments
Question 6
Refer to the exhibit.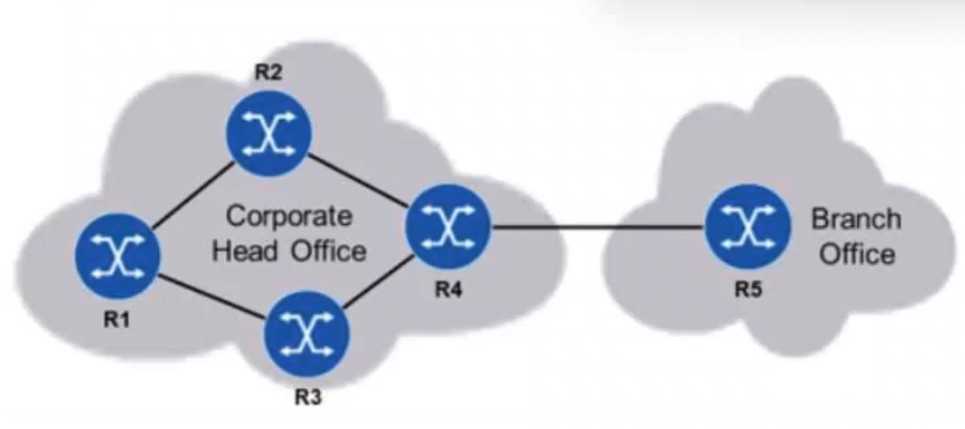
Static routing is to be used in a network between a corporate head office and a branch office. The
head office has many connected subnetworks, whereas the branch office has one subnetwork and a
single connection to the head office. Which of the following is the most likely configuration on the
head office and branch office routers?
- A. The head office has a default route and the branch office has a specific static route.
- B. The head office and the branch offices both have specific static routes.
- C. The head office and the branch office both have default routes.
- D. The head office has a specific static route and the branch office has a default route.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The head office has many connected subnetworks, so it will typically have a default route to forward
traffic to the branch office (or external networks), since it may not need to define static routes for
each branch network.
The branch office, which has only one subnetwork and a single connection to the head office, will
have a specific static route to reach the head office subnet or other subnets at the head office, since
it only needs to know the specific route to reach the head office's network.
Comments
Question 7
Which of the following statements regarding the databases used by a link-state routing protocol in a
single-are routing domain is FALSE?
- A. The link-state database has the local topology and IP reachability information advertised by all the routers.
- B. The adjacency database contains information about all the links interconnecting the domain’s routers.
- C. The forwarding database contains the optimum next hop for each known prefix.
- D. The link-state database is the same for all routers.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The adjacency database contains information about the state of the router’s adjacencies (i.e., the
routers that it is directly connected to and has established a neighbor relationship with). It does not
store information about all links in the domain; that information is stored in the link-state database.
Comments
Question 8
For a link-state routing protocol, which of the following statements about link-state updates is FALSE?
- A. When a link-state update reaches its maximum age on a router, the router will flood that update to its neighbors.
- B. When a router detects that a link-state update has reached its maximum age, it will request a new update from the source router.
- C. Aging helps ensure that routers that are no longer part of the topology will eventually get removed from the link-state database.
- D. The age value is updated as the link-state update is flooded throughout the network and when it is in the link-state database
Answer:
A
Explanation:
When a link-state update reaches its maximum age, it is removed from the router’s link-state
database, not flooded to its neighbors. This prevents outdated information from continuing to affect
the routing decisions. The router does not flood the aged update; instead, it will typically request a
new link-state advertisement from the original source router if the information is still needed.
Comments
Question 9
A router running a link-state routing protocol detects that one of its neighbors is no longer connected
to it. The router generates a new link-state advertisement to inform other routers of the topology
change. Which of the following is NOT an action that is triggered by this event?
- A. If a router receives the new link-state advertisement, it acknowledges it, stores it, and forwards it to its own neighbors.
- B. If a router receives multiple copies of the new link-state advertisement, it will simply ignore all copies received after the first one.
- C. Every router that receives the new link-state advertisement updates its age field before forwarding it.
- D. Every router that receives the new link-state advertisement runs the SPF algorithm to recalculate its shortest-path tree and its forwarding database.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When a router receives a link-state advertisement (LSA), it does not update the age field before
forwarding it. The age field in an LSA is typically updated by the originating router or during the
process of forwarding the LSA within the network. Routers do not modify the age field upon receiving
and forwarding an LSA.
Comments
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.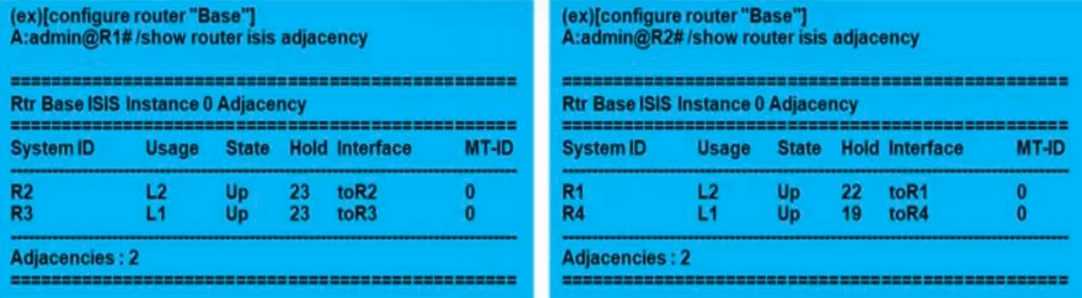
Routers R1, R2, R3, and R4 are running IS-IS. Assuming all interfaces are added to IS-IS as point-to-
point and no commands are issued at the interface level to restrict adjacencies, which of the
following statements is TRUE?
- A. Routers R1 and R2 are L2 routers. Routers R3 and R4 are L1 routers.
- B. Routers R1 and R2 are L2 routers. Routers R3 and R4 are L1/L2 routers.
- C. Routers R1 and R2 are L1/L2 routers. Routers R3 and R4 are L1 routers.
- D. All four routers are L1/L2.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
From the output, we can see that the usage column indicates whether a router is operating as an L1
or L2 router:
Routers R1 and R2 have a usage of L2, meaning they are L2 routers.
Routers R3 and R4 have a usage of L1, meaning they are L1 routers.
The L1/L2 designations refer to whether the routers participate in both Level 1 and Level 2 of IS-IS:
L1 routers only communicate within their own area.
L2 routers communicate between areas.
In this case, R1 and R2 are L2 routers, and R3 and R4 are L1 routers.
Comments
Page 1 out of 3
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 40
page 2