Question 1
A customer enabled NFSv4.0 on an SVM and changed the client mount from NFSv3 to NFSv4.
Afterwards, the customer found that the directory owner was changed from root to nobody.
In this scenario, which statement is true?
- A. The customer did not configure name services on the SVM.
- B. The clients must be restarted to start using NFSv4.
- C. The export policy is not configured properly.
- D. The ID mapping domains do not match between the client and server.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
NFSv4 is a network file system protocol that supports security, performance, and scalability
features.
NFSv4 uses ID mapping to ensure that the permissions of files and directories are consistent
across different NFSv4 servers and clients1
ID mapping is the process of translating the user and group identifiers (UIDs and GIDs) of the local
system to the user and group names (user@domain and group@domain) of the remote system, and
vice versa.
ID mapping is done by the idmapd service, which uses the /etc/idmapd.conf file to
determine the domain name of the system2
ID mapping requires that the NFSv4 server and client have the same domain name configured in the
/etc/idmapd.conf file.
If the domain names do not match, the idmapd service cannot map the UIDs
and GIDs to the user and group names, and the permissions of the files and directories will be shown
as nobody:nobody, which is the default anonymous user3
Therefore, if a customer enabled NFSv4.0 on an SVM and changed the client mount from NFSv3 to
NFSv4, and found that the directory owner was changed from root to nobody, the most likely cause is
that the ID mapping domains do not match between the client and server.
The customer should
check and correct the /etc/idmapd.conf file on both systems, and restart the idmapd service and
remount the NFSv4 share4
Reference:
1: ONTAP 9 - Network File System (NFS) - The Open Group 2: ONTAP 9 - NFSv4 and NFSv4.1
Enhancements - The Open Group 3: NFSv4 mount incorrectly shows all files with ownership as
nobody:nobody - Red Hat Customer Portal 4
: NFSv4 mountpoint shows incorrect ownerships as
nobody:nobody in CentOS/RHEL - The Geek Diary
Comments
Question 2
You have a NetApp ONTAP cluster consisting of four NetApp FAS8200 controllers with two NetApp
CN1610 cluster switches running ONIAP 9.8 software. You are receiving several alert messages
stating that the cluster network has degraded. After troubleshooting, you determine that the errors
are being generated from Node 2, interface e0b.
In this scenario, what should you do first to solve this problem?
- A. Replace the Twinax cable between Node 2, Interface e0b. and the NetApp CN1610 switch.
- B. Replace the motherboard on Node 2.
- C. Replace both NetApp CN1610 switches.
- D. Replace the NetApp CN1610 switch that connects to Node 2, interface e0b.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A Twinax cable is a type of copper cable that is used to connect cluster ports to cluster switches1
.
A cluster port is a network port that is configured for cluster communication and data access2
.
A cluster switch is a network switch that is used to interconnect the nodes in a cluster and provide
redundancy and load balancing3
.
A cluster network is a network that enables cluster communication and data access between the
nodes in a cluster and external clients4
.
A cluster network can be degraded due to various reasons, such as misconfiguration, malfunction, or
excessive link errors on the cluster ports or the cluster switches.
Link errors are errors that occur on the physical layer of the network, such as CRC errors, length
errors, alignment errors, or dropped packets.
Link errors can indicate a problem with the cable, the switch port, the network interface card (NIC),
or the cable connector.
In this scenario, the alert messages state that the cluster network has degraded and the errors are
being generated from Node 2, interface e0b.
The first step to solve this problem is to replace the Twinax cable between Node 2, interface e0b and
the NetApp CN1610 switch, as this could be the source of the link errors.
Replacing the cable could resolve the issue and restore the cluster network to a healthy state.
If replacing the cable does not solve the problem, then other steps may be required, such as checking
the switch port, the NIC, or the cable connector, or replacing the switch or the
motherboard. Reference:
: Cluster network cabling, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Cluster ports, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Cluster switches, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
: Cluster network, ONTAP 9 Documentation Center
[5]: How to troubleshoot CLUSTER NETWORK DEGRADED error messages, NetApp Knowledge Base
[6]: Cluster network degraded due to high CRC errors on cluster ports, NetApp Knowledge Base
Comments
Question 3
Your customer has mounted an NFS SVM from a Linux client unci performance is very poor. The
customer is certain that they have jumbo frames enabled. They have verified an MTU of 9000 on
both the Linux client and the broadcast domain on the NetApp ONTAP 9.8 cluster.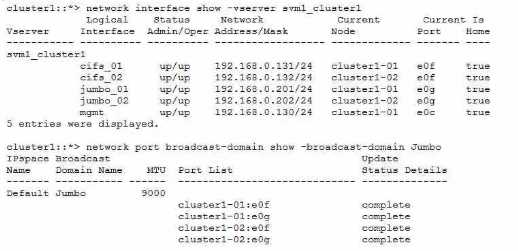
Referring to the exhibit, which ONTAP command will help isolate a possible MTU mismatch?
A.
B.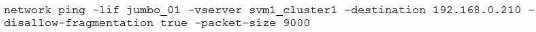
C.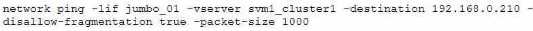
D.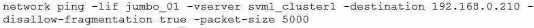
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The ONTAP command that will help isolate a possible MTU mismatch is network ping -lif jumbo_01 -
vserver svm1_cluster1 -destination 192.168.0.210 -disallow-fragmentation true -packet-size 5000.
This command will send a ping packet of 5000 bytes from the logical interface (LIF) jumbo_01 to the
destination IP address 192.168.0.210, without allowing fragmentation. If the ping fails, it means that
there is an MTU mismatch somewhere along the path.
If the ping succeeds, it means that the MTU is
consistent and the problem is elsewhere12. Reference: 1: Check the MTU network setting on the
storage system | NetApp Documentation 2
: How to adjust the MTU for an ONTAP interface - NetApp
Knowledge Base
Comments
Question 4
You have a customer complaining of long build times from their NetApp ONTAP-based datastores.
They provided you packet traces from the controller and client. Analysis of these traces shows an
average service response time of 1 ms. QoS output confirms the same. The client traces are reporting
an average of 15 ms in the same time period.
In this situation, what would be your next step?
- A. The cluster is responding slowly and requires further investigation using performance archives.
- B. The client that reports high latency should be investigated.
- C. The cluster interconnects should be investigated.
- D. A sync core should be triggered.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The question describes a scenario where the controller and client have a significant difference in
their reported latency for the same datastores.
The controller’s latency is 1 ms, which is within the normal range for ONTAP-based datastores1
.
The client’s latency is 15 ms, which is much higher than the controller’s latency and could indicate a
performance issue on the client side2
.
Therefore, the next step is to investigate the client that reports high latency and identify the possible
causes, such as network congestion, misconfiguration, resource contention, or application issues23
.
The other options are not relevant or appropriate for this scenario, because:
A) The cluster is not responding slowly, as the controller’s latency is low and QoS output confirms the
same.
C)
The cluster interconnects are not likely to be the cause of the latency difference, as they are used
for communication between nodes within the cluster, not between the controller and the client4
.
D)
A sync core is a diagnostic tool that captures the state of the system at a given point in time, and is
not a troubleshooting step for performance issues5
. Reference:
ONTAP 9 Performance - Resolution Guide - NetApp Knowledge Base
Performance troubleshooting - NetApp
How to troubleshoot performance issues in Data ONTAP 8 7-mode
Cluster interconnect network - NetApp
How to generate a sync core on a node - NetApp
Comments
Question 5
Your customer wants to access a LUN on a FAS 8300 system from a VMware ESXi server through the
FC protocol. They already created a new SVM, volume. LUN, and igroup for this purpose. The
customer reports that the server's FC HBA port Is online, but the LUN does not show up.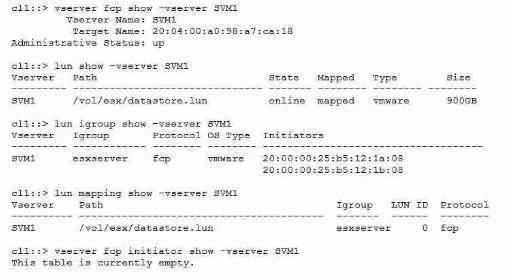
Referring to the exhibit, what is the reason for this problem?
- A. The FC service has not been configured on the SVM.
- B. The zoning on the FC switches Is Incorrect.
- C. The LUN Is not mapped to the correct SCSI ID.
- D. The esxserver igroup contains incorrect IQNs.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To access a LUN on a FAS 8300 system from a VMware ESXi server through the FC protocol, the
customer must configure the FC service on the SVM that owns the LUN. The FC service enables the
SVM to act as an FC target and communicate with the FC initiators on the host. Without the FC
service, the LUN will not be visible to the host, even if the LUN is mapped to an igroup and the FC
LIFs are up. The exhibit shows that the FC service is not configured on the SVM, as the output of the
command vserver fcp initiator show -vserver SVM1 is empty. Therefore, the reason for the problem
is that the FC service has not been configured on the SVM. Reference =
Configure an SVM for
FC
,
Create an FC protocol service
,
Single IQN iSCSI session with ESXi on ONTAP when igroup has two
IQNs
Comments
Question 6
You recently discovered the error message shown below in your ONTAP logs.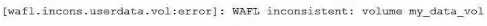
What should be your first action to correct this Issue?
- A. Power cycle all the disk storage shelves that contain drives of the aggregate with the my_data_vol volume.
- B. Determine the root cause behind the inconsistency before attempting any recovery procedure.
- C. Use the storage takeover command on the storage controller that contains my_data_vol.
- D. Use the wafliron command against my_data_vol to solve the inconsistency on the volume.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
= The error message indicates that the volume my_data_vol is WAFL inconsistent, which means that
there is a discrepancy between the data blocks and the metadata in the file system. This can be
caused by various factors, such as hardware failures, software bugs, power outages, or network
disruptions.
The first action to correct this issue is to determine the root cause behind the
inconsistency before attempting any recovery procedure, as recommended by the NetApp
documentation1
. This is because some recovery procedures, such as wafliron or storage takeover,
may not work or may cause further damage if the underlying cause is not resolved. For example, if
the inconsistency is due to a faulty disk or shelf, running wafliron may not fix the problem and may
even corrupt more data.
Therefore, it is important to identify and isolate the cause of the
inconsistency before taking any further steps. Reference = 1
Volume Showing WAFL Inconsistent -
NetApp Knowledge Base
Comments
Question 7
When an administrator tries to create a share for an existing volume named voll, the process fails
with an error.
Referring to the exhibit, what Is the reason for the error?
- A. The volume must have a type of DP.
- B. The volume has not been mounted.
- C. The CIFS service is not authenticating properly with the domain controller.
- D. The CIFS service is not in workgroup mode.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The error message indicates that the specified path “/vol1” does not exist in the namespace
belonging to Vserver “svm1”. This means that the volume “vol1” has not been mounted to the
Vserver’s namespace, which is required for creating a share. The volume type, the CIFS service
status, and the CIFS service mode are not relevant to the
error. Reference =
https://www.netapp.com/support-and-training/netapp-learning-
services/certifications/support-engineer/
https://mysupport.netapp.com/site/docs-and-kb
Comments
Question 8
The motherboard of Node-01 is being replaced. To perform this task, a takeover was Initiated from
Node-02. Node-02 panics showing the string below.
PANIC; Permanent errors on all HA mailbox disks (while marshalling header) in SKprocess
fnmbx_instanceWorker on release 9.5P8 (C)
What has happened in this situation?
- A. While in maintenance mode, the sldiag device show command was executed.
- B. While in maintenance mode, the fcadmin device_map command was executed.
- C. While in maintenance mode, the HA_config show command was executed.
- D. While in maintenance mode, the mailbox destroy local command was executed.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The mailbox disks are the first two disks of the root aggregate on each node of an HA pair. They store
the HA state information and the panic dump files.
The mailbox disks are used for communication
between the HA partners and for takeover and giveback operations1
The mailbox destroy local command is used to destroy the mailbox disks on the local node. This
command is only available in maintenance mode and should be used with extreme caution.
The
command is intended for situations where the mailbox disks are corrupted or inaccessible and need
to be recreated2
If the mailbox destroy local command is executed on a node that is in takeover mode, the node will
panic with the message “Permanent errors on all HA mailbox disks”.
This is because the node will
lose the HA state information and the panic dump files of the partner node, and will not be able to
communicate with the partner node or perform a giveback operation3
Therefore, if the motherboard of Node-01 is being replaced, and a takeover was initiated from Node-
02, and Node-02 panics showing the string “Permanent errors on all HA mailbox disks”, the most
likely cause is that the mailbox destroy local command was executed on Node-02 while in
maintenance mode.
This is a serious error that can result in data loss and system downtime4
Reference:
1: ONTAP 9 - High-Availability Configuration Guide - The Open Group 2: ONTAP 9 - Commands:
Manual Page Reference - The Open Group 3: How to troubleshoot a “Permanent errors on all HA
mailbox disks” panic - NetApp Knowledge Base 4
: One node PANIC : Permanent errors on all HA
mailbox disks - NetApp Knowledge Base
Comments
Question 9
You are deploying NetApp ONTAP Select. When trying to add VMware vCenter to the inventory, you
receive the message shown below.
Credential authentication failed for x.x.x.x with: HostConnectionFailed
In this scenario, how would you correct this problem?
- A. Change the vCenter password.
- B. Change the IP address of the ONTAP Select Deploy VM.
- C. Change the gateway address of the ONTAP Select Deploy VM.
- D. Change the IP address of the vCenter server.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The error message indicates that the ONTAP Select Deploy VM cannot connect to the vCenter server
due to a network issue1
.
One possible cause of this issue is that the IP address of the ONTAP Select Deploy VM is conflicting
with another device on the same network2
.
To correct this problem, you need to change the IP address of the ONTAP Select Deploy VM to a
unique and valid address that can reach the vCenter server2
.
You can change the IP address of the ONTAP Select Deploy VM by using the Deploy web interface or
the Deploy CLI2
.
After changing the IP address, you need to restart the Deploy services and re-add the vCenter server
to the inventory2
. Reference:
: Credential authentication failed with: HostConnectionFailed, NetApp Knowledge Base
: Changing the IP address of the Deploy VM, ONTAP Select 9 Documentation Center
Comments
Question 10
You created a new NetApp ONTAP FlexGroup volume spanning six nodes and 12 aggregates with a
total size of 4 TB. You added millions of files to the FlexGroup volume with a flat directory structure
totaling 2 TB, and you receive an out of apace error message on your host.
What would cause this error?
- A. The maximum number of volume constituents has been reached in the ONTAP software.
- B. All constituent volumes are full.
- C. The inode limit is exceeded in the ONTAP software.
- D. The maxdirsize Is exceeded in the ONTAP software.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The maxdirsize is the maximum size of a directory in a FlexVol or FlexGroup volume. It is determined
by the number of inodes allocated to the directory. If the directory contains more files than the
maxdirsize can accommodate, then the ONTAP software will return an out of space error message to
the host, even if the volume has enough free space.
This can happen when a FlexGroup volume has a
flat directory structure with millions of files, as the maxdirsize is not automatically adjusted for
FlexGroup volumes12. Reference: 1: FlexGroup volumes: Frequently asked questions | NetApp
Documentation 2
: How to increase the maxdirsize of a FlexVol volume - NetApp Knowledge Base
Comments
Page 1 out of 5
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 60
page 2