Question 1
Refer to the exhibit.
What action must be performed to log all the errors raised by the VM Connector?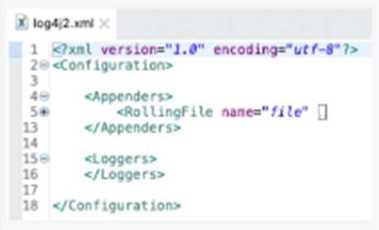
- A. Add <AsyncLOgger name=’orgroute.extensions vm’ level=ERROR’I> inside the Logger tag
- B. Add <AsyncLOgger name=’orgroute.extensions vm’ level=ERROR’/> inside the Appenders tag
- C. Configure <Logger level-‘ERROR’/> inside the VM Connector configuration
- D. Nothing, as error-level events are automatically logged
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To log all the errors raised by the VM Connector, the developer needs to add an async logger with the
name ‘org.mule.extension.vm’ and the level ‘ERROR’ inside the appenders tag of the log4j2.xml file.
This will enable logging all error-level events generated by the VM Connector to the console
appender. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/logging-in-mule#configuring-
custom-logging-settings
Comments
Question 2
A developer deploys an API to CloudHub and applies an OAuth policy on API Manager. During
testing, the API response is slow, so the developer reconfigures the API so that the out-of-the-box
HTTP Caching policy is applied first, and the OAuth API policy is applied second.
What will happen when an HTTP request is received?
- A. In case of a cache hit, both the OAuth and HTTP Caching policies are evaluated; then the cached response is returned to the caller
- B. In case of a cache it, only the HTTP Caching policy is evaluating; then the cached response is returned to the caller
- C. In case of a cache miss, only the HTTP Caching policy is evaluated; then the API retrieves the data from the API implementation, and the policy stores the data to be cached in Object Store
- D. In case of a cache miss, both the OAuth and HTTP Caching policies are evaluated; then the API retrieves the data from the API implementation, and the policy does not store the data in Object Store
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When an HTTP request is received and the HTTP Caching policy is applied first, it checks if there is a
cached response for that request in Object Store. If there is a cache hit, meaning that a valid cached
response exists, then only the HTTP Caching policy is evaluated and the cached response is returned
to the caller without invoking the OAuth policy or the API implementation. If there is a cache miss,
meaning that no valid cached response exists, then both the HTTP Caching policy and the OAuth
policy
are
evaluated
before
invoking
the
API
implementation.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/api-manager/2.x/http-caching-policy#policy-ordering
Comments
Question 3
A system API that communicates to an underlying MySQL database is deploying to CloudHub. The
DevOps team requires a readiness endpoint to monitor all system APIs.
Which strategy should be used to implement this endpoint?
- A. Create a dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status and reachability of the underlying systems
- B. Create a dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status and health of the server
- C. Use an existing resource endpoint of the API
- D. Create a dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status only
Answer:
A
Explanation:
To implement a readiness endpoint to monitor all system APIs, the developer should create a
dedicated endpoint that responds with the API status and reachability of the underlying systems.
This way, the DevOps team can check if the system API is ready to receive requests and if it can
communicate with its backend systems without errors. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-
runtime/4.3/deployment-strategies#readiness-probes
Comments
Question 4
The HTTP Request operation raises an HTTP CONNECTIVITY error.
Which HTTP status code and body are returned to the web client?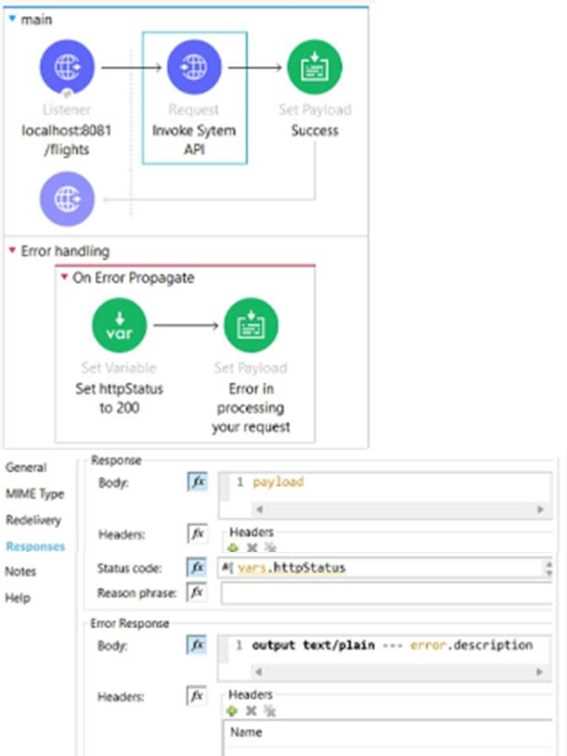
- A. HTTP Status Code:200. Body ‘Error in processing your request
- B. HTTP Status Code:500. Body ‘The HTTP CONNECTIVITY Error description
- D. HTTP Status Code:500. Body ‘Error in processing your request
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When the HTTP Request operation raises an HTTP CONNECTIVITY error, it triggers an on-error-
continue handler that sets a payload with ‘Error in processing your request’. Since no status code is
explicitly set in this handler, it defaults to 500 (INTERNAL SERVER ERROR). Therefore, the web client
receives an HTTP response with status code 500 and body ‘Error in processing your request’.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/error-handling#on-error-continue
Comments
Question 5
A Mule application defines as SSL/TLS keystore properly ‘tis,keystore.keyPassword’’ as secure.
How can this property be referenced to access its value within the application?
- A. #{secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}
- C. ${secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}
- D. p{secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}
Answer:
B
Explanation:
∗∗
secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd
ShortExplanationofCorrectAnswerOnly:Toreferenceasecureproper
tyvaluewithintheapplication,thedeveloperneedstousethesyntax{secure::}. In this case, the property
name is tiskeystore,keyPassword, so the correct syntax is ${secure::tiskeystore,keyPassowrd}.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/secure-configuration-
properties#referencing-secure-properties
Comments
Question 6
In a Mule project, Flow-1 contains a flow-ref to Flow-2 depends on data from Flow-1 to execute
successfully.
Which action ensures the test suites and test cases written for Flow-1 and Flow-2 will execute
successfully?
- A. Chain together the test suites and test cases for Flow-1 and Flow-2
- B. Use ‘’Set Event to pass the input that is needed, and keep the test cases for Flow-1 and Flow-2 independent
- C. Use ‘’Before Test Case’’ To collect data from Flow-1 test cases before running Flow-2 test cases
- D. Use ‘After Test Case’ to produce the data needed from Flow-1 test cases to pass to Flow-2 test cases
Answer:
B
Explanation:
To ensure the test suites and test cases written for Flow-1 and Flow-2 will execute successfully, the
developer should use a Set Event processor to pass the input that is needed by Flow-2, and keep the
test cases for Flow-1 and Flow-2 independent. This way, the developer can isolate the testing of each
flow and avoid coupling them together. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/munit/2.3/munit-test-
flow
Comments
Question 7
A Mule application need to invoice an API hosted by an external system to initiate a process. The
external API takes anywhere between one minute and 24 hours to compute its process.
Which implementation should be used to get response data from the external API after it completes
processing?
- A. Use an HTTP Connector to invoke the API and wait for a response
- B. Use a Scheduler to check for a response every minute
- C. Use an HTTP Connector inside Async scope to invoice the API and wait for a response
- D. Expose an HTTP callback API in Mule and register it with the external system
Answer:
D
Explanation:
To get response data from the external API after it completes processing, the developer should
expose an HTTP callback API in Mule and register it with the external system. This way, the external
API can invoke the callback API with the response data when it is ready, instead of making the Mule
application wait for a long time or poll for a response repeatedly. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/http-listener-ref#callback
Comments
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.
A Mute Object Store is configured with an entry TTL of one second and an expiration interval of 30
seconds.
What is the result of the flow if processing between os’store and os:retrieve takes 10 seconds?
- A. nullPayload
- B. originalPayload
- C. OS:KEY_NOT_FOUND
- D. testPayload
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The result of the flow is nullPayload if processing between os:store and os:retrieve takes 10 seconds.
This is because the entry TTL of the object store is one second, which means that any stored value
expires after one second and is removed from the object store. The expiration interval of 30 seconds
only determines how often the object store checks for expired values, but it does not affect the TTL.
Therefore, when os:retrieve tries to get the value after 10 seconds, it returns nullPayload because
the value has already expired and been removed. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/object-
store/osv2-faq#how-does-the-time-to-live-work
Comments
Question 9
Which plugin or dependency is required to unit test modules created with XML SDK?
- A. XMLUnit
- B. Junit
- C. MUnit Extensions Maven plugin
- D. MUnit Maven plugin
Answer:
C
Explanation:
To unit test modules created with XML SDK, the developer needs to use the MUnit Extensions Maven
plugin. This plugin allows testing XML SDK modules using MUnit by adding a dependency to the
module under test and using a custom processor tag to invoke it. Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-sdk/1.1/xml-sdk#testing
Comments
Question 10
Which statement is true when working with correlation IDS?
- A. The HTTP Listener regenerates correlation IDs regardless of the HTTP request
- B. The Anypoint MQ Connector automatically propagates correlation IDS
- C. The HTTP Listener generates correlation IDS unless a correlation ID is received in the HTTP request
- D. The VM Connector does not automatically propagate correction IDs
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When working with correlation IDs, the HTTP Listener generates correlation IDs unless a correlation
ID is received in the HTTP request. In that case, it propagates the received correlation ID throughout
the flow execution. Correlation IDs are used to track events across different flows or applications.
Reference:
https://docs.mulesoft.com/mule-runtime/4.3/about-mule-message#message-attributes
Comments
Page 1 out of 5
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 60
page 2