Question 1
What is the minimal syntax for declaring an output named foo for an action?
A)
B)
C)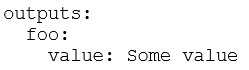
D)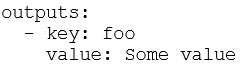
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The correct minimal syntax for declaring an output in GitHub Actions is by using the foo key under
outputs, and associating it with a value (in this case, Some value). This is the simplest form to define
an output in a workflow or action.
Comments
Question 2
When reviewing an action for use, what file defines its available inputs and outputs?
- A. inputs.yml
- B. config.json
- C. defaults.json
- D. workflow.yml
- E. action.yml
Answer:
E
Explanation:
The action.yml file defines the inputs and outputs for a GitHub Action. This file contains metadata
about the action, including the required inputs and outputs, as well as other configurations like the
action's description, runs, and environment setup.
Comments
Question 3
How should you install the bats NPM package in your workflow?
A)
B)
C)
D)
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The correct syntax includes specifying the job (example-job), the runner (ubuntu-latest), and the
necessary step (npm install -g bats) within the workflow. This ensures that the package is installed
properly during the execution of the job.
Comments
Question 4
How can GitHub Actions encrypted secrets be used in if: conditionals within a workflow job?
- A. Set the encrypted secret as a job-level environment variable and then reference the environment variable within the conditional statement.
- B. Create a job dependency that exposes the encrypted secret as a job output, which can then be leveraged in a subsequent dependent job.
- C. Use the secrets context within the conditional statement, e.g. ${{ secrets.MySuperSecret }}.
- D. Use a workflow command to expose the encrypted secret via a step's output parameter and then use the step output in the job's if: conditional.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
GitHub Actions encrypted secrets can be accessed in workflows using the secrets context. You can
directly reference the secret within an if: conditional using ${{ secrets.MySuperSecret }} to determine
whether a job or step should run based on the secret's value.
Comments
Question 5
As a DevOps engineer, you are developing a container action. You need to execute a cleanup script
after completing the main script execution. Which code block should be used to define the cleanup
script?
A.
B.
C.
D.
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
- D. Option D
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The correct syntax for specifying a cleanup script to be run after the main entry point is executed in a
Docker-based GitHub Action is to use the post key. This ensures that cleanup.sh runs after the main
script (main.sh) has completed.
Comments
Question 6
Which default GitHub environment variable indicates the name of the person or app that initiated a
workflow?
- A. ENV_ACTOR
- B. GITHUB_WORKFLOW_ACTOR
- C. GITHUB_ACTOR
- D. GITHUB_USER
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The GITHUB_ACTOR environment variable indicates the name of the person or app that initiated the
workflow. This variable is automatically provided by GitHub in the workflow and can be used to
identify the user or application triggering the workflow.
Comments
Question 7
You are a developer, and your container jobs are failing on a self-hosted runner. Which requirements
must you check to ensure that the self-hosted runner is properly configured? (Choose two.)
- A. The self-hosted runner is running a Linux operating system.
- B. The self-hosted runner is running a Windows operating system.
- C. Docker is installed on the self-hosted runner.
- D. Kubernetes is installed on the self-hosted runner.
- E. The service status of Kubernetes is "active".
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
While Docker can run on various operating systems, Linux is often the most common and preferred
OS for containerized workloads. Docker works well on Linux and is a widely-used platform for
running containers.
For container jobs to run on a self-hosted runner, Docker must be installed and properly configured
on the runner. Docker is required to build and run containerized workloads in a GitHub Actions
workflow.
Comments
Question 8
Which choices represent best practices for publishing actions so that they can be consumed reliably?
(Choose two.)
- A. repo name
- B. tag
- C. commit SHA
- D. organization name
- E. default branch
Answer:
B, C
Explanation:
Using a tag is a best practice because tags are immutable and represent a fixed version of your
action. By referencing tags, consumers of your action can be assured they are using a stable and
specific version of the action, which helps in avoiding issues with breaking changes.
The commit SHA is another reliable way to specify a particular version of an action. By referencing a
specific commit SHA, consumers can ensure they are using exactly the code that was written at that
moment, avoiding the potential for changes in the future.
Comments
Question 9
You need to create new workflows to deploy to an unfamiliar cloud provider. What is the fastest and
safest way to begin?
- A. Create a custom action to wrap the cloud provider's CLI.
- B. Search GitHub Marketplace for verified actions published by the cloud provider.
- C. Use the actions/jenkins-plugin action to utilize an existing Jenkins plugin for the cloud provider.
- D. Search GitHub Marketplace for actions created by GitHub.
- E. Download the CLI for the cloud provider and review the associated documentation.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Searching the GitHub Marketplace for verified actions published by the cloud provider is the quickest
and safest approach. Many cloud providers offer verified GitHub Actions that are maintained and
optimized to interact with their services. These actions typically come with the correct configurations
and best practices, allowing you to get started quickly without reinventing the wheel.
Comments
Question 10
GitHub-hosted runners support which capabilities? (Choose two.)
- A. automatic patching of both the runner and the underlying OS
- B. automatic file-system caching between workflow runs
- C. support for Linux, Windows, and mac
- D. support for a variety of Linux variations including CentOS, Fedora, and Debian
- E. requiring a payment mechanism (e.g., credit card) to use for private repositories
Answer:
C, D
Explanation:
GitHub-hosted runners automatically handle patching, meaning they will be kept up to date with the
latest security updates and software patches for both the runner environment and the underlying
operating system.
GitHub-hosted runners support Linux, Windows, and macOS, giving you flexibility to run workflows
on different operating systems without needing to manage your own self-hosted runners.
Comments
Page 1 out of 7
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 72
page 2