Question 1
What are two ways in which an EVPN-signaled VXLAN is different from a multicast-signaled VXLAN?
(Choose two.)
- A. An EVPN-signaled VXLAN can perform autodiscovery of VTEPs using IS-IS.
- B. An EVPN-signaled VXLAN can perform autodiscovery of VTEPs using BGP.
- C. An EVPN-signaled VXLAN is less resource intensive.
- D. An EVPN-signaled VXLAN features slower and more complete convergence.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
Multicast-Signaled VXLAN:
In traditional multicast-signaled VXLAN, VTEPs (VXLAN Tunnel Endpoints) use multicast to flood and
learn about remote VTEPs. This method relies on multicast in the underlay network to distribute
BUM (Broadcast, Unknown unicast, and Multicast) traffic.
This approach can be resource-intensive due to the need for multicast group management and
increased network traffic, especially in large deployments.
EVPN-Signaled VXLAN:
EVPN-signaled VXLAN uses BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) to signal the presence of VTEPs and
distribute MAC address information. BGP is used for VTEP autodiscovery and the distribution of
endpoint information.
This method is more efficient because it reduces the reliance on multicast, instead using BGP control-
plane signaling to handle VTEP discovery and MAC learning, which reduces the overhead on the
network and improves scalability.
Correct Statements:
B . An EVPN-signaled VXLAN can perform autodiscovery of VTEPs using BGP: This is correct because
EVPN uses BGP for VTEP autodiscovery, making it more efficient and scalable compared to multicast-
based methods.
C . An EVPN-signaled VXLAN is less resource-intensive: This is correct because it eliminates the need
for multicast flooding in the underlay, instead using BGP for signaling, which is less demanding on
network resources.
Incorrect Statements:
A . An EVPN-signaled VXLAN can perform autodiscovery of VTEPs using IS-IS: This is incorrect
because EVPN relies on BGP, not IS-IS, for VTEP discovery and signaling.
D . An EVPN-signaled VXLAN features slower and more complete convergence: This is incorrect;
EVPN with BGP typically provides faster convergence due to its use of a control plane rather than
relying on data plane learning.
Data Center Reference:
EVPN-VXLAN is widely adopted in modern data center designs due to its scalability, efficiency, and
reduced resource consumption compared to multicast-based VXLAN solutions. It leverages the
strengths of BGP for control-plane-driven operations, resulting in more efficient and scalable
networks.
Comments
Question 2
You are implementing VXLAN broadcast domains in your data center environment. Which two
statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
- A. A VXLAN packet does not contain a VLAN ID.
- B. The VNI must match the VLAN tag to ensure that the remote VTEP can decapsulate VXLAN packets.
- C. Layer 2 frames are encapsulated by the source VTEP.
- D. The VNI is a 16-bit value and can range from 0 through 16.777.215.
Answer:
AC
Explanation:
VXLAN Overview:
VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN) is a network virtualization technology that encapsulates Layer 2
Ethernet frames into Layer 3 UDP packets for transmission over an IP network. It allows the creation
of Layer 2 overlay networks across a Layer 3 infrastructure.
Understanding VXLAN Components:
VTEP (VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint): A VTEP is responsible for encapsulating and decapsulating Ethernet
frames into and from VXLAN packets.
VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier): A 24-bit identifier used to distinguish different VXLAN segments,
allowing for up to 16 million unique segments.
Correct Statements:
C . Layer 2 frames are encapsulated by the source VTEP: This is correct. In a VXLAN deployment, the
source VTEP encapsulates the original Layer 2 Ethernet frame into a VXLAN packet before
transmitting it over the IP network to the destination VTEP, which then decapsulates it.
A . A VXLAN packet does not contain a VLAN ID: This is correct. The VXLAN header does not carry the
original VLAN ID; instead, it uses the VNI to identify the network segment. The VLAN ID is local to the
switch and does not traverse the VXLAN tunnel.
Incorrect Statements:
B . The VNI must match the VLAN tag to ensure that the remote VTEP can decapsulate VXLAN
packets: This is incorrect. The VNI is independent of the VLAN tag, and the VLAN ID does not need to
match the VNI. The VNI is what the remote VTEP uses to identify the correct VXLAN segment.
D . The VNI is a 16-bit value and can range from 0 through 16,777,215: This is incorrect because the
VNI is a 24-bit value, allowing for a range of 0 to 16,777,215.
Data Center Reference:
VXLAN technology is critical for modern data centers as it enables scalability and efficient
segmentation without the constraints of traditional VLAN limits.
Comments
Question 3
You are deploying an IP fabric using EBGP and notice that your leaf devices are advertising and
receiving all the routes. However, the routes are not installed in the routing table and are marked as
hidden.
Which two statements describe how to solve the issue? (Choose two.)
- A. You need to configure as-override.
- B. You need to configure a next-hop self policy.
- C. You need to configure loops 2.
- D. You need to configure multipath multiple-as.
Answer:
BD
Explanation:
Issue Overview:
The leaf devices in an IP fabric using eBGP are advertising and receiving all routes, but the routes are
not being installed in the routing table and are marked as hidden. This typically indicates an issue
with the BGP configuration, particularly with next-hop handling or AS path concerns.
Corrective Actions:
B . You need to configure a next-hop self policy: This action ensures that the leaf devices modify the
next-hop attribute to their own IP address before advertising routes to their peers. This is particularly
important in eBGP setups where the next-hop may not be directly reachable by other peers.
D . You need to configure multipath multiple-as: This setting allows the router to accept multiple
paths from different autonomous systems (ASes) and use them for load balancing. Without this, the
BGP process might consider only one path and mark others as hidden.
Incorrect Statements:
A . You need to configure as-override: AS-override is used to replace the AS number in the AS-path
attribute to prevent loop detection issues in MPLS VPNs, not in a typical eBGP IP fabric setup.
C . You need to configure loops 2: There is no specific BGP command loops 2 relevant to resolving
hidden routes in this context. It might be confused with allowas-in, which is used to allow AS path
loops under certain conditions.
Data Center Reference:
Proper BGP configuration is crucial in IP fabrics to ensure route propagation and to prevent routes
from being marked as hidden. Configuration parameters like next-hop self and multipath multiple-as
are common solutions to ensure optimal route installation and load balancing in a multi-vendor
environment.
Comments
Question 4
In your EVPN-VXAN environment, you want to prevent a multihomed server from receiving multiple
copies of BUM traffic in active/active scenarios. Which EVPN route type would satisfy this
requirement?
- A. Type 8
- B. Type 7
- C. Type 4
- D. Type 5
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Understanding the Scenario:
In an EVPN-VXLAN environment, when using multi-homing in active/active scenarios, there's a risk
that a multihomed server might receive duplicate copies of Broadcast, Unknown unicast, and
Multicast (BUM) traffic. This is because multiple VTEPs might forward the same BUM traffic to the
server.
EVPN Route Types:
Type 4 Route (Ethernet Segment Route): This route type is used to advertise the Ethernet Segment
(ES) to which the device is connected. It is specifically used in multi-homing scenarios to signal the ES
and its associated Ethernet Tag to all the remote VTEPs. The Type 4 route includes information that
helps prevent BUM traffic duplication in active/active multi-homing by using a split-horizon
mechanism, which ensures that traffic sent to a multihomed device does not get looped back.
Explanation:
The Type 4 route is crucial for ensuring that in a multi-homed setup, particularly in an active/active
configuration, BUM traffic does not result in duplication at the server. The route helps coordinate
which VTEP is responsible for forwarding the BUM traffic to the server, thereby preventing duplicate
traffic.
Data Center Reference:
Type 4 routes are essential for managing multi-homing in EVPN to avoid the issues of BUM traffic
duplication, which could otherwise lead to inefficiencies and potential network issues.
Comments
Question 5
You want to convert an MX Series router from a VXLAN Layer 2 gateway to a VXLAN Layer 3 gateway
for VNI 100. You have already configured an IRB interface. In this scenario, which command would
you use to accomplish this task?
- A. set protocols isis interface irb.100 passive
- B. set vlans VLAN-100 13-interface irb.100
- C. set bridge-domains VLAN-100 routing-interface irb.100
- D. set protocols ospf area 0.0.0.0 interface irb.100 passive
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Scenario Overview:
Converting an MX Series router from a VXLAN Layer 2 gateway to a VXLAN Layer 3 gateway involves
transitioning the router's functionality from simply bridging traffic within a VXLAN segment to
routing traffic between different segments.
Key Configuration Requirement:
IRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging) Interface: An IRB interface allows for both Layer 2 switching
and Layer 3 routing. To enable routing for a specific VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier), the IRB interface
must be associated with the routing function in the corresponding bridge domain.
Correct Command:
C . set bridge-domains VLAN-100 routing-interface irb.100: This command correctly binds the IRB
interface to the bridge domain, enabling Layer 3 routing functionality within the VXLAN for VNI 100.
This effectively transitions the device from operating solely as a Layer 2 gateway to a Layer 3
gateway.
Data Center Reference:
This configuration step is essential when converting a Layer 2 VXLAN gateway to a Layer 3 gateway,
enabling the MX Series router to route between VXLAN segments.
Comments
Question 6
You manage an IP fabric with an EVPN-VXLAN overlay. You have multiple tenants separated using
multiple unique VRF instances. You want to determine the routing information that belongs in each
routing instance's routing table.
In this scenario, which property is used for this purpose?
- A. the VRF target community
- B. the routing instance type
- C. the VRF table label
- D. the route distinguisher value
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Understanding VRF and Routing Instances:
In an EVPN-VXLAN overlay network, multiple tenants are separated using unique VRF (Virtual
Routing and Forwarding) instances. Each VRF instance maintains its own routing table, allowing for
isolated routing domains within the same network infrastructure.
Role of Route Distinguisher:
Route Distinguisher (RD): The RD is a unique identifier used in MPLS and EVPN environments to
distinguish routes belonging to different VRFs. The RD is prepended to the IP address in the route
advertisement, ensuring that routes from different tenants remain unique even if they use the same
IP address range.
Correct Property:
D. the route distinguisher value: This is the correct answer because the RD is crucial in determining
which routing information belongs to which VRF instance. It ensures that each VRF’s routing table
only contains relevant routes, maintaining isolation between tenants.
Data Center Reference:
The RD is a key element in MPLS and EVPN-based multi-tenant environments, ensuring proper
routing segregation and isolation for different VRFs within the data center fabric.
Comments
Question 7
Exhibit.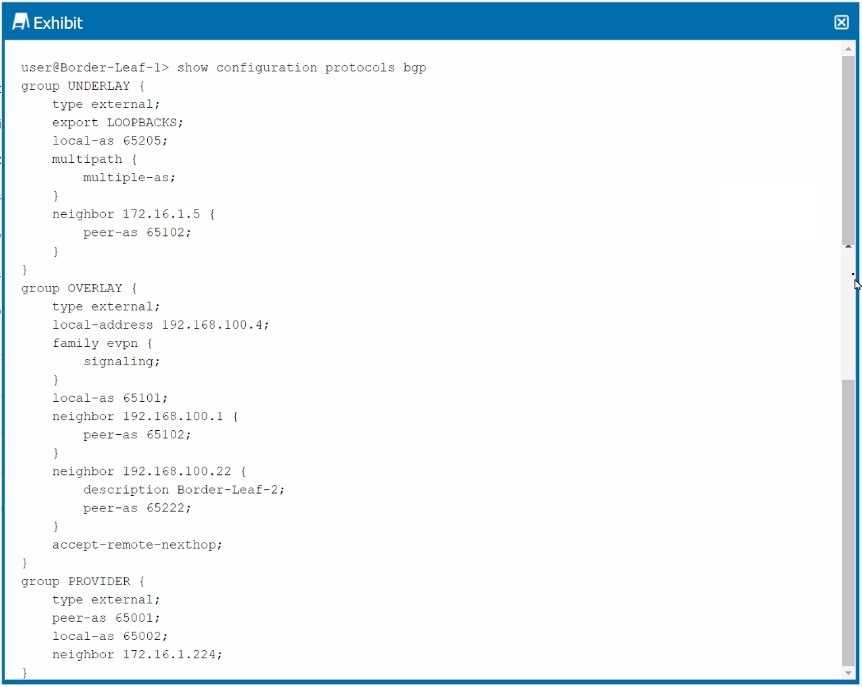
You are troubleshooting a DCI connection to another data center The BGP session to the provider is
established, but the session to Border-Leaf-2 is not established. Referring to the exhibit, which
configuration change should be made to solve the problem?
- A. set protocols bgp group overlay export loopbacks
- B. delete protocols bgp group UNDERLAY advertise-external
- C. set protocols bgp group PROVIDER export LOOPBACKS
- D. delete protocols bgp group OVERLAY accept-remote-nexthop
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Understanding the Configuration:
The exhibit shows a BGP configuration on a Border-Leaf device. The BGP group UNDERLAY is used for
the underlay network, OVERLAY for EVPN signaling, and PROVIDER for connecting to the provider
network.
The OVERLAY group has the accept-remote-nexthop statement, which is designed to accept the next-
hop address learned from the remote peer as is, without modifying it.
Problem Identification:
The BGP session to Border-Leaf-2 is not established. A common issue in EVPN-VXLAN environments
is related to next-hop reachability, especially when accept-remote-nexthop is configured.
In typical EVPN-VXLAN setups, the next-hop address should be reachable within the overlay network.
However, the accept-remote-nexthop can cause issues if the next-hop IP address is not directly
reachable or conflicts with the expected behavior in the overlay.
Corrective Action:
D. delete protocols bgp group OVERLAY accept-remote-nexthop: Removing this command will ensure
that the device uses its own IP address as the next-hop in BGP advertisements, which is standard
practice in many EVPN-VXLAN setups. This change should help establish the BGP session with
Border-Leaf-2.
Data Center Reference:
Proper handling of BGP next-hop attributes is critical in establishing and maintaining stable BGP
sessions, especially in complex multi-fabric environments like EVPN-VXLAN. Removing accept-
remote-nexthop aligns with best practices in many scenarios.
Comments
Question 8
You are asked to automatically provision new Juniper Networks devices in your network with
minimal manual intervention Before you begin, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. You must have a DHCP server that provides the location of the software image and configuration files.
- B. You must have a system log (syslog) server to manage system log messages and alerts.
- C. You must have an NTP server to perform time synchronization.
- D. You must have a file server that stores software image and configuration files.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP):
ZTP is a feature that allows for the automatic provisioning of devices with minimal manual
intervention. It is widely used in large-scale deployments to quickly bring new devices online.
Key Requirements for ZTP:
A . DHCP Server: A DHCP server is crucial for ZTP as it provides the necessary information to new
devices, such as the IP address, the location of the software image, and configuration files.
D . File Server: The file server is where the software image and configuration files are stored. The
device downloads these files during the provisioning process.
Incorrect Options:
B . Syslog Server: While a syslog server is important for logging and monitoring, it is not a
requirement for the initial provisioning process.
C . NTP Server: An NTP server is used for time synchronization, which is essential for accurate logging
and operation but not specifically required for ZTP.
Data Center Reference:
ZTP simplifies the deployment process by automating the initial configuration steps, relying heavily
on DHCP for communication and a file server for delivering the necessary configuration and
software.
Comments
Question 9
You are selling up an EVPN-VXLAN architecture (or your new data center. this initial deployment will
be less than 50 switches: however, it could scale up to 250 switches over time supporting 1024
VLANs. You are still deciding whether to use symmetric or asymmetric routing.
In this scenario, which two statements are correct? (Choose two.)
- A. Symmetric routing needs an extra VLAN with an IRB interface for each L3 VRF instance.
- B. Asymmetric routing is easier lo monitor because of the transit VNI.
- C. Symmetric routing supports higher scaling numbers.
- D. Asymmetric routing routes traffic on the egress switch.
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Routing in EVPN-VXLAN:
Symmetric Routing: Traffic enters and exits the VXLAN network through the same VTEP, regardless of
the source or destination. This approach simplifies routing decisions, especially in large networks,
and is generally more scalable.
Asymmetric Routing: The routing occurs on the egress VTEP. This method can be simpler to deploy in
smaller environments but becomes complex as the network scales, particularly with larger numbers
of VNIs and VLANs.
Correct Statements:
C . Symmetric routing supports higher scaling numbers: Symmetric routing is preferred in larger
EVPN-VXLAN deployments because it centralizes routing decisions, which can be more easily
managed and scaled.
D . Asymmetric routing routes traffic on the egress switch: This is accurate, as asymmetric routing
means the routing decision is made at the final hop, i.e., the egress VTEP before the traffic reaches its
destination.
Incorrect Statements:
A . Symmetric routing needs an extra VLAN with an IRB interface for each L3 VRF instance: This is not
accurate. Symmetric routing does not require an extra VLAN per VRF; rather, it uses the same
VLAN/VNI across the network, simplifying routing and VLAN management.
B . Asymmetric routing is easier to monitor because of the transit VNI: Asymmetric routing is not
necessarily easier to monitor; in fact, it can add complexity due to the split routing logic between
ingress and egress points.
Data Center Reference:
The choice between symmetric and asymmetric routing in an EVPN-VXLAN environment depends on
network size, complexity, and specific operational requirements. Symmetric routing is generally
more scalable and easier to manage in large-scale deployments.
Comments
Question 10
Your organization is implementing EVPN-VXLAN and requires multiple overlapping VLAN-IDs. You
decide to use a routing-instance type mac-vrf to satisfy this request.
Which two statements are correct in this scenario? (Choose two.)
- A. Host-facing interfaces must be configured using a service-provider style configuration.
- B. Host-facing interfaces must be configured using enterprise-style configuration.
- C. Spine-facing interfaces must be configured using an enterprise-style configuration.
- D. The routing-instance service type can be VLAN-based.
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
Understanding the Scenario:
EVPN-VXLAN deployments often involve scenarios where multiple tenants or applications require
overlapping VLAN IDs, which can be managed using the mac-vrf routing instance type. This allows
you to segregate traffic within the same VLAN ID across different tenants.
Host-facing Interface Configuration:
A . Host-facing interfaces must be configured using a service-provider style configuration: This is
correct. In mac-vrf configurations, host-facing interfaces (those connecting end devices) typically
follow a service-provider style configuration, where each customer or tenant's traffic is isolated even
if overlapping VLAN IDs are used.
B . Host-facing interfaces must be configured using enterprise-style configuration: This is incorrect for
mac-vrf instances because enterprise-style configurations are more common in simpler, less
segmented networks.
Routing Instance Service Type:
D . The routing-instance service type can be VLAN-based: This is correct. The service type in mac-vrf
can indeed be VLAN-based, which is particularly useful in scenarios where VLAN ID overlap is needed
between different tenants or services.
Data Center Reference:
The mac-vrf instance type is powerful for handling complex multi-tenant environments in EVPN-
VXLAN, especially when dealing with overlapping VLAN IDs across different segments of the
network.
Comments
Page 1 out of 6
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 65
page 2