Question 1
The figure shows the Router-LSA generated by a router. Which of the following statements are true
based on the LSA?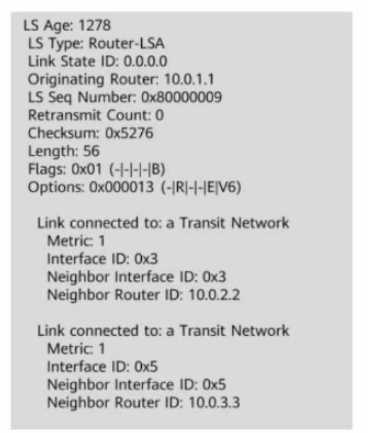
- A. The router is an ASBR.
- B. At least one interface on the router belongs to area 0.
- C. The router is an ABR.
- D. At least one interface on the router belongs to a stub area.
Answer:
B, C
Comments
Question 2
On the OSPFv3 network shown in the figure, OSPFv3 is enabled on the interfaces connecting R1, R2,
and R3. The router ID of each router is 10.0.X.X, where X is the number of the router. If you check
detailed information about an LSA on R3, the command output shows that the LSA is generated by
R2 and describes the IPv6 prefix address associated with the Router-LSA.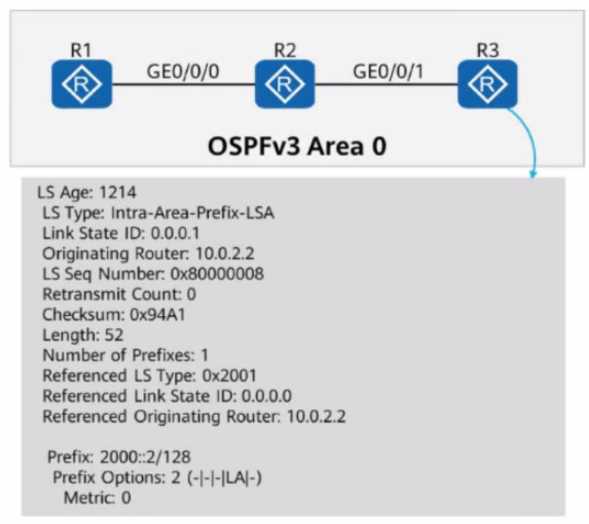
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 3
R1 and R2 use directly connected interfaces to establish an EBGP peer relationship. R1 imports 2000::
1/128 to BGR By default, which of the following is the next hop of the route from R2 to 2000:: 1/128?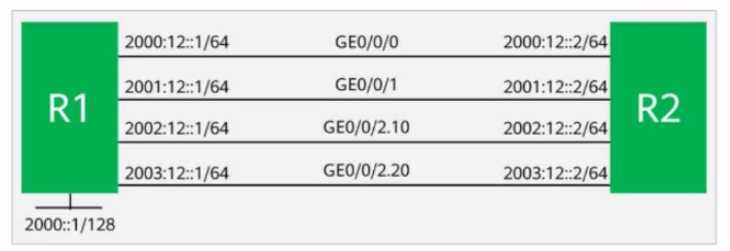
- A. 2002: 12:: 1
- B. 2001:12.1
- C. 2003:12::1
- D. 2000:12::1
Answer:
D
Comments
Question 4
On the OSPFv3 network shown in the figure, area 1 is a common are
a. Which of the following statements are true?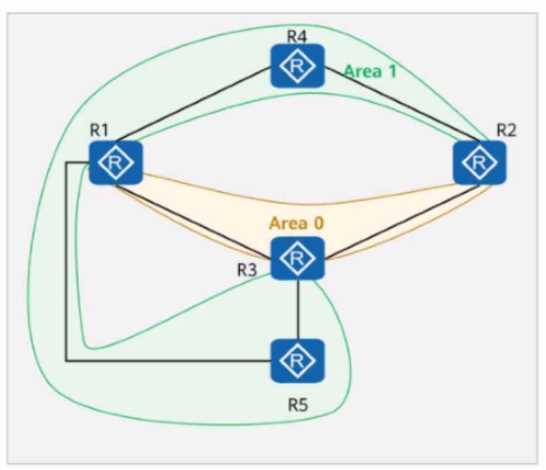
- A. The LSDBs of R1, R2, and R3 are the same.
- B. If R5 imports an external route, R4 does not need to rely on the Inter-Area-Router-LSA to calculate the external route.
- C. R1, R2, and R3 generate Inter-Area-Prefix-LSAs.
- D. The LSDBs of R4 and R5 are the same.
Answer:
C, D
Comments
Question 5
On the OSPFv3 network shown in the figure, area 1 is a stub area, area 2 is a common area, and area
3 is an NSS
- A. Router-LSA
- B. Link-LSA
- C. Intra-Area-Prefix-LSA
- D. AS-External-LSA
Answer:
D
Comments
Question 6
To support the processing and calculation of IPv6 routes, IS-IS adds a new NLPID to TLV 129. The
NLPID is an 8-bit field that identifies network layer protocol packets. Which of the following is the
NLPID of IPv6?
- A. 232
- B. 142
- C. 204
- D. 236
Answer:
B
Comments
Question 7
On the 05PFv3 network shown in the figure, each interface of R1 and R2 has two IPv6 addresses.
Although the IPv6 address prefixes of R1 and R2 are different, they can still be used to establish an
OSPFv3 neighbor relationship. If R2 is the DR, the Intra-Area-Prefix-LSA generated by R2 contains
four prefixes.
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 8
On the OSPFv3 network shown in the figure, the IPv6 address of Loopback0 on R3 is 2000-3/128, and
OSPFv3 is enabled. Which of the following statements are true?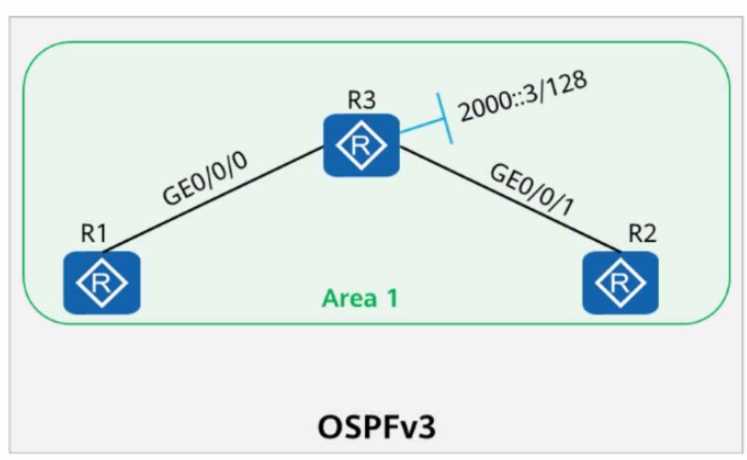
- A. R2 definitely generates a Link-LSA.
- B. The Link-LSA generated by R2 does not exist in the LSDB of Rl.
- C. Rl definitely generates a Network-LSA.
- D. R3 definitely generates an Intra-Area-Prefix-LSA.
Answer:
A, B, D
Comments
Question 9
Which of the following TLVs is added to IS-IS to support multi-topology?
- A. TLV229
- B. TLV232
- C. TLV236
- D. TLV129
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 10
If the display ospfv3 peer verbose command is run to check OSPFv3 neighbor information, the
command output contains information such as the peer router ID, global unicast address of the peer
interface, and neighbor status.
- A. TRUE
- B. FALSE
Answer:
A
Comments
Page 1 out of 15
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 156
page 2