Question 1
Which type of media should the IR team be handling as they seek to understand the root cause of an
incident?
A. Restored media from full backup of the infected host
B. Media from the infected host, copied to the dedicated IR host
C. Original media from the infected host
D. Bit-for-bit image from the infected host
Answer:
A
By imaging the media with tools such as dd or Ghost and analyzing the copy, you preserve the
original media for later analysis so that the results can be recreated by another competent examiner
if necessary.
Comments
Question 2
An incident response team is handling a worm infection among their user workstations. They created
an IPS signature to detect and block worm activity on the border IPS, then removed the worm’s
artifacts or workstations triggering the rule. Despite this action, worm activity continued for days
after. Where did the incident response team fail?
A. The team did not adequately apply lessons learned from the incident
B. The custom rule did not detect all infected workstations
C. They did not receive timely notification of the security event
D. The team did not understand the worm’s propagation method
Answer:
B
Identifying and scoping an incident during triage is important to successfully handling a security
incident. The detection methods used by the team didn’t detect all the infected workstations.
Comments
Question 3
A legacy server on the network was breached through an OS vulnerability with no patch available.
The server is used only rarely by employees across several business units. The theft of information
from the server goes unnoticed until the company is notified by a third party that sensitive
information has been posted on the Internet. Which control was the first to fail?
A. Security awareness
B. Access control
C. Data classification
D. Incident response
Answer:
C
The legacy system was not properly classified or assigned an owner. It is critical that an organization
identifies and classifies information so proper controls and measures should be put in place. The
ultimate goal of data classification is to make sure that all information is properly protected at the
correct level.
This was not a failure of incident response, access control or security awareness training.
Comments
Question 4
Analyze the screenshot below. Which of the following attacks can be mitigated by these
configuration settings?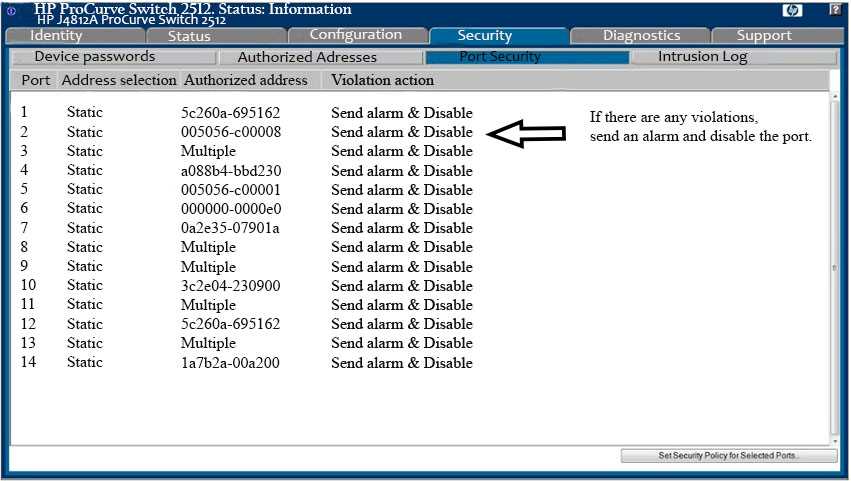
A. A Denial-of-Service attack using network broadcasts
B. A Replay attack
C. An IP masquerading attack
D. A MAC Flood attack
Answer:
D
Both BPDU Guard and Root Guard are used to prevent a new switch from becoming the Root Bridge.
They are very similar but use different mechanisms.
Rootguard allows devices to use STP, but if they send superior BDPUs (i.e. they attempt to become
the Root Bridge), Root Guard disables the port until the offending BPDUs cease. Recovery is
automatic.
If Portfast is enabled on a port, BPDU Guard will disable the port if a BPDU is received. The port stays
disabled until it is manually re-enabled. Devices behind such ports cannot use STP, as the port would
be disabled as soon as they send BPDUs (which is the default behavior of switches).
Comments
Question 5
Of the following pieces of digital evidence, which would be collected FIRST from a live system
involved in an incident?
A. Event logs from a central repository
B. Directory listing of system files
C. Media in the CDrom drive
D. Swap space and page files
Answer:
D
Best practices suggest that live response should follow the order of volatility, which means that you
Memory
Swap or page file
Network status and current / recent network connections
Running processes
Open files
Comments
Question 6
Which of the following attacks would use “..” notation as part of a web request to access restricted
files and directories, and possibly execute code on the web server?
- A. URL directory
- B. HTTP header attack
- C. SQL injection
- D. IDS evasion
- E. Cross site scripting
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 7
At the start of an investigation on a Windows system, the lead handler executes the following
commands after inserting a USB drive. What is the purpose of this command? C:\ >dir / s / a dhsra d:
\ > a: \ IRCD.txt
A. To create a file on the USB drive that contains a listing of the C: drive
B. To show hidden and archived files on the C: drive and copy them to the USB drive
C. To copy a forensic image of the local C: drive onto the USB drive
D. To compare a list of known good hashes on the USB drive to files on the local C: drive
Answer:
C
This command will create a text file on the collection media (in this case you would probably be using
a USB flash drive) named IRCD.txt that should contain a recursive directory listing of all files on the
desk.
Comments
Question 8
Why might an administrator not be able to delete a file using the Windows del command without
specifying additional command line switches?
- A. Because it has the read-only attribute set
- B. Because it is encrypted
- C. Because it has the nodel attribute set
- D. Because it is an executable file
Answer:
A
Comments
Question 9
Why would the pass action be used in a Snort configuration file?
A. The pass action simplifies some filtering by specifying what to ignore.
B. The pass action passes the packet onto further rules for immediate analysis.
C. The pass action serves as a placeholder in the snort configuration file for future rule updates.
D. Using the pass action allows a packet to be passed to an external process.
E. The pass action increases the number of false positives, better testing the rules.
Answer:
A
The pass action is defined because it is sometimes easier to specify the class of data to ignore rather
than the data you want to see. This can cut down the number of false positives and help keep down
the size of log data.
False positives occur because rules failed and indicated a threat that is really not one. They should be
minimized whenever possible.
The pass action causes the packet to be ignored, not passed on further. It is an active command, not
a placeholder.
Comments
Question 10
On which layer of the OSI Reference Model does the FWSnort utility function?
A. Physical Layer
B. Data Link Layer
C. Transport Layer
D. Session Layer
E. Application Layer
Answer:
C
The FWSnort utility functions as a transport layer inline IPS.
Comments
Page 1 out of 8
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 88
page 2