Question 1
What is the best explanation of how FortiManager helps with mass provisioning?
- A. It upgrades the OS of each FortiGate device.
- B. It provides local FortiGuard Distribution Server (FDS) services to the network.
- C. It uses templates to configure the same settings on many devices simultaneously.
- D. It sends email alerts when new devices connect.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
FortiManager helps with mass provisioning by using templates that allow administrators to configure
the same settings on multiple FortiGate devices simultaneously, streamlining deployment and
management.
Comments
Question 2
What is the purpose of ADOM revisions?
- A. ADOM revisions find unused, duplicate, and unnecessary firewall policies and objects.
- B. ADOM revisions show specific changes in a policy package when it is installed.
- C. ADOM revisions compare previous snapshots of the Policy Package and ADOM-level objects with the device-level database.
- D. ADOM revisions save the current state of all policy packages and objects for an ADOM.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
ADOM revisions save the current state of all policy packages and objects within an ADOM, allowing
administrators to track changes over time and revert to previous configurations if needed.
Comments
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit.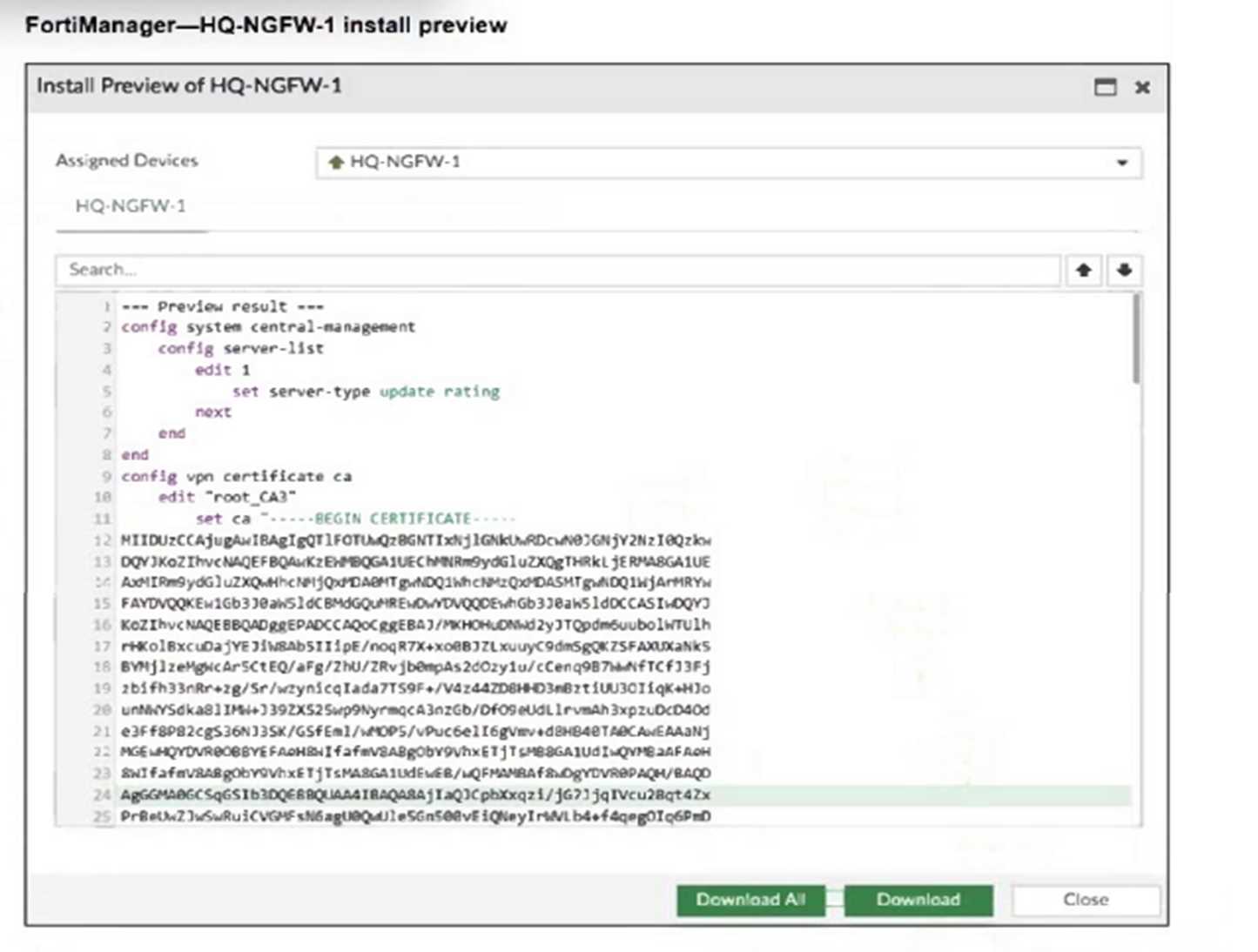
An administrator assigned a new policy package to FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1. In the installation preview,
they noticed some settings they did not modify and are unsure about the changes.
Based on the exhibit, which two things will happen if they continue with the installation? (Choose
two.)
- A. FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 can use FortiManager firmware templates to upgrade firmware and ratings.
- B. FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 can contact the FortiManager acting as FortiGuard Distribution Server (FDS) to download FortiGuard updates.
- C. FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 will use the root_CA3 certificate in firewall address objects or policies.
- D. FortiManager will install the CA certificate named root_CA3 to authenticate FortiGate-to- FortiManager communication protocol (FGFM) tunnel connections with FortiGate HQ- NGFW-1.
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
The configuration includes a server-list with server-type set to "update rating," which enables
FortiGate HQ-NGFW-1 to contact FortiManager as a FortiGuard Distribution Server (FDS) for
FortiGuard updates.
The installation includes a root_CA3 certificate, which FortiManager will install on FortiGate HQ-
NGFW-1 to authenticate FGFM tunnel connections between the devices.
Comments
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.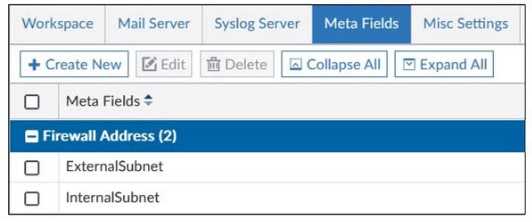
An administrator created two new meta fields in FortiManager.
Which operation can you perform with these parameters?
- A. You can add them to objects as custom attributes.
- B. You can export them to be used in other ADOMs.
- C. You can use them as variables in scripts.
- D. You can invoke them using the $ character.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Meta fields in FortiManager can be added to objects as custom attributes, allowing administrators to
categorize and add additional information to firewall objects for easier management and
identification.
Comments
Question 5
Push updates are failing on a FortiGate device located behind a network address translation (NAT)
device?
Which two settings should the administrator check to correct this problem? (Choose two.)
- A. Make sure the NAT device IP address and the correct ports are configured on FortiManager.
- B. Make sure FortiGuard updates and web service are enabled on the FortiGuard service interface.
- C. Make sure the virtual IP address and the correct ports are configured on the NAT device.
- D. Make sure the Bind to IP address option on the FortiGuard service interface is set to the virtual IP address from the NAT device.
Answer:
A, C
Explanation:
FortiManager must have the NAT device's IP address and correct ports configured to communicate
properly with the FortiGate behind NAT.
The NAT device must have the correct virtual IP address and ports configured to allow push updates
to reach the FortiGate device.
Comments
Question 6
The administrator uses FortiManager to push a CLI script using the Remote FortiGate Directly (via
CLI) option to configure an IPsec VPN. However, when running the script, the administrator receives
the following error:
config vpn ipsec phase2-interface [parameter(s) invalid. detail: object mismatch]
What must the administrator do to resolve the script error and successfully apply the IPsec
configuration?
- A. Add the end command after finishing the IPsec phase 1-interface configuration block.
- B. Use IPsec templates to deploy provisioning templates.
- C. Add a second config vpn ipsec phase2-interface block without linking it to phase1.
- D. Run the script using the policy package or ADOM database method.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Running the script through the policy package or ADOM database method allows FortiManager to
properly interpret object relationships and dependencies in the IPsec configuration, preventing
object mismatch errors when pushing complex VPN settings directly via CLI.
Comments
Question 7
An administrator has a FortiGate-HQ device with VDOMs—root, HR and Facilities, currently managed
under the FortiManager ADOM—Site1. They try to move VDOM HR to the FortiManager ADOM—
Site2, but it does not work.
Why is the administrator not able to move FortiGate-HQ VDOM HR to FortiManager ADOM—Site2?
- A. The FortiGate-HQ must be managed under the FortiManager ADOM—root to allow moving its VDOMs to different ADOMs.
- B. The administrator must have full access in the device layer of FortiGate-HQ VDOM-root before they can VDOMs to different ADOMs.
- C. FortiManager must be in ADOM normal mode, which does not allow VDOMs to be managed separately.
- D. The administrator must delete the FortiGate-HQ device from FortiManager and add it again using the Add Device wizard before moving the VDOM.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
FortiGate devices must be managed under the FortiManager ADOM corresponding to the root VDOM
to allow their individual VDOMs to be moved and managed in different ADOMs. Managing the root
VDOM in a different ADOM prevents moving subordinate VDOMs across ADOMs.
Comments
Question 8
Refer to the exhibit.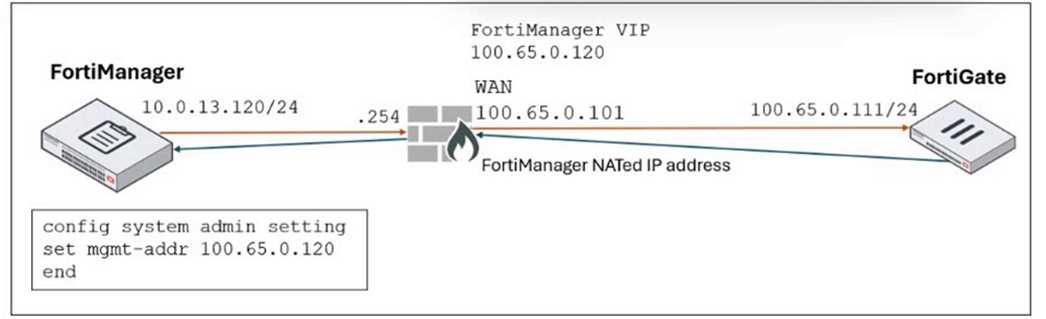
FortiManager is operating behind a network address translation (NAT) device, and the administrator
configured the FortiManager NATed IP address under the FortiManager system administration
settings.
What is the expected result during discovery?
- A. FortiManager sets both the 100.65.0.120 IP address and 10.0.13.120 IP address on FortiGate.
- B. FortiManager sets both the 100.65.0.120 IP address and 100.65.0.101 IP address on FortiGate.
- C. FortiManager sets the 100.65.0.101 IP address on FortiGate.
- D. FortiManager sets the 100.65.0.120 IP address on FortiGate.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
When FortiManager is behind a NAT device, setting the NATed IP address (100.65.0.120) in the
system admin settings causes FortiManager to use that NATed IP address for communication and
configuration with FortiGate during discovery and management operations.
Comments
Question 9
An administrator configures a new BGP peer in the FortiManager device-level database of FortiGate.
They reinstall the policy package to the managed FortiGate device without any errors. However,
when the administrator logs in to FortiGate, they do not see the BGP configuration changes.
What is the most likely reason why FortiManager did not push the BGP peer changes to FortiGate?
- A. The administrator must run a sanity check on FortiManager to make sure the database is not corrupted.
- B. Fortigate has a BGP template assigned on the FortiManager database.
- C. The administrator must use the Install Wizard and select Install device settings only to push BGP settings
- D. The FortiGate firmware version is different from the FortiManager ADOM version.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
If a BGP template is assigned to the FortiGate device on FortiManager, device-level BGP
configurations made directly in the device-level database are overridden by the template settings, so
the changes do not get pushed to the device.
Comments
Question 10
Company policy dictates that any time a change is made to a policy package on FortiManager an
ADOM revision is created before the change installed, and that revision is held for a minimum of
90 days.
Over the past three months, each installed change has resulted in several unused policies and
duplicate objects.
The FortiManager administrator plans to upgrade the FortiGate devices and then upgrade the
FortiManager ADOM from version 7.4 to 7.6.
Which action can the administrator take to avoid slow ADOM upgrades?
- A. Check and repair the global configuration database before upgrading.
- B. Export firewall policies to Excel, delete them on the ADOM. then reimport them after upgrading the ADOM.
- C. Find unused firmware templates, then delete them before upgrading.
- D. Limit ADOM revisions before upgrading.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Limiting ADOM revisions reduces the number of stored historical configurations, which helps avoid
performance degradation and slow ADOM upgrades caused by a large volume of revisions.
Comments
Page 1 out of 3
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 33
page 2