Question 1
Which two statements are true about link-state routing protocols? (Choose two.)
- A. The advertisement exchange is mainly triggered by a change in the network.
- B. Each router uses a reliable update mechanism to exchange topology information with its neighbors. C Link-state routing protocols mainly use hop-counts to determine the link cost
- D. A distance vector algorithm is very processor intensive compared to Dijkstra's algorithm.
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
Link-state routing protocols are one of the two main classes of routing protocols used in packet
switching networks for computer communications, the other being distance-vector routing
protocols. Examples of link-state routing protocols include Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) and
Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS). The basic concept of link-state routing is that
every node constructs a map of the connectivity to the network, in the form of a graph, showing
which nodes are connected to which other nodes. Each node then independently calculates the next
best logical path from it to every possible destination in the network. Each collection of best paths
will then form each node’s routing table.
Two statements that are true about link-state routing protocols are:
The advertisement exchange is mainly triggered by a change in the network. Link-state routing
protocols use a flooding mechanism to distribute information about the network topology to all
routers in the same area or domain. This information is encapsulated in link-state packets (LSPs) or
link-state advertisements (LSAs), which contain information about the router, its directly connected
links, and the state of those links. LSPs or LSAs are sent only when there is a change in the topology,
such as a link failure or recovery, or when a periodic refresh timer expires. This way, link-state routing
protocols can quickly adapt to network changes and maintain an accurate and consistent view of the
network.
Each router uses a reliable update mechanism to exchange topology information with its neighbors.
Link-state routing protocols use a reliable update mechanism to ensure that all routers receive and
acknowledge the LSPs or LSAs sent by their neighbors. This mechanism involves sending hello
messages to establish and maintain adjacencies with neighbors, sending acknowledgment messages
to confirm the receipt of LSPs or LSAs, and requesting missing or outdated LSPs or LSAs from
neighbors. This mechanism ensures that all routers have a synchronized database of LSPs or LSAs,
which is used to build a complete network connectivity map and to calculate the shortest path to
destinations.
Reference:
Link-state routing protocol - Wikipedia
,
Ericsson IP Networking - Routing Protocols
Comments
Question 2
Which operating system is used in Ericsson Router 6000 products?
- A. SE-OS
- C. ERS
- D. IPOS
- E. Junos
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The operating system used in Ericsson Router 6000 products is ERS (Ericsson Router Software). ERS is
based on IPOS (IP Operating System), which is a common operating system for Ericsson’s IP portfolio.
ERS provides advanced features and functionality for IP transport, such as MPLS, Segment Routing,
QoS, IPSec, synchronization, SDN, and more. ERS also supports seamless integration with Ericsson
Radio System and Ericsson Network Manager.
Reference:
Router 6000 Series - Ericsson
,
Router 6675 Datasheet - Winncom
Comments
Question 3
What network information is, without additional configuration, shared between two iBGP neighbors
by default?
- A. BGP routes learned from an OSPF neighbor
- B. IP address information of loopback interfaces
- C. BGP routes learned from eBGP neighbors
- D. IP address information from all directly connected interfaces
Answer:
C
Explanation:
iBGP works by exchanging routing information between two or more routers within an AS. Each
router sends its own routing table to its neighbors, which contains information about the networks it
knows and how they can be reached from that router. By default, iBGP neighbors only share BGP
routes learned from eBGP neighbors, which are routers in different ASes. This is because iBGP
assumes that all routers within an AS have consistent internal routing information provided by an
IGP, such as OSPF or IS-IS. Therefore, iBGP neighbors do not need to share IP address information of
loopback interfaces or directly connected interfaces, unless explicitly configured to do so by using
commands such as neighbor update-source or network.
Reference:
iBGP Ultimate Guide | How iBGP Is Different From eBGP
,
Ericsson IP Networking - Routing
Protocols
Comments
Question 4
An IS-IS router has been assigned the NSAP address: 49.00F0.0100.5012.3010.00.
What is the Area ID to which the router belongs?
- A. 49.00F0
- B. 49.00F0.0100
- C. 5012.3010.00
- D. 00F0 0100
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The Area ID to which the router belongs is 49.00F0.0100. The Area ID is a variable-length field in the
NSAP address that identifies the area to which the router belongs. The Area ID can be between 1 and
13 bytes long, but it must start and end with an octet (8 bits). The NSAP address is composed of three
parts: the authority and format identifier (AFI), the area ID, and the system ID. The AFI is a one-octet
field that indicates the format and authority of the rest of the address. The system ID is a fixed-length
field of six octets that uniquely identifies the router within an area. The NSAP address also has a
network selector (NSEL) field, which is a one-octet field that identifies the network layer service to
which a packet should be sent. For IS-IS routers, the NSEL must always be 00.
In this question, the NSAP address is 49.00F0.0100.5012.3010.00. This means that:
The AFI is 49, which indicates a private address.
The Area ID is 00F0.0100, which is four octets long and starts and ends with an octet.
The system ID is 5012.3010, which is six octets long and identifies the router within the area.
The NSEL is 00, which indicates IS-IS.
Therefore, the answer is B.
Reference:
Ericsson IP Networking - Routing Protocols
,
IS-IS NSAP address - Cisco
Community
,
Understanding IS-IS NSAP Addresses - Todd Lammle, LLC
,
IS-IS - Nokia
,
Network service
access point address - Wikipedia
Comments
Question 5
P routers forward packets based on the ______.
- A. flow label
- B. B. VPN label
- C. C. LSP label
- D. D. inner label
Answer:
C
Explanation:
P routers forward packets based on the LSP label. The LSP label is the label that corresponds to the
label-switched path (LSP) that is established between two PE routers in an MPLS network. The LSP
label is also called the outer label or the transport label, because it is used to transport packets
across the MPLS core network. P routers are also called LSRs (label switch routers) or transit routers,
because they switch packets based on their labels or remove the labels. P routers do not need to
look at the IP header or any other information in the packet, except for the top label in the label
stack. P routers perform one of three possible operations on labels: swap, pop, or PHP (penultimate
hop popping). In a swap operation, the label is swapped with a new label, and the packet is
forwarded along the path associated with the new label. In a pop operation, the label is removed
from the packet, and the packet is forwarded based on its IP header or another label in the stack. In a
PHP operation, the label is removed from the packet at the last P router before reaching the egress
PE router, and the packet is forwarded without any label to the egress PE router.
The LSP label is different from other types of labels that may be used in MPLS networks, such as VPN
labels or service labels. These labels are used to identify different VPNs or services that run over
MPLS networks, such as Layer 2 VPNs, Layer 3 VPNs, traffic engineering, or QoS. These labels are also
called inner labels or payload labels, because they are related to the payload of the packet. These
labels are not used by P routers for forwarding decisions, but only by PE routers for delivering
packets to their destinations.
Therefore, the answer is C.
Reference:
Ericsson IP Networking - Routing Protocols
,
MPLS Fundamentals: Forwarding Labeled
Packets - Cisco Press
,
MPLS Labels and Devices - NetworkLessons.com
,
Multiprotocol Label Switching
- Wikipedia
,
VPN Packet Forwarding > MPLS/VPN Architecture Overview | Cisco Press
,
Basic concepts
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
Comments
Question 6
Review the exhibit.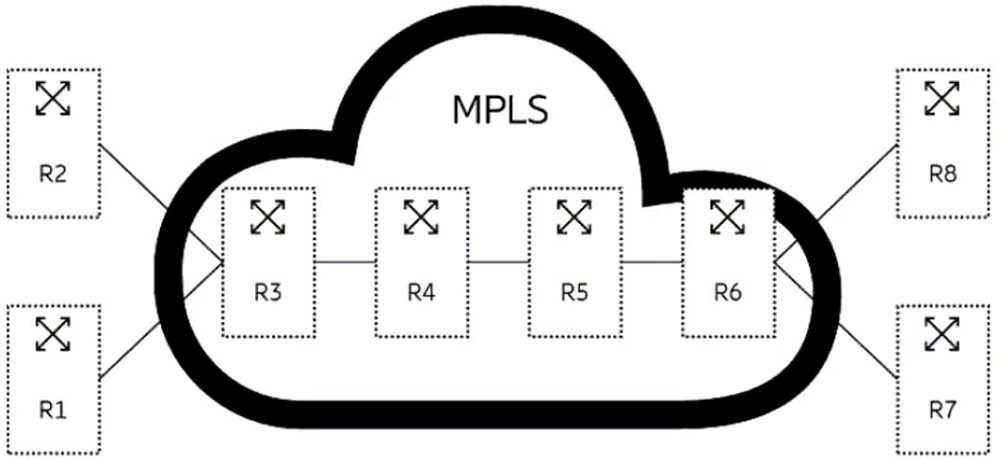
In the exhibit, which action is performed by router R4?
- A. pop
- B. push
- C. PHP
- D. swap
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In the exhibit, router R4 is performing a swap action. This means that router R4 is replacing the
incoming label with a new label and forwarding the packet to the next hop along the LSP. In this case,
router R4 receives a packet with label 20 from router R3 and swaps it with label 30 before sending it
to router R5.
The exhibit shows an example of an MPLS network with four routers: R1, R2, R3, and R4. Router R1 is
the ingress PE router and router R4 is the egress PE router. Router R2 and R3 are P routers. Router R1
assigns label 10 to the packet and sends it to router R2. Router R2 swaps label 10 with label 20 and
sends it to router R3. Router R3 swaps label 20 with label 30 and sends it to router R4. Router R4
removes label 30 from the packet and forwards it based on its IP header or another label in the stack.
⋆
Therefore, the answer is D.
Reference:
MPLS Label Switching | MPLS Operation | Push, Swap,Push
IPCisco
,
A Complete Guide
to Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) - G2
,
Multiprotocol Label Switching - Wikipedia
Comments
Question 7
In a company network, a host sends an Ethernet frame destined to the address FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF.
What will an Ethernet switch do with this frame?
- A. It will forward the frame to only one port.
- B. It will forward the frame to all ports.
- C. It will drop it.
- D. It will send the frame only to management port.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
An Ethernet switch will forward the frame to all ports when the destination address is
FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. This is because this address is the broadcast MAC address, which means that the
frame is intended for all devices on the same LAN segment. The switch does not need to look up its
MAC address table to find a matching entry for this address, but simply floods the frame out of all
ports except the one where it received the frame. This way, the frame reaches every device on the
LAN segment, regardless of their MAC addresses. Reference:
Ethernet - Wireshark
,
Broadcast MAC
Address - omnisecu.com
Comments
Question 8
Which two statements are true about route summarization? (Choose two.)
- A. It reduces the size of a routing table.
- B. It reduces signaling.
- C. It summaries the routing table entries into a default route
- D. It improves the best route calculation.
Answer:
A, B
Explanation:
Route summarization is a technique that reduces the number of routes that a router advertises to its
neighbors by creating a single summary route that covers multiple subnets or networks. Route
summarization has several benefits, such as:
It reduces the size of a routing table, which saves memory and CPU resources on the router. A
smaller routing table also improves the lookup efficiency and convergence time of the routing
protocol.
It reduces signaling, which means that less bandwidth is consumed by routing updates and less
processing is required by neighboring routers. This also enhances the stability and scalability of the
network, as fewer routing changes are propagated.
It improves route aggregation, which means that more specific routes are replaced by a less specific
route that can be advertised to other autonomous systems or routing domains. This simplifies the
inter-domain routing and hides the internal topology details.
Route summarization does not necessarily summarize the routing table entries into a default route,
although a default route can be considered a special case of route summarization where all
destinations are covered by one route. Route summarization also does not improve the best route
calculation, as it may introduce suboptimal routing or black holes if not done
properly. Reference:
Introduction to Route Summarization - NetworkLessons.com
,
Route
Summarization > Example for Understanding Route Summarization - Cisco Press
Comments
Question 9
Which two label actions are performed by a P router? (Choose two.)
- A. push
- B. php
- C. drop
- D. swap
Answer:
B, D
Explanation:
A P router is a provider router that is part of the service provider’s core network in an MPLS
environment. A P router does not have any customer routes or VPN information, but only has
information about how to reach other P routers and PE routers in the same MPLS domain. A P router
performs label switching, which means that it forwards labeled packets based on their top label in
the label stack. A P router can perform two possible label actions:
Swap: The P router replaces the incoming label with a new label that corresponds to the next hop
along the label-switched path (LSP). The new label is determined by looking up the label forwarding
information base (LFIB) based on the incoming label and interface.
PHP: The P router removes the top label from the packet at the penultimate hop before reaching the
egress PE router. This is done to avoid an extra lookup on the egress PE router, which can forward the
packet based on its IP header or another label in the stack.
A P router does not perform push or drop actions on labels. A push action means adding one or more
labels to the packet, which is done by an ingress PE router when initiating an LSP. A drop action
means discarding a packet, which is done by any router when there is no matching entry in its LFIB or
routing table. Reference:
Provider (P) Router in IP MPLS Network - Cisco Community
,
MPLS
⋆
Fundamentals: Forwarding Labeled Packets - Cisco Press
,
MPLS Label Switching | MPLS Operation |
Push, Swap,Push
IPCisco
Comments
Question 10
How is a BGP session established between two routers?
- A. The BGP router sends a unicast NOTIFICATION message.
- B. The BGP router sends a unicast OPEN message.
- C. The BGP router sends a multicast CONNECT message.
- D. The BGP router sends a multicast HELLO packet.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A BGP session is established between two routers by sending a unicast OPEN message. BGP uses TCP
as its transport protocol, which means that before exchanging any BGP information, a TCP
connection must be established between the routers. The TCP connection uses port 179 as both
source and destination port. After establishing a TCP connection, each router sends an OPEN
message to its neighbor, containing parameters such as BGP version number, AS number, hold time,
BGP identifier, and optional capabilities. The OPEN message also serves as a keepalive message for
BGP. If both routers agree on these parameters, they proceed to exchange UPDATE messages
containing routing information and establish a BGP session.
A BGP router does not send a NOTIFICATION message to establish a session, but rather to terminate
a session due to an error or a manual shutdown. A BGP router does not send a CONNECT message,
as this is a TCP state, not a BGP message. A BGP router does not send a multicast HELLO packet, as
this is an OSPF message, not a BGP message. Reference:
BGP Neighbor States > BGP Fundamentals |
Cisco Press
,
Demystifying BGP Session Establishments - Packet Pushers
,
The TCP/IP Guide - BGP
Connection Establishment: Open Messages
Comments
Page 1 out of 5
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 60
page 2