Question 1
How many times must BGP be configured when running symmetric IRB with two VFRs?
- A. 3
- B. 5
- C. 2
- D. 4
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When running symmetric Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) with two Virtual Forwarding Routers
(VFRs), BGP must be configured twice. Each VFR will have its own BGP instance to handle the routing
information.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC Routing Guide
Dell Networking Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 2
DRAG DROP
What is the correct order of steps for data flow in asymmetric IRB frame encapsulation?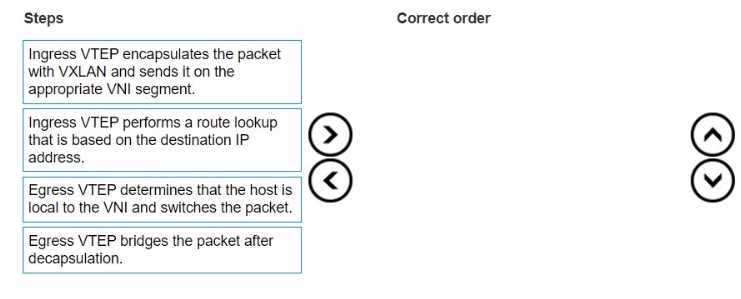
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Ingress VTEP performs a route lookup that is based on the destination IP address.
Ingress VTEP encapsulates the packet with VXLAN and sends it on the appropriate VNI segment.
Egress VTEP determines that the host is local to the VNI and switches the packet.
Egress VTEP bridges the packet after decapsulation.
Steps and Correct Order:
Ingress VTEP performs a route lookup that is based on the destination IP address.
The ingress VTEP (Virtual Tunnel Endpoint) first needs to determine the next hop for the packet. This
involves performing a route lookup using the destination IP address.
Ingress VTEP encapsulates the packet with VXLAN and sends it on the appropriate VNI segment.
Once the route lookup is complete, the ingress VTEP encapsulates the packet in a VXLAN header,
which includes the appropriate VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier) segment, and forwards it.
Egress VTEP determines that the host is local to the VNI and switches the packet.
The egress VTEP receives the encapsulated VXLAN packet, decapsulates it, and then checks its local
VNI to determine if the destination host is within the same VNI.
Egress VTEP bridges the packet after decapsulation.
After determining the destination host's locality, the egress VTEP bridges the packet to the
appropriate interface to deliver it to the final destination.
Reference:
Dell Technologies Networking - SONiC
Dell Enterprise SONiC Deployment Guide
These steps provide a comprehensive guide to understand the correct order of operations in
asymmetric IRB (Integrated Routing and Bridging) frame encapsulation within a VXLAN environment.
Comments
Question 3
What does the show vian command display?
- A. All configured VLANs
- B. Only VLANs in an active state
- C. All 4094 VLANs
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The show vlan command displays all configured VLANs on the device, including their status, ports,
and other relevant details. It does not limit the display to only active VLANs or all possible VLANs but
shows those that are currently configured.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC Command Reference Guide
Dell Networking Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 4
Which two things does the no vrrp 100 address-family ipv6 command delete?
- A. Identifier
- B. Interface
- C. Version
- D. Address-family
- E. Authentication
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
The no vrrp 100 address-family ipv6 command deletes the VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy
Protocol) identifier (A) and the address-family configuration (D) for VRRP group 100. This effectively
removes the VRRP configuration for the specified address family.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC documentation
VRRP Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 5
An administrator obtains the following CLI output:
How much time does the local system take to detect remote failures without receiving packets?
- A. 600 milliseconds
- B. 900milliseconds
- C. 1200 milliseconds
- D. 800 milliseconds
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The local timers in the BFD (Bidirectional Forwarding Detection) configuration show a detect
multiplier of 4 and a receive interval of 300ms. The time taken to detect remote failures is calculated
as detect multiplier × receive interval = 4 × 300ms = 1200ms.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC documentation
BFD Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 6
Which two elements are configured when RoCE is enabled?
- A. IB
- B. ETS
- C. PFC
- D. TCP
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
When RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) is enabled, Enhanced Transmission Selection (ETS) and
Priority Flow Control (PFC) are two key elements that need to be configured. ETS allows for
bandwidth allocation among different traffic classes, and PFC provides lossless Ethernet operation
for specific traffic classes to support low-latency, high-performance network communication.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC documentation
RDMA over Converged Ethernet Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 7
What are the supported modes for the QSFP28 ports on an S5248F?
- A. 1x100G, 1x40 G, 2x50 G, and 4x25 G
- B. 1x100G, 1x40 G, 4x25 G, and 4x10 G
- C. 1x200G, 1x100 G, 1x40 G, and 4x25 G
- D. 1x400G, 2x200 G, 4x25 G. and 4x10 G
Answer:
A
Explanation:
The QSFP28 ports on an S5248F switch support multiple modes, including 1x100G, 1x40G, 2x50G,
and 4x25G. These modes provide flexibility in network design and enable the switch to support
different types of network connections and bandwidth requirements.
Reference:
Dell S5248F Switch Data Sheet
Dell Technologies InfoHub
Comments
Question 8
What are two characteristics of route maps in Enterprise SONIC?
- A. Route-map names are not case-sensitive.
- B. The permit or deny clause In route maps permits or rejects the matching routes from being redistributed.
- C. They are a series of commands that contain a matching criterion and action.
- D. Each route map clause has the type values of Match. Set. and Act.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
Route maps in Enterprise SONIC are used for controlling and modifying routing information. They
contain a series of commands with matching criteria and actions. The permit or deny clause within
route maps determines whether the matching routes are permitted or denied from being
redistributed.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC Route Map Configuration Guide
Dell Networking Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 9
Which network devices route unencapsulated user traffic in a symmetric IRB overlay network?
- A. Source VTEP and destination VTEP
- B. Leaf router and spine router
- C. Capability extended next hop router and leaf router
- D. Autonomous system boundary router and source VTEP
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In a symmetric Integrated Routing and Bridging (IRB) overlay network, the Source Virtual Tunnel End
Point (VTEP) and the Destination VTEP route unencapsulated user traffic. Symmetric IRB ensures that
routing occurs at both the ingress and egress VTEPs, allowing for optimized traffic flow and efficient
network operations.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC documentation
VXLAN Configuration Guide
Comments
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.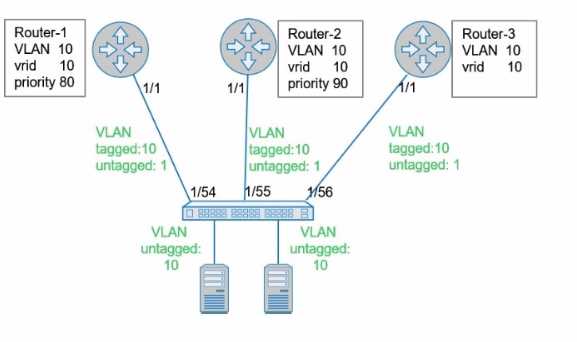
What is the primary VRRP router for VRRP group 10?
- A. Router-1
- B. Router-2
- C. Router-3
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Based on the exhibit, Router-2 has the highest priority (90) in VRRP group 10. In VRRP, the router
with the highest priority becomes the primary (master) router. Therefore, Router-2 is the primary
VRRP router for VRRP group 10.
Reference:
Dell Technologies SONiC VRRP Configuration Guide
VRRP Protocol Overview
Comments
Page 1 out of 4
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 45
page 2