Question 1
A data analyst is attempting to drop a table my_table. The analyst wants to delete all table metadata
and data.
They run the following command:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS my_table;
While the object no longer appears when they run SHOW TABLES, the data files still exist.
Which of the following describes why the data files still exist and the metadata files were deleted?
A. The table's data was larger than 10 GB
B. The table did not have a location
C. The table was external
D. The table's data was smaller than 10 GB
E. The table was managed
Answer:
C
An external table is a table that is defined in the metastore, but its data is stored outside of the
Databricks environment, such as in S3, ADLS, or GCS. When an external table is dropped, only the
metadata is deleted from the metastore, but the data files are not affected. This is different from a
managed table, which is a table whose data is stored in the Databricks environment, and whose data
files are deleted when the table is dropped. To delete the data files of an external table, the analyst
needs to specify the PURGE option in the DROP TABLE command, or manually delete the files from
the storage system. Reference:
DROP TABLE
,
Drop Delta table features
,
Best practices for dropping a
managed Delta Lake table
Comments
Question 2
After running DESCRIBE EXTENDED accounts.customers;, the following was returned:
Now, a data analyst runs the following command:
DROP accounts.customers;
Which of the following describes the result of running this command?
A. Running SELECT * FROM delta. `dbfs:/stakeholders/customers` results in an error.
B. Running SELECT * FROM accounts.customers will return all rows in the table.
C. All files with the .customers extension are deleted.
D. The accounts.customers table is removed from the metastore, and the underlying data files are
deleted.
E. The accounts.customers table is removed from the metastore, but the underlying data files are
untouched.
Answer:
E
the accounts.customers table is an EXTERNAL table, which means that it is stored outside the default
warehouse directory and is not managed by Databricks. Therefore, when you run the DROP
command on this table, it only removes the metadata information from the metastore, but does not
delete the actual data files from the file system. This means that you can still access the data using
/stakeholders/customers) or create another table pointing to the same
location. However, if you try to query the table using its name (accounts.customers), you will get an
error because the table no longer exists in the metastore. Reference:
DROP TABLE | Databricks on
AWS
,
Best practices for dropping a managed Delta Lake table - Databricks
Comments
Question 3
Which of the following should data analysts consider when working with personally identifiable
information (PII) data?
A. Organization-specific best practices for Pll data
B. Legal requirements for the area in which the data was collected
C. None of these considerations
D. Legal requirements for the area in which the analysis is being performed
E. All of these considerations
Answer:
E
Data analysts should consider all of these factors when working with PII data, as they may affect the
data security, privacy, compliance, and quality. PII data is any information that can be used to identify
a specific individual, such as name, address, phone number, email, social security number, etc. PII
data may be subject to different legal and ethical obligations depending on the context and location
of the data collection and analysis. For example, some countries or regions may have stricter data
protection laws than others, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European
Union. Data analysts should also follow the organization-specific best practices for PII data, such as
encryption, anonymization, masking, access control, auditing, etc. These best practices can help
prevent data breaches, unauthorized access, misuse, or loss of PII data. Reference:
How to Use Databricks to Encrypt and Protect PII Data
Automating Sensitive Data (PII/PHI) Detection
Databricks Certified Data Analyst Associate
Comments
Question 4
Delta Lake stores table data as a series of data files, but it also stores a lot of other information.
Which of the following is stored alongside data files when using Delta Lake?
A. None of these
B. Table metadata, data summary visualizations, and owner account information
C. Table metadata
D. Data summary visualizations
E. Owner account information
Answer:
C
Delta Lake is a storage layer that enhances data lakes with features like ACID transactions, schema
enforcement, and time travel. While it stores table data as Parquet files, Delta Lake also keeps a
transaction log (stored in the _delta_log directory) that contains detailed table metadata.
Table schema
Partitioning information
Data file paths
Transactional operations like inserts, updates, and deletes
Commit history and version control
This metadata is critical for supporting Delta Lake’s advanced capabilities such as time travel and
efficient query execution. Delta Lake does not store data summary visualizations or owner account
information directly alongside the data files.
Reference: Delta Lake Table Features - Databricks Documentation
Comments
Question 5
Which of the following is an advantage of using a Delta Lake-based data lakehouse over common
data lake solutions?
A. ACID transactions
B. Flexible schemas
C. Data deletion
D. Scalable storage
E. Open-source formats
Answer:
A
A Delta Lake-based data lakehouse is a data platform architecture that combines the scalability and
flexibility of a data lake with the reliability and performance of a data warehouse. One of the key
advantages of using a Delta Lake-based data lakehouse over common data lake solutions is that it
supports ACID transactions, which ensure data integrity and consistency. ACID transactions enable
concurrent reads and writes, schema enforcement and evolution, data versioning and rollback, and
data quality checks. These features are not available in traditional data lakes, which rely on file-based
storage systems that do not support transactions. Reference:
Delta Lake: Lakehouse, warehouse, advantages | Definition
Synapse – Data Lake vs. Delta Lake vs. Data Lakehouse
Data Lake vs. Delta Lake - A Detailed Comparison
Building a Data Lakehouse with Delta Lake Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
Comments
Question 6
Which of the following benefits of using Databricks SQL is provided by Data Explorer?
A. It can be used to run UPDATE queries to update any tables in a database.
B. It can be used to view metadata and data, as well as view/change permissions.
C. It can be used to produce dashboards that allow data exploration.
D. It can be used to make visualizations that can be shared with stakeholders.
E. It can be used to connect to third party Bl cools.
Answer:
B
Data Explorer is a user interface that allows you to discover and manage data, schemas, tables,
models, and permissions in Databricks SQL. You can use Data Explorer to view schema details,
preview sample data, and see table and model details and properties.
Administrators can view and
change owners, and admins and data object owners can grant and revoke
permissions1
. Reference:
Discover and manage data using Data Explorer
Comments
Question 7
The stakeholders.customers table has 15 columns and 3,000 rows of dat
a. The following command is run: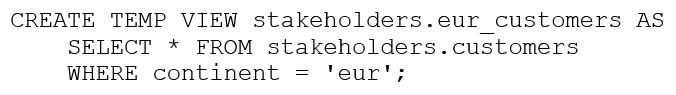
After running SELECT * FROM stakeholders.eur_customers, 15 rows are returned. After the
command executes completely, the user logs out of Databricks.
After logging back in two days later, what is the status of the stakeholders.eur_customers view?
A. The view remains available and SELECT * FROM stakeholders.eur_customers will execute correctly.
B. The view has been dropped.
C. The view is not available in the metastore, but the underlying data can be accessed with SELECT *
FROM delta. `stakeholders.eur_customers`.
D. The view remains available but attempting to SELECT from it results in an empty result set because
data in views are automatically deleted after logging out.
E. The view has been converted into a table.
Answer:
A
In Databricks, a view is a saved SQL query definition that references existing tables or other views.
Once created, a view remains persisted in the metastore (such as Unity Catalog or Hive Metastore)
until it is explicitly dropped.
Views do not store data themselves but reference data from underlying tables.
Logging out or being inactive does not delete or alter views.
Unless a user or admin explicitly drops the view or the underlying data/table is deleted, the view
continues to function as expected.
Therefore, after logging back in—even days later—a user can still run SELECT * FROM
stakeholders.eur_customers, and it will return the same data (provided the underlying table hasn’t
changed).
Reference: Views - Databricks Documentation
Comments
Question 8
A data analyst created and is the owner of the managed table my_ table. They now want to change
ownership of the table to a single other user using Data Explorer.
Which of the following approaches can the analyst use to complete the task?
A. Edit the Owner field in the table page by removing their own account
B. Edit the Owner field in the table page by selecting All Users
C. Edit the Owner field in the table page by selecting the new owner's account
D. Edit the Owner field in the table page by selecting the Admins group
E. Edit the Owner field in the table page by removing all access
Answer:
C
The Owner field in the table page shows the current owner of the table and allows the owner to
change it to another user or group. To change the ownership of the table, the owner can click on the
Owner field and select the new owner from the drop-down list.
This will transfer the ownership of
the table to the selected user or group and remove the previous owner from the list of table access
control entries1
A .
Removing the owner’s account from the Owner field will not change the ownership of the table,
but will make the table ownerless2
.
B .
Selecting All Users from the Owner field will not change the ownership of the table, but will grant
all users access to the table3
.
D .
Selecting the Admins group from the Owner field will not change the ownership of the table, but
will grant the Admins group access to the table3
.
E .
Removing all access from the Owner field will not change the ownership of the table, but will
revoke all access to the table4
. Reference:
: Change table ownership
: Ownerless tables
: Table access control
: Revoke access to a table
Comments
Question 9
A data analyst has a managed table table_name in database database_name. They would now like to
remove the table from the database and all of the data files associated with the table. The rest of the
tables in the database must continue to exist.
Which of the following commands can the analyst use to complete the task without producing an
error?
A. DROP DATABASE database_name;
B. DROP TABLE database_name.table_name;
C. DELETE TABLE database_name.table_name;
D. DELETE TABLE table_name FROM database_name;
E. DROP TABLE table_name FROM database_name;
Answer:
B
The DROP TABLE command removes a table from the metastore and deletes the associated data files.
The syntax for this command is DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] [database_name.]table_name;. The optional
IF EXISTS clause prevents an error if the table does not exist. The optional database_name. prefix
specifies the database where the table resides. If not specified, the current database is used.
Therefore, the correct command to remove the table table_name from the database database_name
and all of the data files associated with it is DROP TABLE database_name.table_name;. The other
commands are either invalid syntax or would produce undesired results. Reference:
Databricks -
DROP TABLE
Comments
Question 10
A data analyst runs the following command:
SELECT age, country
FROM my_table
WHERE age >= 75 AND country = 'canada';
Which of the following tables represents the output of the above command?
A)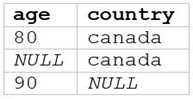
B)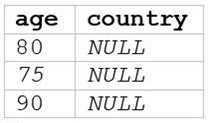
C)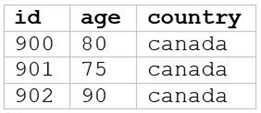
D)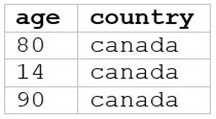
E)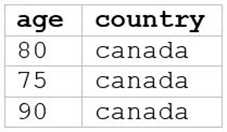
A. Option A
B. Option B
C. Option C
D. Option D
E. Option E
Answer:
E
The SQL query provided is designed to filter out records from “my_table” where the age is 75 or
above and the country is Canada. Since I can’t view the content of the links provided directly, I need
to rely on the image attached to this question for context. Based on that, Option E (the image
attached) represents a table with columns “age” and “country”, showing records where age is 75 or
above and country is Canada. Reference: The answer can be inferred from understanding SQL queries
and their outputs as per Databricks documentation:
Databricks SQL
Comments
Page 1 out of 6
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 65
page 2