Question 1
Which of the following could provide a lightweight and private connection to a remote box?
- A. Site-to-site VPN
- B. Telnet
- C. Console
- D. Secure Shell
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol used to securely access remote devices over an unsecured network. It
provides encrypted command-line access and is a lightweight and secure method of remote
administration.
A . Site-to-site VPN connects entire networks, not just a single host.
B . Telnet is not secure; it transmits data (including credentials) in plaintext.
C . Console access is direct via serial cable, not remote.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ N10-009 Official Objectives: 2.6 – Configure and troubleshoot remote access.
Comments
Question 2
A network technician is troubleshooting network latency and has determined the issue to be
occuring two network switches( Switch10 and Switch11). Symptoms reported included poor video
performance and slow file copying. Given the following informtion:
Which of the following should the technician most likely do to resolve the issue?
- A. Disable automatic negotiation on Switch11.
- B. Modify Switch10 MTU value to 1500.
- C. Configure STP on both switches.
- D. Change the native VLAN on the ports.
Answer:
B
Comments
Question 3
Which of the following network devices converts wireless signals to electronic signals?
- A. Router
- B. Firewall
- C. Access point
- D. Load balancer
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Role of an Access Point (AP):
Wireless to Wired Conversion: An access point (AP) is a device that allows wireless devices to
connect to a wired network using Wi-Fi. It converts wireless signals (radio waves) into electronic
signals that can be understood by wired network devices.
Functionality:
Signal Conversion: The AP receives wireless signals from devices such as laptops, smartphones, and
tablets, converts them into electronic signals, and transmits them over the wired network.
Connectivity: APs provide a bridge between wireless and wired segments of the network, enabling
seamless communication.
Comparison with Other Devices:
Router: Directs traffic between different networks and may include built-in AP functionality but is not
primarily responsible for converting wireless to electronic signals.
Firewall: Protects the network by controlling incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules,
not involved in signal conversion.
Load Balancer: Distributes network or application traffic across multiple servers to ensure reliability
and performance, not involved in signal conversion.
Deployment:
APs are commonly used in environments where wireless connectivity is needed, such as offices,
homes, and public spaces. They enhance mobility and provide flexible network access.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ study materials on wireless networking and access points.
Comments
Question 4
Which of the following disaster recovery metrics is used to describe the amount of data that is lost
since the last backup?
- A. MTTR
- B. RTO
- C. RPO
- D. MTBF
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Definition of RPO:
Recovery Point Objective (RPO) is a disaster recovery metric that describes the maximum acceptable
amount of data loss measured in time. It indicates the point in time to which data must be recovered
to resume normal operations after a disaster.
For example, if the RPO is set to 24 hours, then the business could tolerate losing up to 24 hours'
worth of data in the event of a disruption.
Why RPO is Important:
RPO is critical for determining backup frequency and helps businesses decide how often they need to
back up their data. A lower RPO means more frequent backups and less potential data loss.
Comparison with Other Metrics:
MTTR (Mean Time to Repair): Refers to the average time required to repair a system or component
and return it to normal operation.
RTO (Recovery Time Objective): The maximum acceptable length of time that a computer, system,
network, or application can be down after a failure or disaster occurs.
MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures): The predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a
system during operation.
How RPO is Used in Disaster Recovery:
Organizations establish RPOs to ensure that they can recover data within a timeframe that is
acceptable to business operations. This involves creating a backup plan that meets the RPO
requirements.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ study materials and certification guides.
Comments
Question 5
Which of the following fiber connector types is the most likely to be used on a network interface
card?
- A. LC
- B. SC
- C. ST
- D. MPO
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Definition of Fiber Connector Types:
LC (Lucent Connector): A small form-factor fiber optic connector with a push-pull latching
mechanism, commonly used for high-density applications.
SC (Subscriber Connector or Standard Connector): A larger form-factor connector with a push-pull
latching mechanism, often used in datacom and telecom applications.
ST (Straight Tip): A bayonet-style connector, typically used in multimode fiber optic networks.
MPO (Multi-fiber Push On): A connector designed to support multiple fibers (typically 12 or 24
fibers), used in high-density cabling environments.
Common Usage:
LC Connectors: Due to their small size, LC connectors are widely used in network interface cards
(NICs) and high-density environments such as data centers. They allow for more connections in a
smaller space compared to SC and ST connectors.
SC and ST Connectors: These are larger and more commonly used in patch panels and older fiber
installations but are less suitable for high-density applications.
MPO Connectors: Primarily used for trunk cables in data centers and high-density applications but
not typically on individual network interface cards.
Selection Criteria:
The small form-factor and high-density capabilities of LC connectors make them the preferred choice
for network interface cards, where space and connection density are critical considerations.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ study materials on fiber optics and connector types.
Comments
Question 6
A network administrator wants to implement security zones in the corporate network to control
access to only individuals inside of the corporation. Which of the following security zones is the best
solution?
- A. Extranet
- B. Trusted
- C. VPN
- D. Public
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Introduction to Security Zones:
Security zones are logical segments within a network designed to enforce security policies and
control access. They help in segregating and securing different parts of the network.
Types of Security Zones:
Trusted Zone: This is the most secure zone, typically used for internal corporate networks where only
trusted users have access.
Extranet: This zone allows controlled access to external partners, vendors, or customers.
VPN (Virtual Private Network): While VPNs are used to create secure connections over the internet,
they are not a security zone themselves.
Public Zone: This zone is the least secure and is typically used for public-facing services accessible by
anyone.
Trusted Zone Implementation:
The trusted zone is configured to include internal corporate users and resources. Access controls,
firewalls, and other security measures ensure that only authorized personnel can access this zone.
Internal network segments, such as the finance department, HR, and other critical functions, are
usually placed in the trusted zone.
Example Configuration:
Firewall Rules: Set up rules to allow traffic only from internal IP addresses.
Access Control Lists (ACLs): Implement ACLs on routers and switches to restrict access based on IP
addresses and other criteria.
Segmentation: Use VLANs and subnetting to segment and isolate the trusted zone from other zones.
Explanation of the Options:
A . Extranet: Suitable for external partners, not for internal-only access.
B . Trusted: The correct answer, as it provides controlled access to internal corporate users.
C . VPN: A method for secure remote access, not a security zone itself.
D . Public: Suitable for public access, not for internal corporate users.
Conclusion:
Implementing a trusted zone is the best solution for controlling access within a corporate network. It
ensures that only trusted internal users can access sensitive resources, enhancing network security.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ guide detailing security zones and their implementation in a corporate network
(see page Ref 9†Basic Configuration Commands).
Comments
Question 7
Which of the following attacks can cause users who are attempting to access a company website to
be directed to an entirely different website?
- A. DNS poisoning
- B. Denial-of-service
- C. Social engineering
- D. ARP spoofing
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Network segmentation involves dividing a network into smaller segments or subnets. This is
particularly important when integrating OT (Operational Technology) devices to ensure that these
devices are isolated from other parts of the network. Segmentation helps protect the OT devices
from potential threats and minimizes the impact of any security incidents. It also helps manage
traffic and improves overall network performance.Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials.
Comments
Question 8
A network administrator is troubleshooting issues with a DHCP server at a university. More students
have recently arrived on campus, and the users are unable to obtain an IP address. Which of the
following should the administrator do to address the issue?
- A. Enable IP helper.
- B. Change the subnet mask.
- C. Increase the scope size.
- D. Add address exclusions.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The issue is that more students have arrived on campus, meaning the available IP addresses are
exhausted. To fix this, the administrator should increase the DHCP scope size to allow more devices
to obtain IP addresses.
Breakdown of Options:
A . Enable IP helper – IP helper is used to forward DHCP requests across different subnets. However,
the problem here is that the DHCP scope is full, not that requests are not reaching the server.
B . Change the subnet mask – The subnet mask determines the number of available hosts, but
changing it without increasing the IP pool does not help.
C . Increase the scope size – Correct answer. Expanding the DHCP scope provides more IP addresses
for assignment.
D . Add address exclusions – Exclusions reserve IP addresses, which would further reduce available
addresses instead of solving the issue.
Reference:
CompTIA Network+ (N10-009) Official Study Guide – Domain 2.4: Compare and contrast IP
addressing schemes.
RFC 2131: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Comments
Question 9
SIMULATION
A network technician needs to resolve some issues with a customer's SOHO network.
The customer reports that some of the devices are not connecting to the network, while others
appear to work as intended.
INSTRUCTIONS
Troubleshoot all the network components and review the cable test results by Clicking on each
device and cable.
Diagnose the appropriate component(s) by identifying any components with a problem and
recommend a solution to correct each problem.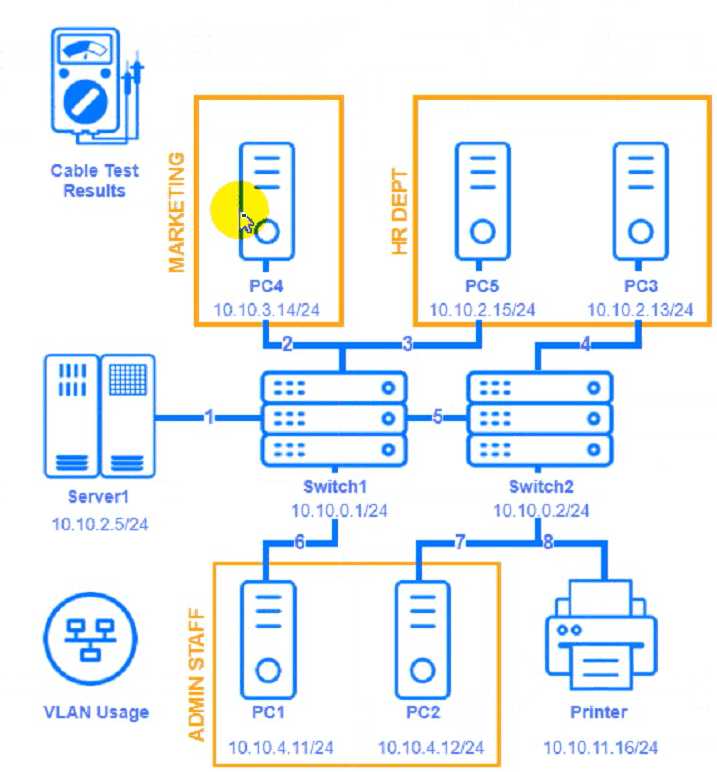

Cable Test Results:
Cable 1: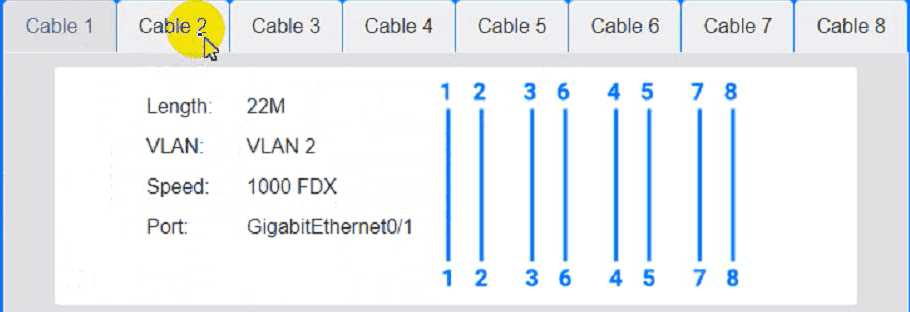
Cable 2:
Cable 3: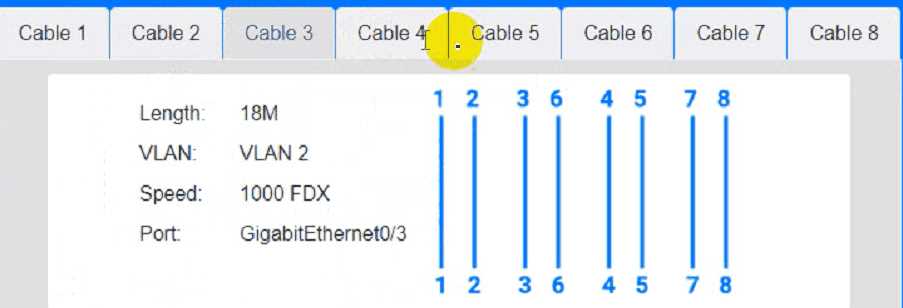
Cable 4: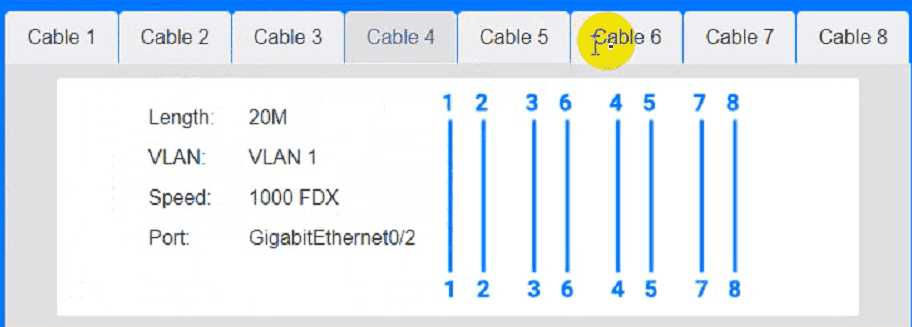
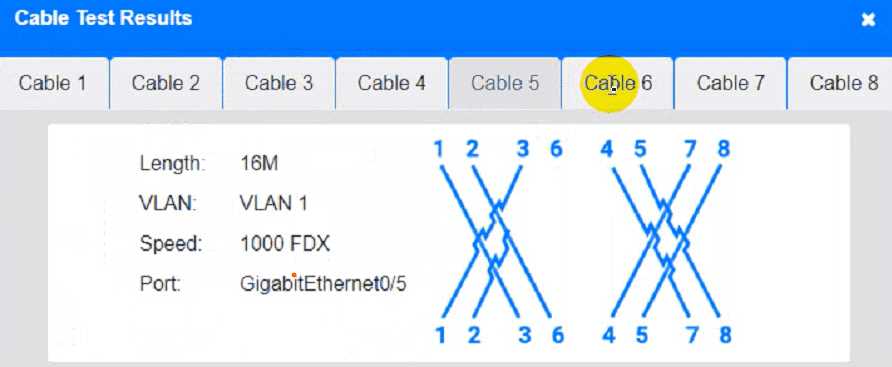
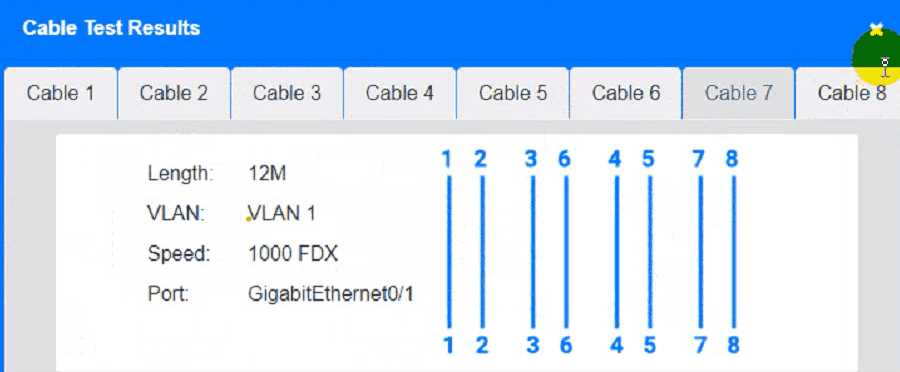
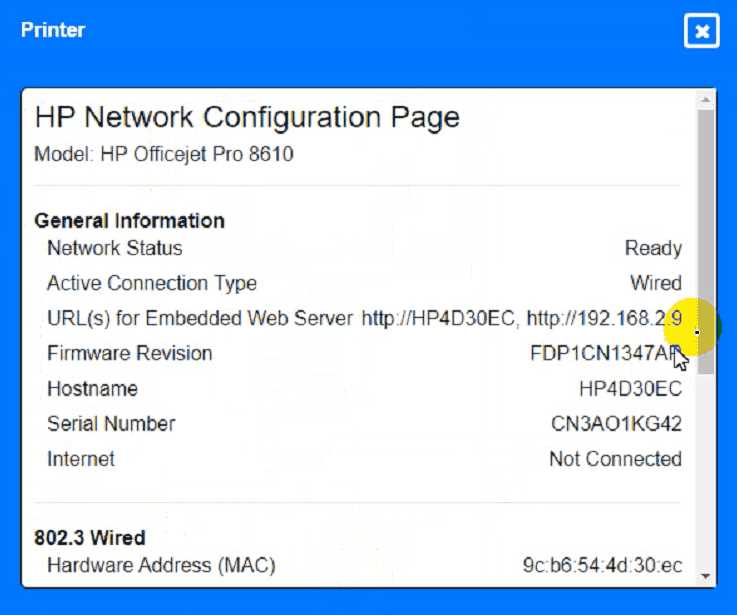
Answer:
See the
Explanation for
detailed information
on this simulation.
Explanation:
(Note: Ips will be change on each simulation task, so we have given example answer for the
understanding)
To troubleshoot all the network components and review the cable test results, you can use the
following steps:
Click on each device and cable to open its information window.
Review the information and identify any problems or errors that may affect the network connectivity
or performance.
Diagnose the appropriate component(s) by identifying any components with a problem and
recommend a solution to correct each problem.
Fill in the remediation form using the drop-down menus provided.
Here is an example of how to fill in the remediation form for PC1:
The component with a problem isPC1.
The problem isIncorrect IP address.
The solution isChange the IP address to 192.168.1.10.
You can use the same steps to fill in the remediation form for other components.
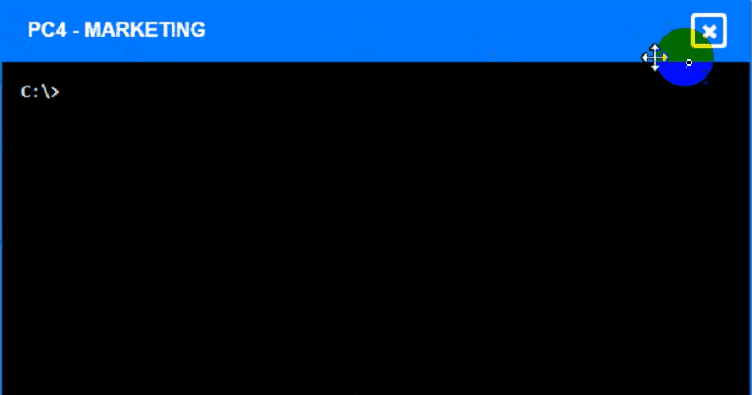
To enter commands in each device, you can use the following steps:
Click on the device to open its terminal window.
Enter the commandipconfig /allto display the IP configuration of the device, including its IP address,
subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS servers.
Enter the commandping <IP address>to test the connectivity and reachability to another device on
the network by sending and receiving echo packets. Replace <IP address> with the IP address of the
destination device, such as 192.168.1.1 for Core Switch 1.
Enter the commandtracert <IP address>to trace the route and measure the latency of packets from
the device to another device on the network by sending and receiving packets with increasing TTL
values. Replace <IP address> with the IP address of the destination device, such as 192.168.1.1 for
Core Switch 1.
Here is an example of how to enter commands in PC1:
Click on PC1 to open its terminal window.
Enter the commandipconfig /allto display the IP configuration of PC1. You should see that PC1 has
an incorrect IP address of 192.168.2.10, which belongs to VLAN 2 instead of VLAN 1.
Enter the commandping 192.168.1.1to test the connectivity to Core Switch 1. You should see that
PC1 is unable to ping Core Switch 1 because they are on different subnets.
Enter the commandtracert 192.168.1.1to trace the route to Core Switch 1. You should see that PC1
is unable to reach Core Switch 1 because there is no route between them.
You can use the same steps to enter commands in other devices, such as PC3, PC4, PC5, and Server
1.
Comments
Question 10
A network administrator is connecting two Layer 2 switches in a network. These switches must
transfer data in multiple networks. Which of the following would fulfill this requirement?
- A. Jumbo frames
- B. 802.1Q tagging
- C. Native VLAN
- D. Link aggregation
Answer:
B
Explanation:
802.1Q tagging, also known as VLAN tagging, is used to identify VLANs on a trunk link between
switches. This allows the switches to transfer data for multiple VLANs (or networks) over a single
physical connection. This method ensures that traffic from different VLANs is properly separated and
managed across the network.Reference: CompTIA Network+ study materials.
Comments
Page 1 out of 42
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 422
page 2