Question 1
A network engineer is establishing a wireless network for handheld inventory scanners in a
manufacturing company's warehouse. The engineer needs an authentication mechanism for these
scanners that uses the Wi-Fi network and works with the company's Active Directory. The business
requires that the solution authenticate the users and authorize the scanners. Which of the following
provides the best solution for authentication and authorization?
- A. TACACS+
- B. RADIUS
- C. LDAP
- D. PKI
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Using a RADIUS server with 802.1X on the Wi-Fi infrastructure allows the scanners (and their users)
to be authenticated against Active Directory and mapped to the correct authorization policies.
TACACS+ is geared toward device management, LDAP alone doesn’t handle the Wi-Fi 802.1X
handshake, and PKI by itself wouldn’t provide the user-to-device authorization flow needed. RADIUS
gives you both authentication and authorization tied into AD.
Comments
Question 2
A company is migrating an application to the cloud for modernization. The engineer needs to provide
dependencies between application and database tiers in the environment. Which of the following
should the engineer reference in order to best meet this requirement?
- A. Internal knowledge base article
- B. CMDB
- C. WBS
- D. Diagram of physical server locations
- E. SOW
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A Configuration Management Database (CMDB) explicitly maps and documents the relationships and
dependencies among configuration items, such as your application and database tiers, making it the
ideal reference when migrating to the cloud.
Comments
Question 3
A network administrator recently deployed new Wi-Fi 6E access points in an office and enabled 6GHz
coverage. Users report that when they are connected to the new 6GHz SSID, the performance is
worse than the 5GHz SSID. The network administrator suspects that there is a source of 6GHz
interference in the office. Using the troubleshooting methodology, which of the following actions
should the network administrator do next?
- A. Test to see if the changes have improved network performance.
- B. Use a spectrum analyzer and check the 6GHz spectrum.
- C. Document the list of channels that are experiencing interference.
- D. Change the channels being used by the 6GHz radios in the APs.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Before making configuration changes, you should verify and pinpoint the suspected interference
source by analyzing the 6 GHz band. A spectrum analyzer will reveal any non-Wi-Fi transmissions or
overlapping noise that’s degrading performance, allowing you to target your remediation effectively.
Comments
Question 4
A SaaS company is launching a new product based in a cloud environment. The new product will be
provided as an API and should not be exposed to the internet. Which of the following should the
company create to best meet this requirement?
- A. A transit gateway that connects the API to the customer's VPC
- B. Firewall rules allowing access to the API endpoint from the customer's VPC
- C. A VPC peering connection from the API VPC to the customer's VPC
- D. A private service endpoint exposing the API endpoint to the customer's VPC
Answer:
D
Explanation:
AWS PrivateLink (a private service endpoint) lets you expose your API over an interface endpoint
directly into each customer’s VPC without ever traversing the public internet, ensuring the service
remains fully private.
Comments
Question 5
A network administrator is configuring firewall rules to lock down the network from outside attacks.
Which of the following should the administrator configure to create the most strict set of rules?
- A. URL filtering
- B. File blocking
- C. Network security group
- D. Allow List
Answer:
D
Explanation:
By explicitly permitting only known, approved traffic and blocking everything else by default, an
allow-list policy enforces the strictest firewall posture.
Comments
Question 6
A network engineer is installing new switches in the data center to replace existing infrastructure.
The previous network hardware had administrative interfaces that were plugged into the existing
network along with all other server hardware on the same subnet. Which of the following should the
engineer do to better secure these administrative interfaces?
- A. Connect the switch management ports to a separate physical network.
- B. Disable unused physical ports on the switches to keep unauthorized users out.
- C. Set the administrative interfaces and the network switch ports on the same VLAN.
- D. Upgrade all of the switch firmware to the latest hardware levels.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
Segregating management interfaces onto their own dedicated network ensures that administrative
access is isolated from general user and server traffic, greatly reducing the attack surface and
preventing lateral movement if the production network is compromised.
Comments
Question 7
A network administrator receives a ticket from one of the company's offices about video calls that
work normally for one minute and then get very choppy. The network administrator pings the video
server from that site to ensure that it is reachable: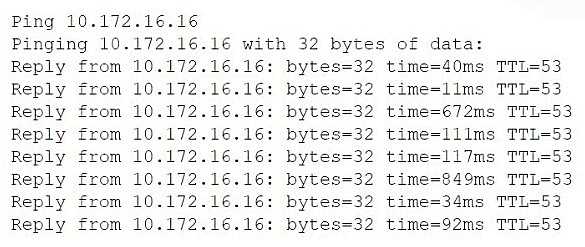
Which of the following is most likely the cause of the video call issue?
- A. Throughput
- B. Jitter
- C. Latency
- D. Loss
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The wildly varying ping response times (from 11 ms up to 849 ms) indicate high packet-delay
variation, which causes the video stream to become choppy after a short period. That fluctuation in
latency is known as jitter.
Comments
Question 8
A network architect is designing a solution to place network core equipment in a rack inside a data
center. This equipment is crucial to the enterprise and must be as secure as possible to minimize the
chance that anyone could connect directly to the network core. The current security setup is:
In a locked building that requires sign in with a guard and identification check.
In a locked data center accessible by a proximity badge and fingerprint scanner.
In a locked cabinet that requires the security guard to call the Chief Information Security Officer
(CISO) to get permission to provide the key.
Which of the following additional measures should the architect recommend to make this equipment
more secure?
- A. Make all engineers with access to the data center sign a statement of work.
- B. Set up a video surveillance system that has cameras focused on the cabinet.
- C. Have the CISO accompany any network engineer that needs to do work in this cabinet.
- D. Require anyone entering the data center for any reason to undergo a background check.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Recording and monitoring all activity at the cabinet greatly strengthens security by providing a real-
time deterrent, an audit trail of who accessed it and when, and forensic evidence if an incident ever
occurs.
Comments
Question 9
An organization has centralized logging capability at the on-premises data center and wants a
solution that can consolidate logging from deployed cloud workloads. The organization would like to
automate the detection and alerting mechanism. Which of the following best meets the
requirements?
- A. IDS/IPS
- B. SIEM
- C. Data lake
- D. Syslog
Answer:
B
Explanation:
A Security Information and Event Management system ingests and normalizes logs from on-premises
and cloud sources, applies automated correlation rules for detection, and issues alerts, exactly
matching the need for centralized logging, analysis, and automated notification.
Comments
Question 10
Security policy states that all inbound traffic to the environment needs to be restricted, but all
external outbound traffic is allowed within the hybrid cloud environment. A new application server
was recently set up in the cloud. Which of the following would most likely need to be configured so
that the server has the appropriate access set up? (Choose two.)
- A. Application gateway
- B. IPS
- C. Port security
- D. Firewall
- E. Network security group
- F. Screened subnet
Answer:
D, E
Explanation:
A perimeter firewall enforces the organization’s “deny inbound by default, allow all outbound” policy
at the edge of the cloud environment, while an Azure-style NSG applies the same rule set at the
VM/subnet level. Together they ensure no inbound connections slip through and that outbound
traffic remains unrestricted.
Comments
Page 1 out of 8
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 84
page 2