Question 1
[Cisco Equipment and Related Hardware]
When should a crossover UTP cable be used instead of a straight-through cable when connecting
network devices?
- A. To connect electrically like devices
- B. To connect a PC to a wireless access point
- C. To connect a switch to a router
- D. To connect electrically unlike devices
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A crossover UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cable is used to connect two similar devices directly. This
includes:
Switch to switch
Router to router
PC to PC
The crossover cable reverses the transmit and receive pairs, allowing for proper communication
between like devices without the need for an intermediary device.
Conversely, a straight-through cable is used to connect dissimilar devices, such as:
PC to switch
Router to switch
PC to router
This cable maintains the same wiring on both ends, suitable for connecting different types of devices.
Therefore, when connecting electrically like devices, a crossover cable is appropriate.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Cisco Equipment and Related
Hardware
===========
Comments
Question 2
[Cisco IOS Software Basics]
How many bits are borrowed from the default host portion of the address to create subnets in a Class
B network with a subnet mask 255.255.255.0?
- B. 5 bits
- C. 3 bits
- D. 8 bits
Answer:
D
Explanation:
In a Class B network, the default subnet mask is 255.255.0.0, which allocates:
16 bits for the network portion
16 bits for the host portion
When the subnet mask is changed to 255.255.255.0, it becomes:
24 bits for the network portion
8 bits for the host portion
This indicates that 8 bits have been borrowed from the host portion to create additional subnets.
Borrowing bits allows for the division of the original network into smaller sub-networks, enhancing
organization and security within the network.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Cisco IOS Software Basics
Comments
Question 3
[Cisco Equipment and Related Hardware]
What is the function of an access layer device?
- A. Provides high-speed data transport between buildings or different parts of the campus
- B. Serves as the entry point for end-user devices to connect to the network
- C. Provides secure external access to internal network components
- D. Connects remote offices to the main corporate network
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In the hierarchical network design model, the access layer is the first layer and serves as the entry
point for end-user devices to connect to the network. This layer connects user devices such as PCs, IP
phones, wireless access points, printers, and scanners to the network. It facilitates the initial
connection between end-user devices and the network infrastructure. The access layer also enforces
security policies and provides services such as VLAN membership, port security, and Quality of
Service (QoS).
Options A, C, and D refer to functions typically associated with the core or distribution layers, or with
WAN connectivity, rather than the access layer.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Cisco Equipment and Related
Hardware
===========
Comments
Question 4
[Wireless Device Support]
Which term describes the physical range of radio frequency coverage provided by an access point in
a wireless topology?
- A. Service Set Identifier (SSID)
- B. Basic Service Area (BSA)
- C. Wireless LAN (WLAN)
- D. Wireless LAN Controller (WLC)
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In wireless networking, the Basic Service Area (BSA) refers to the physical area of radio frequency
coverage provided by an access point (AP) in a Basic Service Set (BSS). The BSA defines the coverage
area where wireless clients can connect to the network through the AP. The size and shape of a BSA
depend on various factors, including the AP's transmit power, antenna type, and physical
environment.
Option A, the Service Set Identifier (SSID), is the network name broadcast by the AP. Option C,
Wireless LAN (WLAN), refers to the overall wireless network. Option D, Wireless LAN Controller
(WLC), is a device that manages multiple APs in a network.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Wireless Device Support
===========
Comments
Question 5
[Device Configuration and Verification]
Which two configuration parameters are most critical to ensure optimal performance when
configuring a network port for a newly installed IP phone in an enterprise environment? (Choose
two.)
- A. VLAN assignment
- B. Link aggregation
- C. Spanning Tree Protocol
- D. Power over Ethernet
- E. QoS classification
Answer:
A, D
Explanation:
When configuring a network port for a newly installed IP phone, two critical parameters to ensure
optimal performance are:
VLAN Assignment: Assigning the correct VLANs is essential for segregating voice and data traffic.
Typically, a separate voice VLAN is configured to prioritize voice traffic and enhance security.
Power over Ethernet (PoE): PoE allows the switch to supply power to the IP phone over the same
Ethernet cable used for data transmission. This eliminates the need for separate power supplies and
simplifies installation.
While QoS classification (Option E) is important for prioritizing voice traffic, it is typically configured
at a broader network level. Link aggregation (Option B) and Spanning Tree Protocol (Option C) are
more relevant to network redundancy and loop prevention, respectively, and are not directly critical
for the initial configuration of an IP phone port.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Device Configuration and
Verification
===
Comments
Question 6
Which deployment scenarios are Cisco 8000 Series routers primarily designed for?
- A. remote branch offices and retail locations
- B. service provider and web-scale networks
- C. small business and home office networks
- D. campus LAN access and distribution layers
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Cisco 8000 Series routers are primarily designed for service provider and web-scale networks,
offering high-performance routing capabilities to handle large-scale, high-bandwidth environments
typically found in service provider infrastructures and data centers.
Comments
Question 7
DRAG DROP
[Cisco IOS Software Basics]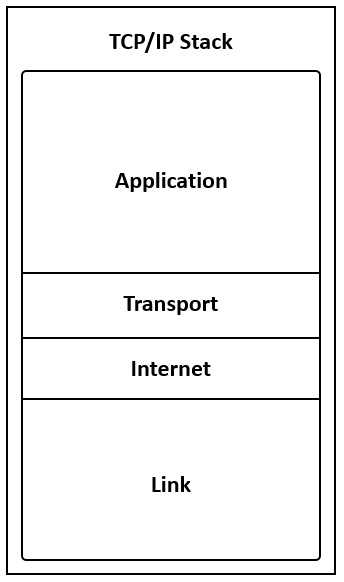
Refer to the exhibit. Drag and drop the steps in the TCP/IP encapsulation process from the left onto
the corresponding layer on the right.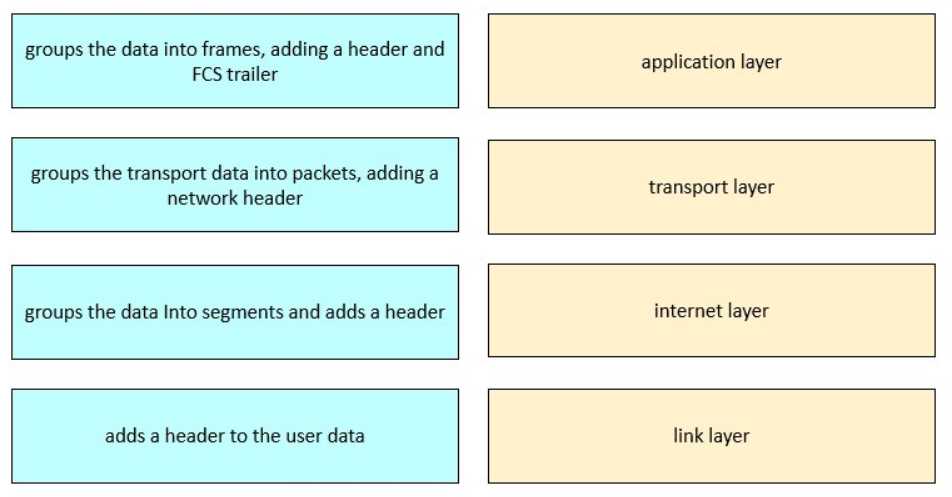
Answer:
None
Explanation:
The FLDTEC training describes the TCP/IP encapsulation as a step-by-step process where data is
passed down through the layers of the TCP/IP model:
Application Layer: User data is created (email, file, request) and the application layer adds the
application header, creating a data payload.
Transport Layer: The data is segmented. Each segment receives a transport-layer header (TCP/UDP),
enabling proper sequencing and error handling at the destination.
Internet Layer: Segments are encapsulated into packets (IP datagrams), with an IP header added to
facilitate routing between networks.
Link Layer: Finally, packets are framed with Layer 2 headers and trailers (including the Frame Check
Sequence for error detection), creating a frame ready to be transmitted on the physical medium.
This layered encapsulation ensures interoperability and troubleshooting clarity, which is why it is
emphasized in FLDTEC’s IOS Software Basics module.
Comments
Question 8
[Cisco Equipment and Related Hardware]
Which Cisco switch series is designed to handle the combined responsibilities of core and
distribution layers in a converged architecture?
- A. Meraki MS400 Series
- B. Catalyst 6500 E-Series
- C. Catalyst 1300 Series
- D. Catalyst 9000 Series
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Cisco Catalyst 9000 Series is engineered to address the evolving needs of modern enterprise
networks by integrating the functionalities of both the core and distribution layers into a unified,
converged architecture. This series offers advanced capabilities such as high-speed data forwarding,
enhanced security features, and support for automation and programmability, making it suitable for
scalable and efficient network designs.
The Catalyst 9000 Series includes models like the Catalyst 9500 and 9600, which are optimized for
core and distribution roles, providing high throughput and reliability. These switches support
advanced features like Software-Defined Access (SD-Access) and are designed to meet the demands
of cloud-scale and security-focused environments.
Wikipedia+2Cisco+2Cisco+2
In contrast, the Meraki MS400 Series (Option A) is tailored for cloud-managed aggregation and lacks
the comprehensive feature set required for core functionalities. The Catalyst 6500 E-Series (Option
B), while historically significant, is considered a legacy platform and may not support the latest
advancements in network convergence. The Catalyst 1300 Series (Option C) is designed for small to
medium-sized businesses and is not intended for core or distribution layer deployments.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Cisco Equipment and Related
Hardware
Comments
Question 9
DRAG DROP
[Device Configuration and Verification]
Drag and drop the configuration tasks for restoring software from the left onto the corresponding
commands on the right.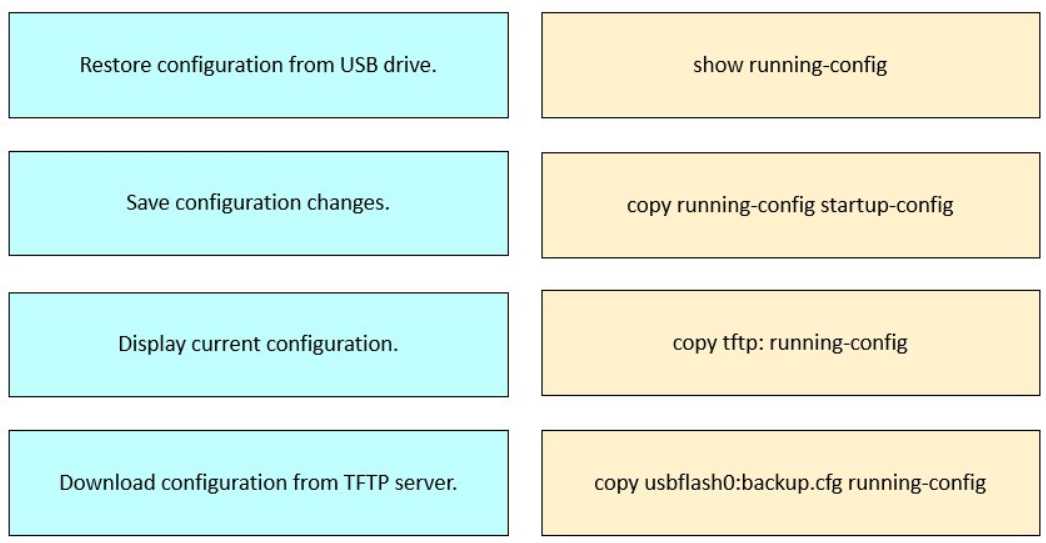
Answer:
None
Explanation: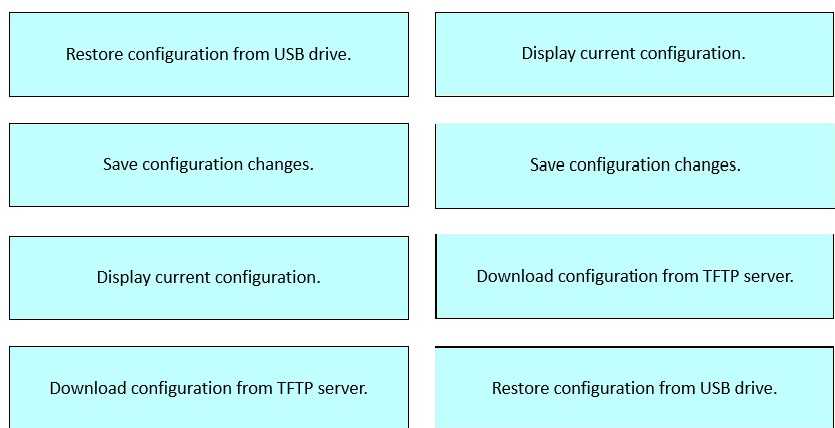
These command associations are part of Cisco IOS essentials taught in FLDTEC's "Device
Configuration and Verification" topic. Here's how each command functions:
show running-config
Displays the active configuration stored in RAM.
This command is used to verify the current settings on a Cisco device.
copy running-config startup-config
Saves the current running configuration to NVRAM, ensuring the configuration persists after a
reboot.
This is critical after making changes to device settings.
copy tftp: running-config
Loads a configuration from a TFTP server and applies it to the current running configuration.
Often used during remote device setup or restoration.
copy usbflash0:backup.cfg running-config
Restores a saved configuration file from a USB drive.
Useful in field operations where physical backup media is used during maintenance.
These tasks are routine for field technicians performing configuration backups, restorations, and
diagnostics in Cisco environments.
Comments
Question 10
[Maintenance and RMA Procedures]
Which command is used to download a copied configuration file from a TFTP server to merge it with
the running configuration of a replacement Cisco device?
- A. load tftp: running-config
- B. copy tftp: startup-config
- C. copy tftp: running-config
- D. merge tftp: running-config
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The command copy tftp: running-config is used to retrieve a configuration file from a TFTP server and
merge it with the current running configuration of a Cisco device. This operation is additive, meaning
it integrates the new configuration commands into the existing running configuration without
removing any pre-existing commands unless explicitly overridden.
This method is particularly useful when restoring configurations to a replacement device, as it allows
for the seamless integration of necessary settings without disrupting the current operational state.
In contrast, using copy tftp: startup-config would overwrite the startup configuration file, which could
lead to unintended consequences upon the next device reload. The options load tftp: running-config
and merge tftp: running-config are not valid Cisco IOS commands.
Reference: Supporting Cisco Devices for Field Technicians (FLDTEC) – Maintenance and RMA
Procedures
Cisco
===========
Comments
Page 1 out of 9
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 99
page 2