Question 1
Where can an Appian Developer connect with and share their expertise with other Appian
Developers?
- A. Appian Learning Paths via Appian Academy
- B. Appian Knowledge Base
- C. Appian Community discussions
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Appian Community discussions provide a platform for Appian Developers to connect with, share
expertise, and learn from each other. The community is a vibrant space where developers can ask
questions, share solutions, and discuss best practices related to Appian development. While Appian
Learning Paths via Appian Academy and Appian Knowledge Base are valuable resources for learning
and troubleshooting, the Community discussions specifically facilitate peer-to-peer interaction and
knowledge sharing among developers.
Reference: Appian Community Website
Comments
Question 2
You created and published a new process model.
The process model has a start form with two synchronous subprocesses with 40 and 66 nodes each.
All nodes are chained from the start node through the subprocesses to the end node. After the tasks
and subprocesses, there is a second User Input Task in which the user can confirm the entries and
add a comment.
When testing as a normal Acme business user, you see that the confirmation screen is not shown to
you.
What might be the reason for this behavior?
- A. The maximum number of activity chained nodes is exceeded and breaks.
- B. The second User Input Task is assigned to the process initiator.
- C. The second User Input Task is assigned to the Acme business user group.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
In Appian, there is a limitation on the number of activities that can be chained in a process, known as
the "chaining limit." If a process model exceeds this limit, which includes synchronous subprocesses
and their nodes, the process may break or not behave as expected. In this scenario, with two large
subprocesses chained from start to end, the maximum number of activity chained nodes could be
exceeded, resulting in the confirmation screen not being shown. Adjusting the process model to
reduce chaining or using asynchronous patterns where possible can help mitigate this issue.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Process Model Best Practices
Comments
Question 3
Your customer wants to change the name of a field of an existing Custom Data Type (CDT) to match a
renamed database field.
The CDT is backed by a database entity, whose data store has the Automatically Update Database
Schema option disabled. The old column name was BIRTHDATE and the new column name is
DATE_OF_BIRTH.
How should you proceed?
- A. Download the CDT as XSD, make the appropriate changes, and re-upload the XSD. Verify and publish the data store.
- B. Rename the field in the record type in Appian to automatically update the CDT field.
- C. Rename the field in the CDT in Appian. Verify and publish the data store.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
When a field name in an existing Custom Data Type (CDT) needs to be changed to match a renamed
database field, and the Automatically Update Database Schema option is disabled, the correct
approach is to rename the field in the CDT within Appian. After renaming the field in the CDT to
match the new database column name (from BIRTHDATE to DATE_OF_BIRTH in this case), you should
verify the changes and publish the data store to reflect the updates. This approach ensures that the
Appian data model remains in sync with the underlying database schema.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Data Types and Data Stores
Comments
Question 4
Which step can be critical in passing information from a form back to a process model?
- A. Configure the Data Management tab.
- B. Configure the activity class parameters of a Write to Data Store Entity node, a
- C. Configure inputs on the Data tab of a User Input Task.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The critical step in passing information from a form back to a process model is to configure inputs on
the Data tab of a User Input Task. When you create a User Input Task, it includes a form for users to
interact with. The data entered into this form can be mapped to process variables via the Data tab
configuration. This ensures that the information collected in the form is available to the process for
further use.
Reference: Appian Documentation - User Input Tasks
Comments
Question 5
Review the following expression rule:
ri!name is defined as "Maria".
ri!directory is defined as the following:
What is the expected output?
- A. Maria
- B. 0
- C. 1
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Given that ri!name is defined as "Maria" and ri!directory contains two a!map() structures, one of
which includes the name "Maria," the expression wherecontains(ri!name, index(ri!directory,
"name")) will evaluate as follows: The index() function will return a list of values from ri!directory for
the key "name," which will be {"Maria", "Steven"}. The wherecontains() function will then check
where "Maria" is found within this list. Since "Maria" is the first element, the function will return a
list of indices where "Maria" is found, in this case, {1}. Appian lists are 1-indexed, so the first position
is represented by 1, not 0.
Reference: Appian Expression Language Documentation - Functions
Comments
Question 6
HOTSPOT
Match each scenario to the correct relationship type in your data model design.
Note: Each relationship type will be used once. To change your responses, you may deselect your
response by clicking the blank space at the top of the selection list.
Answer:
None
Explanation:
"You have a product with basic fields and an additional detailed product description with all the
technical details that is regularly updated." - One-to-many
"You have many employees on multiple projects." - Many-to-many
"You have an order with order items." - One-to-many
A one-to-many relationship is used when a single record from one table (product) is associated with
multiple records in another table (product descriptions).
A many-to-many relationship exists when multiple records from one table (employees) are
associated with multiple records from another table (projects).
An order with order items also represents a one-to-many relationship where one order can have
multiple order items.
Reference:
Appian Documentation: Data Modeling in Appian
Comments
Question 7
You are configuring a Related Action for an entity-backed record type.
What is the proper domain prefix to reference the record data that will be passed into the Process
Model as context for the Record Action?
- A. ac!
- B. pv!
- C. rv!
Answer:
B
Explanation:
When configuring a Related Action for an entity-backed record type, the proper domain prefix to
reference the record data passed into the Process Model as context for the Record Action is pv!. This
prefix stands for process variables, which are used to pass data into and out of a process model. In
the context of a Related Action, pv! would be used to reference the specific process variables that are
configured to receive the record data.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Process Variables and Record Types
Comments
Question 8
HOTSPOT
Match each Appian Design Object name to the most applicable use case.
Note: Each use case will be used once or not at all. To change your responses, you may deselect your
response by clicking the blank space at the top of the selection list.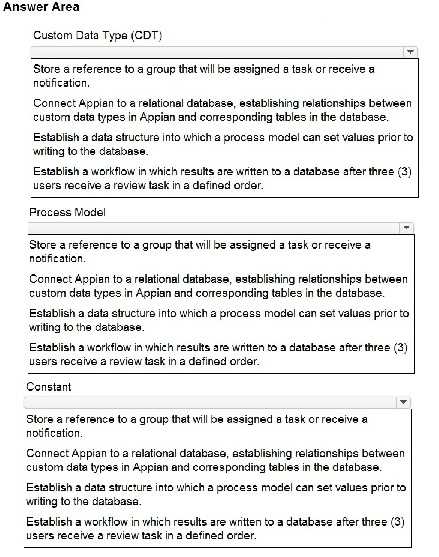
Answer:
None
Explanation:
Custom Data Type (CDT): Connect Appian to a relational database, establishing relationships
between custom data types in Appian and corresponding tables in the database.
Process Model: Establish a data structure into which a process model can set values prior to writing
to the database.
Constant: Store a reference to a group that will be assigned a task or receive a notification.
Custom Data Types (CDTs) define the structure of data within Appian and can be mapped to existing
database tables to leverage relational database functionalities. They establish how data is structured
and stored in the Appian application.
Process Models depict the workflow and logic of a business process. They can include user and
automated tasks, and they can manipulate and store data before, during, and after the execution of
the process.
Constants are reusable static values that can be referenced within Appian. They can store values like
group references, which can then be used for task assignment or notification purposes in process
models or other expressions.
Reference:
Appian Documentation: Data Types, Process Models, Constants
Comments
Question 9
You are configuring an employee onboarding User Input Task that will be assigned to the human
resources group.
Based on the default behavior for task assignments, which statement is valid?
- A. Multiple users can accept the task at the same time up until the point that the first user completes it.
- B. For each user in the group, a task is generated and assigned to them to complete.
- C. One user in the group can accept the task for themselves and complete it.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Based on the default behavior for task assignments in Appian, when a User Input Task is assigned to a
group, any one member of the group can accept the
task. Once accepted, the task becomes locked to that user, and they are responsible for completing
it. This prevents multiple users from working on the same task simultaneously and ensures clear
accountability.
Reference: Appian Documentation - Task Assignments and User Input Tasks
Comments
Question 10
You are using a local variable in an expression rule to describe the height of an applicant.
Which statement correctly describes the application of Appian best practices for naming your local
variable?
- A. local!hoaa - This employs the naming convention of abbreviating "Height of an applicant" to minimize both the typing required by developers and the length of code Appian is required to parse.
- B. local!applicantHeight - This employs the naming convention of specifically describing the value contained by the variable.
- C. local!x - This employs the naming convention of using algebraic variables for a value that may either change over time or be used by future developers for other purposes.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The best practice for naming variables in Appian is to use clear and descriptive names that convey
the purpose or content of the variable. Therefore, local!applicantHeight is the best option as it
precisely describes the value contained by the variable, which is the height of an applicant. This
naming convention aids in readability and maintainability of the code, making it easier for
developers to understand and modify the code in the future.
Reference: Appian Best Practices - Expression Writing and Naming Conventions
Comments
Page 1 out of 5
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 59
page 2