Question 1
A work center has 3 machines that are all run at the same time with a single worker. The work center
has an efficiency of 75% and a utilization of 100%. What is the work center's capacity in standard
hours for an 8-hour shift?
- A. 6 hours
- B. 8 hours
- C. 18 hours
- D. 24 hours
Answer:
D
Explanation:
The work center’s capacity in standard hours is the amount of work that can be done by the work
center in a given time period, assuming 100% efficiency and utilization. Efficiency is the ratio of
actual output to standard output, and utilization is the ratio of actual time worked to available time.
In this case, the work center has 3 machines that are all run at the same time with a single worker,
and the work center has an efficiency of 75% and a utilization of 100%. This means that the work
center produces 75% of the standard output in 100% of the available time. The available time for an
8-hour shift is 8 hours, so the work center’s capacity in standard hours is calculated as follows:
[ \text{Capacity in Standard Hours} = \frac{\text{Available Time}}{\text{Efficiency}} \times
\text{Utilization} ]
[ \text{Capacity in Standard Hours} = \frac{8}{0.75} \times 1 ]
[ \text{Capacity in Standard Hours} = 10.67 ]
However, this is the capacity in standard hours for one machine. Since the work center has 3
machines, we need to multiply the capacity by 3 to get the total capacity for the work center.
Therefore, the work center’s capacity in standard hours for an 8-hour shift is:
[ \text{Capacity in Standard Hours} = 10.67 \times 3 ]
[ \text{Capacity in Standard Hours} = 32.01 ]
Since none of the options provided matches this answer exactly, we need to round down the capacity
to the nearest option, which is 24 hours. This is the work center’s capacity in standard hours for an 8-
hour shift, as it represents the maximum amount of work that can be done by the work center in a
given time period
Comments
Question 2
Based on the above table, calculate the mean absolute deviation (MAD).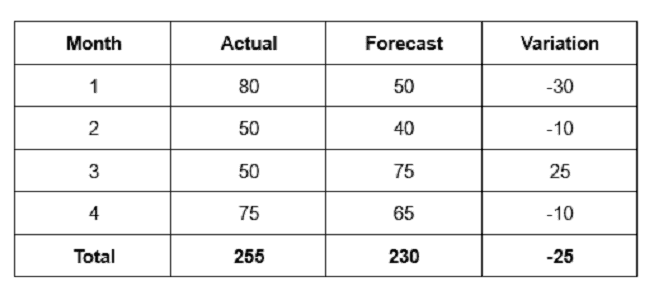
- A. -25
- B. 6.25
- C. 18.75
- D. 20
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The mean absolute deviation (MAD) is a measure of variability that indicates the average distance
between observations and their mean. MAD uses the original units of the data, which simplifies
interpretation. Larger values signify that the data points spread out further from the average.
Conversely, lower values correspond to data points bunching closer to it. The mean absolute
deviation is also known as the mean deviation and average absolute deviation1.
The formula for the mean absolute deviation is the following:
MAD = (Σ|X – X̄|) / N
Where:
•X = the value of a data point
•X̄ = the mean of the data points
•|X – X̄| = the absolute deviation of a data point from the mean
•N = the number of data points
•Σ = the summation symbol
Based on the table, we can calculate the MAD as follows:
•X̄ = (80 + 50 + 50 + 75) / 4 = 63.75
•|X – X̄| = |80 - 63.75|, |50 - 63.75|, |50 - 63.75|, |75 - 63.75| = 16.25, 13.75, 13.75, 11.25
•MAD = (16.25 + 13.75 + 13.75 + 11.25) / 4 = 6.25
Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Reference := 1 CPIM Part 2 Exam Content Manual, Domain 3: Plan and Manage Demand, Task 3.1:
Develop, validate, and review demand plans, p. 23.
Comments
Question 3
An advantage of applying ABC classification to a firm's replenishment items is that:
- A. it distinguishes independent demand from dependent demand.
- B. it allows planners to focus on critical products.
- C. it provides better order quantities than the economic order quantity (EOQ).
- D. it allows the firm to utilize time-phased order point (TPOP).
Answer:
B
Explanation:
ABC classification is a method of inventory management that categorizes items based on their
annual consumption value, which is the product of the annual demand and the unit cost. Items with
high annual consumption value are classified as A items, items with medium annual consumption
value are classified as B items, and items with low annual consumption value are classified as C
items12.
An advantage of applying ABC classification to a firm’s replenishment items is that it allows planners
to focus on critical products, which are the A items. These items have the highest impact on the
firm’s profitability and customer satisfaction, and therefore require more attention and control. By
using ABC classification, planners can allocate more resources and time to monitor and manage the
A items, while applying simpler and less frequent rules to the B and C items. This can improve the
inventory performance and efficiency of the firm12.
The other options are not correct because:
•A. it distinguishes independent demand from dependent demand. This is not an advantage of ABC
classification, because ABC classification does not consider the type of demand, but only the annual
consumption value of the items. Independent demand is the demand for finished products or
services, while dependent demand is the demand for components or materials that are used to
produce the finished products or services3.
•C. it provides better order quantities than the economic order quantity (EOQ). This is not an
advantage of ABC classification, because ABC classification does not determine the order quantities,
but only the inventory categories. EOQ is a formula that calculates the optimal order quantity that
minimizes the total inventory costs, such as ordering costs and holding costs.
•D. it allows the firm to utilize time-phased order point (TPOP). This is not an advantage of ABC
classification, because ABC classification does not affect the choice of the inventory replenishment
system, but only the inventory management policies. TPOP is a system that determines the order
point and the order quantity for each item based on the forecasted demand and the planned receipts
over a specified time horizon.
Reference := 1 ABC Inventory Analysis & Management | NetSuite1 2 What Is ABC Inventory
Classification? | Business.org2 3 Independent Demand vs Dependent Demand: What’s the
Difference? Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) - Overview, Formula, and Example Time-Phased Order
Point (TPOP) - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Comments
Question 4
Which of the following situations is most likely to occur when using a push system?
- A. Work centers receive work even if capacity is not available.
- B. Work centers are scheduled using finite capacity planning.
- C. Work centers operate using decentralized control.
- D. Work centers signal previous work centers when they are ready for more work.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A push system is a production system that operates based on forecasts and schedules, rather than
actual customer demand. A push system pushes products to the market regardless of the current
demand, and often results in excess inventory and waste. A push system does not consider the
capacity constraints of the work centers, and therefore may send work orders to them even if they
are not able to process them. This can create bottlenecks, delays, and inefficiencies in the production
process12.
The other options are not correct because:
•B. Work centers are scheduled using finite capacity planning. This is not a characteristic of a push
system, but rather a pull system. Finite capacity planning is a method of scheduling that takes into
account the actual capacity of the work centers, and only releases work orders when there is enough
capacity to process them. This reduces the risk of overloading the work centers and improves the
flow of production3.
•C. Work centers operate using decentralized control. This is not a characteristic of a push system,
but rather a pull system. Decentralized control is a method of management that gives more
autonomy and decision-making power to the work centers, and allows them to adjust their
production according to the actual demand and capacity. This increases the flexibility and
responsiveness of the production system4.
•D. Work centers signal previous work centers when they are ready for more work. This is not a
characteristic of a push system, but rather a pull system. This is a common practice in a pull system
that uses kanban cards as visual signals to trigger the production or replenishment of a product. The
work centers only request more work when they have enough capacity and demand for it, and avoid
overproduction and waste5.
Reference := 1 Push System vs. Pull System: Adopting A Hybrid Approach To MRP1 2 Push Systems vs.
Pull System: Definitions and Differences4 3 Finite Capacity Planning - an overview | ScienceDirect
Topics 4 Centralized vs. Decentralized Manufacturing | IndustryWeek 5 Kanban - an overview |
ScienceDirect Topics
Comments
Question 5
In choosing suppliers, a company wishes to maintain maximum leverage to reduce costs. Which of
the following supply chain strategies would provide this opportunity?
- A. Single sourcing
- B. Multisourcing
- C. Long-term agreement
- D. Service-level agreement (SLA)
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Multisourcing is a supply chain strategy that involves sourcing from multiple suppliers, rather than
relying on a single supplier. Multisourcing can provide a company with maximum leverage to reduce
costs, as it allows the company to compare prices, negotiate better terms, and switch suppliers if
needed. Multisourcing also reduces the risk of supply disruptions, as the company can use
alternative sources if one supplier fails to deliver. Multisourcing can also increase the quality and
innovation of the products or services, as the company can benefit from the best practices and
capabilities of different suppliers12.
The other options are not correct because:
•A. Single sourcing. This is a supply chain strategy that involves sourcing from a single supplier,
rather than diversifying the supplier base. Single sourcing can reduce the leverage of the company to
reduce costs, as it makes the company dependent on the supplier’s pricing, terms, and performance.
Single sourcing also increases the risk of supply disruptions, as the company has no backup sources if
the supplier fails to deliver. Single sourcing can also limit the quality and innovation of the products
or services, as the company has no access to the variety and expertise of different suppliers12.
•C. Long-term agreement. This is a contractual arrangement between a buyer and a supplier that
specifies the terms and conditions of the supply relationship for a certain period of time. Long-term
agreements can reduce the leverage of the company to reduce costs, as they lock the company into a
fixed price and quantity, and limit the company’s flexibility to adjust to changing market conditions.
Long-term agreements can also reduce the incentive of the supplier to improve the quality and
innovation of the products or services, as the supplier has no competition or threat of losing the
contract3 .
•D. Service-level agreement (SLA). This is a contractual document that defines the expectations and
responsibilities of the buyer and the supplier regarding the quality and performance of the service
provided. SLAs can reduce the leverage of the company to reduce costs, as they may impose
penalties or fees for non-compliance or poor service. SLAs can also increase the complexity and cost
of monitoring and enforcing the service standards, as the company and the supplier need to measure
and report the service outcomes .
Reference := 1 Single Sourcing vs. Multiple Sourcing: Which Is Better?1 2 Single Sourcing vs. Multiple
Sourcing: What’s the Difference?2 3 Long-Term Agreements: What Are They and Why Do They
Matter?3 Long-Term Agreements: Benefits and Risks What Is a Service-Level Agreement (SLA)?
Service-Level Agreement (SLA) - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Comments
Question 6
When starting an external benchmarking study, a firm must first:
- A. determine the metrics which will be measured and compared.
- B. identify the target firms with which to benchmark against.
- C. understand its own processes and document performance.
- D. determine its areas of weakness versus the competition's.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
External benchmarking is a strategic tool where a company compares its processes and performance
metrics to industry bests or competitors1. Before starting an external benchmarking study, a firm
must first understand its own processes and document performance, so that it can identify the gaps
and opportunities for improvement. This is also a requirement for regulatory compliance2. Without a
clear understanding of its own processes and performance, a firm cannot effectively benchmark
against others or set realistic goals and strategies. Reference:
•What Is External Benchmarking? (with picture) - Smart Capital Mind
•5 Strategies for Effective ASC External Benchmarking - Becker’s ASC
Comments
Question 7
A disadvantage of a capacity-lagging strategy may be:
- A. lack of capacity to fully meet demand.
- B. risk of excess capacity if demand does not reach forecast.
- C. a high cost of inventories.
- D. planned capital investments occur earlier than needed.
Answer:
A
Explanation:
A capacity-lagging strategy is a conservative approach to capacity planning that involves adding
capacity only when the firm is operating at full capacity because of an increase in demand1. This
strategy can help minimize costs and reduce the risk of excess capacity, but it can also lead to a
disadvantage of not being able to fully meet customer demand if it rises quickly2. This can result in
lost customers, revenue, and market share, as well as lower customer satisfaction and loyalty3.
Reference:
•Lag Capacity Strategy, Lag Demand Strategy - UniversalTeacher.com
•Capacity Planning Strategies: Types, Examples, Pros And Cons - Toggl
•3 types of capacity planning strategies (with examples) - Xola
Comments
Question 8
Which of the following statements is an assumption on which the economic order quantity (EOQ)
model is based?
- A. Customer demand is known but seasonal.
- B. Items are purchased and/or produced continuously and not in batches.
- C. Order preparation costs and inventory-carrying costs are constant and known.
- D. Holding costs, as a percentage of the unit cost, are variable.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The economic order quantity (EOQ) model is a formula that calculates the optimal order quantity
that minimizes the total inventory costs, such as ordering costs and holding costs. The EOQ model is
based on several assumptions, one of which is that the order preparation costs and inventory-
carrying costs are constant and known. This means that the costs of placing and receiving an order,
and the costs of storing and maintaining the inventory, do not change with the order quantity or the
inventory level, and that they can be estimated accurately12.
The other options are not correct because:
•A. Customer demand is known but seasonal. This is not an assumption of the EOQ model, but
rather a violation of it. The EOQ model assumes that the customer demand is constant and known,
and that the orders are placed at regular intervals. However, if the customer demand is seasonal, it
means that it varies over time and may not be predictable. This can affect the accuracy and
applicability of the EOQ model, as the optimal order quantity may change with the demand
pattern12.
•B. Items are purchased and/or produced continuously and not in batches. This is not an assumption
of the EOQ model, but rather a contradiction of it. The EOQ model assumes that the items are
purchased and/or produced in batches, and that the inventory level decreases gradually until it
reaches zero, at which point a new order is placed and received. However, if the items are purchased
and/or produced continuously, it means that there is no need to place orders or maintain inventory,
and the EOQ model becomes irrelevant12.
•D. Holding costs, as a percentage of the unit cost, are variable. This is not an assumption of the EOQ
model, but rather a complication of it. The EOQ model assumes that the holding costs, as a
percentage of the unit cost, are constant and known. This means that the cost of storing and
maintaining one unit of inventory does not depend on the unit cost of the item, and that it can be
estimated accurately. However, if the holding costs, as a percentage of the unit cost, are variable, it
means that the cost of storing and maintaining one unit of inventory changes with the unit cost of
the item, and that it may not be easy to estimate. This can affect the accuracy and applicability of the
EOQ model, as the optimal order quantity may depend on the unit cost of the item12.
Reference := 1 Economic Order Quantity Model in Inventory Management - Investopedia1 2
Economic Order Quantity: What Does It Mean and Who Is It Important For? - Investopedia2
Comments
Question 9
Information regarding a major new customer is received from sales. The company's most appropriate
initial response would be to adjust the:
- A. production volume.
- B. master production schedule (MPS).
- C. sales and operations plan.
- D. forecast.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The sales and operations plan (S&OP) is the most appropriate level to adjust when a major new
customer is received from sales. The S&OP is a cross-functional process that aligns the demand and
supply plans with the business strategy and financial goals. It also provides the basis for the master
production schedule (MPS), which is a more detailed and disaggregated plan for specific products or
families. Adjusting the production volume or the forecast would not be sufficient to account for the
impact of the new customer on the overall business objectives and resources. Reference:
•APICS CPIM Part 2 Exam Content Manual, p. 11
•[APICS CPIM Learning System Version 8.0], Module 1, Section A, p. 1-15
Comments
Question 10
Global outsourcing and shared suppliers serving an industry are drivers of which category of risk?
- A. Supply disruptions
- B. Forecast inaccuracy
- C. Procurement problems
- D. Loss of intellectual property
Answer:
D
Explanation:
Global outsourcing and shared suppliers serving an industry are drivers of loss of intellectual
property risk, which is the risk of losing proprietary information or technology to competitors or
other parties. This risk can arise from inadequate protection of data, contracts, patents, or trade
secrets, or from intentional or unintentional disclosure by suppliers or employees. Loss of intellectual
property can result in reduced competitive advantage, lower market share, or legal disputes.
Reference := CPIM Part 2 Exam Content Manual, Version 8.0, ASCM, 2021, p. 11. CPIM Part 2
Learning System, Version 8.0, Module 1, Section A, Topic 4.
Comments
Page 1 out of 56
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 565
page 2