Question 1
An Adobe Commerce Architect is planning to create a new action that will add gift registry items to
the customer's quote. What should the Architect do to guarantee that private content blocks are
updated?
- A. Mark the controller by setting no-cache HTTP headers
- B. Invalidate the status of gift registry indexers
- C. Specify a new action in a sections.xml configuration file
Answer:
C
Explanation:
Private content blocks are sections of the page that are specific to each customer and are not cached
by the server. To update these blocks when a customer performs an action, such as adding a gift
registry item to the quote, the Adobe Commerce Architect needs to specify the new action in a
sections.xml configuration file. This file defines which blocks need to be updated for each action and
how often they should be updated. By doing this, the Architect can ensure that the private content
blocks are refreshed with the latest data from the server. Reference:
Private content | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
Configure private content | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
Comments
Question 2
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to scope a bespoke news section for a merchants Adobe
Commerce storefront. The merchant's SEO agency requests that the following URL structure:
news/{date}/{article_url_key}, where {date} is the publication date of the article, and
{article_url_key} is the URL key of the article.
The Architect scopes that a news entity type will be created. The date and URL key data will be
stored against each record and autogenerated on save. The values will be able to be manually
overridden.
- A. The Architect needs to manage routing this functionality and adhere to best practice. Which two options should the Architect consider to meet these requirements? (Choose two.)
- B. Create a standard controller route and mapping the internal URLs (such as news/article/view/id/i) to rewrites that are generated on save and then stored in the URL rewrites table.
- C. Create a custom router that runs before the standard router and matches the news portion of the URL, then looks for and loads a news article by matching the date and URL key parts of the URL
- D. Create a plugin that intercepts Magento\Framework\App\Action: :(), looks for the news portion of the URL, and if it matches, loads the relevant news article by matching the URL date and URL key parts.
- E. Create a standard controller route and an index/index controller class that loads the relevant news article by matching the URL date and URL key parts.
Answer:
BC
Explanation:
These two options are both valid ways to manage routing for the bespoke news section and adhere
to best practice. Option B leverages the existing URL rewrite functionality of Adobe Commerce,
which allows creating custom URLs for any entity type and storing them in the database. This option
requires creating a standard controller route for the news entity type, such as news/article/view/id/i,
where i is the news article ID. Then, on saving each news article, a rewrite rule is generated that
maps the internal URL to the desired SEO-friendly URL, such as news/{date}/{article_url_key}. The
rewrite rule is stored in the url_rewrite table, which is used by the standard router to match and
redirect requests.
Option
C
involves
creating
a
custom
router
class
that
implements
\Magento\Framework\App\RouterInterface and runs before the standard router in the routing
process. The custom router class can match the news portion of the URL and extract the date and
URL key parts from it. Then, it can look for and load a news article that matches those values using a
model or repository class. If a match is found, it can set the request parameters accordingly and
dispatch the request to a controller action that renders the news article page.
Reference:
Routing | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
URL Rewrites | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Custom Router | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Comments
Question 3
An external system integrates functionality of a product catalog search using Adobe Commerce
GraphQL API. The Architect creates a new attribute my_attribute in the admin panel with frontend
type select-Later, the Architect sees that Productlnterf ace already has the field my_attribute, but
returns an Int value. The Architect wants this field to be a new type that contains both option id and
label.
To meet this requirement, an Adobe Commerce Architect creates a new module and file
etc/schema.graphqls that declares as follows:
After calling command setup:upgrade, the introspection of Productlnterface field my_attribute
remains Int. What prevented the value type of field my_attribute from changing?
- A. The Magento_CatalogGraphQI module occurs later in sequence than the Magento_GraphQI module and merging output of dynamic attributes schema reader overrides types declared in schema.graphqls
- B. The fields of Productlnterface are checked during processing schema.graphqls files. If they have a corresponding attribute, then the backendjype of product attribute is set for field type.
- C. The interface Productlnterface is already declared in Magento.CatalogGraphQI module. Extending requires use of the keyword extend before a new declaration of Productlnterface.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
According to the Adobe Commerce documentation, to extend an existing GraphQL interface, the
keyword extend must be used before the interface name. This indicates that the new declaration is
adding or modifying fields to the existing interface, rather than redefining it. If the keyword extend is
omitted, the new declaration will be ignored and the original interface will be used. In this case, the
Architect wants to change the type of the my_attribute field in the ProductInterface interface, which
is already declared in the Magento.CatalogGraphQl module. Therefore, the Architect should use the
keyword extend before declaring the ProductInterface interface in the schema.graphqls file of the
custom module. This will allow the Architect to override the type of the my_attribute field from Int
to MyAttributeType.
Reference:
Extend existing schema | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Schema language with GraphQL | Adobe Commerce
Comments
Question 4
An Adobe Commerce store owner sets up a custom customer attribute "my.attribute".
An Architect needs to display additional content on the home page, which should display only to
Customers with "my.attribute" of a certain value and be the same content for all of them. The
website is running Full Page Cache.
With simplicity in mind, which two steps should the Architect take to implement these
requirements? (Choose two.)
- A. Add a new context value of "my_attribute" to Magento\Framework\App\Http\Context
- B. Create a Customer Segment and use 'my.attribute' in the conditions
- C. Add a custom block and a pHTML template with the content to the cmsjndexjndex.xml layout
- D. Add a dynamic block with the content to the Home Page
- E. Use customer-data JS library to retrieve "my.attribute" value
Answer:
AD
Explanation:
To display additional content on the home page based on a custom customer attribute, the Architect
needs to do the following steps:
Add a new context value of “my_attribute” to Magento\Framework\App\Http\Context. This will
allow the Full Page Cache to generate different versions of the page for customers with different
values of “my.attribute”. The context value can be set using a plugin on the
Magento\Customer\Model\Context class.
Add a dynamic block with the content to the Home Page. A dynamic block is a type of content block
that can be configured to display only to specific customer segments or conditions. The Architect can
use the ‘my.attribute’ in the conditions of the dynamic block and assign it to the Home Page in the
Content > Blocks section of the Admin Panel. Reference:
Private content | Magento 2 Developer Documentation
Dynamic Blocks | Adobe Commerce 2.3 User Guide - Magento
Comments
Question 5
An Adobe Commerce Architect designs a data flow that contains a new product type with its own
custom pricing logic to meet a merchant requirement. Which three steps are required when adding a
product type with custom pricing? (Choose three.)
- A. Content of the etc/product_types.xml file
- B. Data patch to register the new product type
- C. Hydrator for attributes belonging to the new product type
- D. New price model extending \Magento\Catalog\Model\Product\Type\Price
- E. Custom type model extended from the abstract Product Type model
- F. A new class with custom pricing logic, extending the abstract Product model class
Answer:
ADE
Explanation:
To add a product type with custom pricing, the Architect needs to do the following steps:
Create a content of the etc/product_types.xml file that defines the new product type, its label,
model, index priority, and price model.
This file is used to register the new product type and its
associated classes in Magento1
.
Create a new price model that extends \Magento\Catalog\Model\Product\Type\Price and
implements the custom pricing logic for the new product type.
The price model is responsible for
calculating the final price of the product based on various factors, such as special price, tier price,
catalog price rules, etc2
.
Create a custom type model that extends from the abstract Product Type model
(\Magento\Catalog\Model\Product\Type\AbstractType) and overrides the methods related to the
product type behavior, such as prepareForCart, getAssociatedProducts, etc.
The type model defines
how the product type interacts with other components, such as quote, order, cart, etc3
. Reference:
How to add a new product type in Magento 2? (MageStackDay mystery question 1) - Magento Stack
Exchange
Magento 2: How to create custom product types - BelVG Blog
Magento 2: How to create custom product types - BelVG Blog
Comments
Question 6
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to log the result of a ServiceClass:: getData method execution
after all plugins have executed. The method is public, and there are a few plugins declared for this
method. Among those plugins are after and around types, and all have sortOrder specified.
Which solution should be used to meet this requirement?
- A. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value lower than the lowest declared plugin sortOrder and implement aroundGetData method.
- B. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value higher than the highest declared plugin sortOrder and implement afterGetData method.
- C. Declare a new plugin with the sortOrder value higher than the highest declared plugin sortOrder and implement aroundGetData method.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
This solution ensures that the new plugin will execute after all the existing plugins for the
ServiceClass::getData method, and will be able to log the final result of the method execution. The
afterGetData method of the new plugin will receive the result of the method as a parameter, and can
use any logging mechanism to record it. The sortOrder value of the new plugin should be higher than
the highest declared plugin sortOrder, so that it will run last in the sequence of plugins. The after
type of plugin is preferred over the around type of plugin, because it is simpler and more efficient,
and does not require calling the proceed() method.
Reference:
Plugins (Interceptors) | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Plugin best practices | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Comments
Question 7
While developing a new functionality for a website in developer mode with all cache types enabled,
an Adobe Commerce Developer needs to add \Magento\Sales\Model\Service\InvoiceService
SinvoiceService as a new dependency to an existing page action controller in
Vendor\CustomModule\Controller\Index\Index . This is accomplished as follows:
After cleaning the f ull_page cache and reloading the page, the developer encounters the following
exception:
Recoverable
Error:
Argument
passed
to
Vendor\CustomModule\Controller\Index\Index::__construct() must be an instance of
\Magento\Sales\Model\Service\InvoiceService [...]
Which action should the Architect recommend to the developer to fix this error?
- A. Clean the block_html cache along with full_page cache.
- B. Add the new \Magento\sales\Model\service\invoiceService Sinvoiceservice dependency at the end of the constructor signature. C. Remove the generated Child ClaSS from generated/code/Vendor/CustomModule/Controller/Index/Index.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
The error is caused by the generated child class not being updated with the new dependency.
Removing the generated child class will allow the system to generate a new child class with the
correct dependency. The generated child class is a proxy class that extends the original controller
class and overrides the constructor to inject the dependencies using the object manager. The
generated child class is created when the system runs in developer mode with cache enabled, to
avoid performance issues. However, when a new dependency is added to the original controller
class, the generated child class does not reflect the change and causes a mismatch in the constructor
arguments. Therefore, deleting the generated child class from the generated/code directory will
solve the problem.
Reference:
Generated code | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Constructor signature change | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Comments
Question 8
A representative of a small business needs an Adobe Commerce Architect to design a custom
integration of a third-party payment solution. They want to reduce the list of controls identified in
their Self-Assessment Questionnaire as much as possible to achieve PCI compliance for their existing
Magento application.
Which approach meets the business needs?
- A. Utilize the Advanced Encryption standard (aes-256) algorithm to encrypt all customer-sensitive data from the payment module.
- B. Utilize the payment provider iframe system to isolate content of the embedded frame from the parent web page.
- C. Utilize a trusted signed certificate issued by a Certification Authority (CA) to secure each connection made by the payment solution protocol via https.
Answer:
B
Explanation:
Using an iframe system for payment integration can help reduce the PCI scope and compliance
burden for the merchant, as the payment data is collected and processed by the payment service
provider (PSP) within the iframe, without touching the merchant’s website or server. This way, the
merchant can leverage the PSP’s PCI certification and avoid storing or transmitting any sensitive
cardholder data on their own system. The iframe also provides a secure barrier between the host
webpage and the loaded page, preventing any access or manipulation of the payment data by
malicious actors.
To implement this approach, the merchant needs to embed the PSP’s payment
form in their checkout page using an iframe element, and configure the communication between the
iframe and the host page using JavaScript123
.
Comments
Question 9
A merchant asks for a new category attribute to allow uploading an additional mobile image against
categories. The merchant utilizes the content staging and preview feature in Adobe Commerce and
wants to schedule and review changes to this new mobile image field.
A
developer
creates
the
attribute
via
a
data
patch
and
adds
it
to
view/adminhtml/ui_component/category_f orm. xml. The attribute appears against the category in
the main form, but does not appear in the additional form when scheduled updates are made.
To change this attribute when scheduling new category updates, which additional action should the
Architect ask the developer to take?
- A. The attribute must have its apply_to field set to "staging" in the data patch file.
- B. The attribute must have <item- name=’’allow_staging" xsi:type=’’boolean’’>true</item> set in the cjt.gopy_for-.xni file under the attributes config' section. C. The attribute must also be added to view/adminhtml/ui_co- component/catalogstaging_category_update_form.xml.
Answer:
C
Explanation:
This action is necessary to make the attribute available for content staging and preview. According to
the Adobe Commerce documentation, the catalogstaging_category_update_form.xml file defines
the fields that are displayed in the Scheduled Changes section of the category form. The file extends
the category_form.xml file and adds additional fields that are specific to content staging, such as
start and end dates, campaign name, description, etc. To include a custom category attribute in the
Scheduled
Changes
section,
the
attribute
must
also
be
declared
in
the
catalogstaging_category_update_form.xml file with the same configuration as in the
category_form.xml file.
Reference:
Content staging | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Create a category attribute | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Comments
Question 10
An Adobe Commerce Architect needs to create a new customer segment condition to enable admins
to specify an Average sales amount' condition for certain segments.
The
Architect
develops
the
custom
condition
under
Vendor\Module\Model\Segment\Condition\AverageSalesAmount with all of its requirements:
During testing, the following error appears:
What should the Architect do to fix the problem?
A)
B)
C)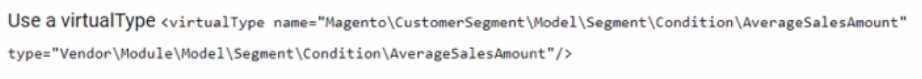
- A. Option A
- B. Option B
- C. Option C
Answer:
B
Explanation:
The error is caused by the missing class declaration for the custom condition class. According to the
Adobe Commerce documentation, to create a custom customer segment condition, the class must
extend the \Magento\CustomerSegment\Model\Condition\AbstractCondition class and implement
the \Magento\CustomerSegment\Model\Condition\Combine\Interface interface. The class must
also declare its name, label, value type, and attribute code properties. Option B is the only option
that correctly declares the class with the required properties and inheritance. Option A and Option C
are incorrect because they do not extend the AbstractCondition class or implement the
CombineInterface interface, and they do not declare the name, label, value type, or attribute code
properties.
Reference:
Create a customer segment condition | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
AbstractCondition | Adobe Commerce Developer Guide
Comments
Page 1 out of 4
Viewing questions 1-10 out of 50
page 2